Filter :
The first few months of a new mom’s life can be beautiful, tough, and also very rewarding, provided you take care of yourself, as much as you do of your little one. Aspects like self-case, positive mental health, and practicing good dietary habits are gaining importance over merely reaching for goals like weight loss.
Many new moms are also committed to losing all that postpartum belly fat as quickly as possible. “How to lose weight after pregnancy?”, “How long does it take for postpartum belly to go away?”, questions like these can even turn into an obsession at times. However, weight loss at the cost of good health and well-being can be detrimental. Poor habits like crash diets can lead to quicker weight gain, not to mention poor physical and mental health.
Here’s how you can achieve your postpartum belly weight loss goals, by doing it in a way that’s gentle and nourishing for your body.
Table of Contents
Aiming for slow and steady postpartum tummy loss has some real benefits, and one way to ensure this is that your diet is packed with all the nutrition you need.
A pilot study conducted indicates that when new mothers follow DASH (Dietary Approach to Stop Hypertension), which focuses on healthy eating, not only did it lead to weight loss, but it also helped them keep it off, permanently.
The DASH diet promotes nutritious food choices without completely prohibiting you from eating any specific kinds of food. Some key aspects of the diet are:
Eating meals on time also really helps to improve metabolism, thus aiding in faster weight loss. Before implementing any substantial changes in your diet, talk to your doctor to understand the possible risks and benefits.
Whether you bring in walking, or any other form of physical activity, it helps to develop a routine that consistently helps you raise your metabolism levels. Weaving in postpartum belly exercises like tummy crunches on a daily basis can help you beat any “belly after baby” stress weighing on your mind.
These days, tons of workouts are available on the Internet, especially for moms looking to lose post-pregnancy belly fat, and tighten those muscles. “Baby and me” workout classes are also gaining popularity, especially with moms who do not have house help; the baby also gets to have a fun time with mommy! Ensure that you follow a credible instructor and do not experience fatigue while working out.
In case of any medical complications, make sure you get a sign-off from the doctor before indulging in any strenuous routines.
“How do I lose the baby weight?”, while this is an important priority for new mothers, no doubt, focusing on emotional well-being alongside physical fitness is just as important. Taking care of yourself as much as caring for your little one is important. An important aspect of the weight loss journey that we hardly pay much attention to is acknowledging the value of positive mental health.
Introducing daily pranayamas (breathing) and asanas (yoga postures) helps you improve overall mental health, and address common disorders like postpartum depression.
Watch out for symptoms like extreme sadness or anger without any warning, a feeling of having to go through the motions while getting through the day, feelings of anxiety, guilt, as well as irritation.
Staying connected to yourself and your needs via meditation is a powerful experience. There are several meditations available online, especially for new moms, and they can help you relax and unwind, mentally, especially if practised every day, even if it is for just a few minutes.
Additionally, asking for help from loved ones when you need it, having conversations with friends and family, and communicating your needs, are all healthy practice.
Watch the video, Dr Aruna Kalra (Director- Obstetrics & Gynaecology at the CK Birla Hospital) sharing some important tips on how to lose weight after childbirth.
The human body, when continuously deprived of sleep, sets off a domino effect that slows down your metabolism. It leads to the release of the stress hormone cortisol, which signals to your body that it needs to conserve energy by hanging on to fat, especially post-pregnancy tummy fat. Sleep deprivation also triggers other behaviours like stress eating, irritability and lack of focus.
Yet, lack of sleep is something most new moms fall prey, too, as they always aim to place the baby’s needs first. One century’s old tried and tested hack that works is to sleep whenever your baby sleeps.
Breastfeeding your baby up to six months or more helps build up natural immunity. The most organic way to understand how often to breastfeed is to follow your baby’s lead.
You might not realise this, but one of the unique side effects of regular breastfeeding is faster weight loss and in particular post-pregnancy tummy fat. It also helps to restore the uterus to its original size much faster. Another unique benefit is that it helps to reduce the risks of diabetes, breast cancer and ovarian cancer in young mothers.
Keeping yourself hydrated when you are breastfeeding is especially important. Consume water, milk and juices. Include vegan milk options like almond and peanuts, which come with power-packed nutritional value.
Read: What you can do to prevent breast sagging post pregnancy
Motherhood can be an even more enjoyable experience if you bring balance and harmony into it early on. Building positive personal habits will make you emotionally and physically stronger, and nudge you to achieve your postpartum weight loss goals, faster.
So set new routines in place, receive the nutrition and support you need and set the stage for a beautiful journey for you and your child.
Your belly is a primary storehouse area of body fat, especially during pregnancy. Hence, it’s natural that it will take some time to lose the fat in your stomach after birth.
Postpartum belly binding is an age-old tradition that provides support and comfort for new mothers. Whether you use a special postpartum belt or a wrap, the effects are the same. However, be careful not to wrap up too tight, as it can put undue pressure on your uterus.
Childbirth is an intense experience, followed by an even more intense caregiving routine for the next six months of you and your baby’s life. Good mental health will keep you motivated, and more invested in your own self-care, as much as in your baby’s well-being.
Also, read: 4 Postpartum complications you must monitor
Has your doctor informed you that the lump in your breast is a fibroadenoma? Do not be alarmed. These types of lumps are commonly-occurring breast lumps that are benign or non-cancerous.
It is important to remember that breast lumps cannot be identified as benign or cancerous without proper examination and maybe a biopsy. Always get any new breast lump checked by a doctor to rule out breast cancer.
Table of Contents
Fibroadenomas are considered to be one of the most common forms of non-cancerous benign breast lump. They can occur in women of any age, however, are more commonly seen in premenopausal and younger women (20 years-30 years of age). In many cases, they shrink and disappear once the woman hits menopause.
A fibroadenoma derives its name from the terms “fibroma” and “adenoma.” It is a benign tumour composed of both fibrous and glandular tissue. These growths can change in size over time—sometimes enlarging, shrinking, or even disappearing—depending on hormonal fluctuations.
On average, fibroadenomas measure between 1 and 2.5 cm in diameter in breast, though in some cases they may exceed 5 cm, in which case they are referred to as giant fibroadenomas.
Read: What to expect when you are diagnosed with Breast cancer
The normal breast tissue often feels lumpy in healthy women. So, you must seek medical help if you observe one or more of the following symptoms.
Also, the following pointers depict some of the unique characteristics of breast fibroadenomas.
Nevertheless, you cannot conclude that it is a breast fibroadenoma merely by sensing these characteristics of the lump. As such, it’s best to consult your doctor for the correct diagnosis. Your doctor would ask you to take a mammogram or an ultrasound, subject to your age and physical condition, whether pregnant or not.
Also Read: Challenges of Young Women with Breast Cancer (Breast Cancer in women under 40)
A breast fibroadenoma lump will feel firm, smooth, rubbery or hard to touch. It will have a well defined shape and is usually painless. If you push them, they are easily movable under the skin. They can increase in size, especially during pregnancy and shrink and disappear after you hit menopause.
The normal breast tissue often feels lumpy in healthy women. Breasts also differ in shape, size and texture amongst women. Performing routine breast self examinations will help you familiarize yourself with your breasts. This will in turn make it easy to detect any changes in the form of size or lumps, immediately. Fibroadenomas seldom cause pain.
This video explains how to perform breast self-examination.
Always remember, you cannot differentiate between a benign (noncancerous) lump or a cancerous lump. Seek immediate medical help if you notice any new growth in your breast or your underarms or any changes in existing lumps.
For women over the age of 40 years, annual breast cancer screening combined with mammograms are recommended to minimise the risk of detecting breast cancer at later stages.
Although the true underlying cause of breast fibroadenomas is still unclear, research suggests that it might be linked to the changing levels of your reproductive hormones. This is probably why they occur mainly during your reproductive years, grow in size during pregnancy or if you undergo hormonal therapy. It is also likely why they shrink and disappear after you hit menopause.
Also Read: Scarless removal of breast lump: An introduction to VABB
If you’re considering fibroadenoma removal without breast surgery, you should know the types of fibroadenomas.
Complex fibroadenoma can change over time through hyperplasia, a condition that causes an overgrowth of cells. Your pathologist would make its diagnosis after reviewing your biopsy tissue.
Juvenile fibroadenoma commonly occurs in girls and adolescents. While some of these breast lumps may grow, most of them tend to shrink over time and disappear.
Unlike ordinary lumps that are about one to two centimeters in size, giant fibroadenomas can grow larger than two inches. Your doctor would prescribe fibroadenoma breast treatment to remove it since it can press on or replace other breast tissue.
Phyllodes are benign in the beginning, but some tumours can become cancerous. Like giant fibroadenomas, your doctor would suggest the removal of phyllodes tumour.
In general, fibroadenomas do not cause any complications. However, complex fibroadenomas and phyllodes tumours can increase the risk of breast cancer slightly. If your doctor feels that your fibroadenoma is harmless, you might not require any particular treatment other than monitoring the lump for any changes in shape or size. If you do notice any change, you should get it re-examined by the doctor and seek the appropriate treatment.
While fibroadenomas do not generally pose a risk if left untreated, many women still prefer to get them removed. This is not only for their peace of mind but also to preserve or restore the look and feel of the breast.
Many women also choose to manage their fibroadenomas without surgery. This may be due to their apprehension of being operated on, or for any other personal preference. The choice of forgoing surgery must be based on your clinical breast exam, imaging test and biopsy.
If you do decide for non surgical management of fibroadenoma, you must monitor the condition for any changes such as size or shape etc.
Here are some protocols to follow if you decide on treating fibroadenoma without surgery
Some other tips that can help you keep your breasts healthy include:
If your fibroadenoma increases in size, has started paining or shows any other change, get it checked by a doctor immediately.
In certain cases like the phyllode tumour, treatment of fibroadenoma without surgery is not possible. Alternatively, if the presence of the benign lump makes you anxious that you would want to forego fibroadenoma treatment without surgery, your doctor could arrange for excision.
Here are the surgical means to remove fibroadenomas.
In this surgical procedure, the surgeon would remove the breast tissue and send it to the lab to check for the risk of breast cancer.
Fibroadenoma cryoablation is a technique that is used to freeze the lump to destroy it. Here, the surgeon would insert a thin device called the cryoprobe through the breast skin to the fibroadenoma lump. From the device, a gas is released to destroy the tissue.
Also Read: Myths About Breast Cancer
Depending on the characteristics of the lump, your doctor would either propose treatment of fibroadenoma without surgery or strongly suggest removal of the lump from the breast. Discuss your family history, symptoms and medications or treatments you are on with your doctor. This information is significant in arriving at a speedy and accurate diagnosis.
Even if you do not present with any breast problems, you should go for breast cancer screenings routinely (as advised by the doctor). This is because breast cancer can happen to anyone. Breast cancer also does not have any obvious symptoms in the early stages. Routine and regular breast cancer screening is your best bet to detect it in time. Remember early detection is the best protection against breast cancer.
Also, read: Worried about an underarm lump? Find out what it means
Your body doesn’t recover immediately after childbirth: it takes time to get back in shape. The first six weeks after birth are crucial to getting the healing journey started. Even if your focus is on taking care of your baby, there is ample need to make sure that your body is healing correctly.
Post-delivery complications could arise at any time after birth. The complications could occur a few weeks after delivery, or even within the first year after you have given birth.
Women who have delivered a baby, need to keep an eye on the changes happening in their body. These changes could not only be physiological but psychological also.
A gynaecologist checks the new mother over immediately after the delivery to rule out any abnormal bleeding or discomfort in the body. The next check-up happens at six weeks when the body has begun healing itself.
Postpartum complications can occur with either way of delivery – natural birth or delivery via C-section. Here are the most common postpartum complications to watch out for:
Bleeding is natural after delivery. There is a medical term for it, Lochia, which is the combination of blood and mucus that exits the body after childbirth. The heavy bleeding can last up to 3 days post-delivery. Spotting or light bleeding can sometimes continue even up to six weeks.
Lochia is heavier than a normal period. In the first 3-4 days, the bleeding is bright red. Over the next 10 to 30 days, the bleeding slows down gradually and changes colour from pink to brown.
The bleeding is a cause for concern when it is heavy and continues to be heavy even three days after birth. The main signs of haemorrhage include:
Massive blood loss could lead to a sudden drop in blood pressure. The situation can be dire and immediate action needs to be taken.
Tearing in the vagina is quite common with normal vaginal delivery; and with a C-section, the womb is opened externally through the lower abdomen to deliver the baby. In both these situations, the resulting tear is sealed together with stitches. If done incorrectly or without precision, the wound could get infected.
It will take some time for the scars to heal completely. If after delivery, a few bits of the placenta remain behind, your uterus could be susceptible to some common infections after birth.
Signs of an infection include fever, pain during urination, and discharge on-site of the wound. Usually, a single round of antibiotics is enough to treat the infection if detected early.
Infections, when neglected, could lead to severe complications after delivery like:
The new mother must monitor her body to notice any changes that could be attributed to an infection.
Also, read: Common vaginal infections
The symptoms of postpartum depression can show up at any time after you deliver your baby. The ‘baby blues’ that affect women after birth are a result of the roiling hormones in the body. If low feelings persist even after the first few weeks, it leads to postpartum depression.
The signs of depression after birth include:
You must approach your doctor or medical practitioner if these feelings remain for longer. Other than hormones, excess stress can also lead to depression after delivery. A history of depression in the mother or immediate family can also be a contributing factor.
Postpartum depression can be treated first with medication. However, ensure that the medicine your doctor prescribes is safe to consume during breastfeeding. Exploring negative feelings via psychotherapy and counselling can also alleviate the condition.
Postpartum psychosis is more severe and comparatively rarer than postpartum depression. The illness usually appears within two weeks after delivery.
The symptoms of postpartum psychosis are:
The illness is not permanent and can be treated with proper help from professionals. However, the psychosis needs immediate attention as soon as symptoms after birth is seen.
The treatment for postpartum psychosis is similar to depression. But the treatment plans can differ depending on the severity of the condition.
After childbirth, there needs to be a system in place that prioritises the postpartum health of the mother. There are a few easy to apply protocols:
In the case of a C-section, it is essential to take care of the stitches placed on the place of the incision. The procedure involves cutting through several layers of muscles and the uterus which need to heal to get the body into its natural health.
Vaginal delivery almost always tears into the skin between the vagina and the rectum. Keeping this area clean and infection-free requires the utmost attention. Since these wounds are always covered up, they take more time to heal.
Along with the physical recuperation, mothers should spare equal attention to their mental health. While check-ups verify the physical health, an assessment should be made regarding the emotional well-being and overall mood of the mother. Excessive mood swings and violent overtures should be diagnosed at the earliest to provide the best care possible.
Healing postpartum takes time. After delivery, a woman is more aware of how her body is functioning. The first six weeks involve monitoring the physical health of the mother to assess if the healing is on track.
Similar attention should be given to assess the mental health of women as well. In case of any red flags, you should seek an appointment with a mental health professional who specialises in the field.
Most symptoms of postpartum complications can be mistaken for some other ailment. You need to provide your healthcare provider with the date of delivery for your baby. The information can help them in making the right decision regarding the actual cause of your illness.
According to the American Cancer Institute, lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths. Studies suggest that approximately 75,000 new cases of lung cancer are reported each year in India. With such alarming statistics, it’s important to know the warning signs of lung cancer to get the best treatment.
Cell production and cell growth in the body is exceptionally controlled. However, if there is some disturbance in this organised routine, it causes the production of abnormal cells that contain a lot of mutations. The growth of these abnormal cells is cancer.
Lung cancer is the abnormal growth of cells in the lungs. Lung cancer starts in the lungs, but it can quickly spread to the lymph nodes and other parts of the body. Similarly, other cancerous cells can travel through the body and settle in the lungs, causing lung cancer.
Lung cancer can be categorised as a small cell, non-small cell, and lung carcinoid tumour.
Table of Contents
Lung cancer is one of the few types of cancer that can go undetected for a long time. When lung cancer is finally detected, the cancerous cells have already spread into a large part of the lungs.
When cancerous cells from the lung spread to other parts of the body, it is called metastasis. This could cause cancer to show symptoms in the affected body part and result in a misdiagnosis.
The early symptoms of lung cancer, which manifest in the first stage, can also be confused with common ailments like cold or flu. These signs include,
While these are the most common symptoms of lung cancer, they can have other unrelated mild medical causes. However, if any of these signs seem to persist or seem more intense, consult a medical service provider for an accurate lung cancer diagnosis.
With such light and common symptoms, it is challenging to know whether you have lung cancer or another illness. You can, however, be vigilant of some risk factors that could lead to lung cancer.
The symptoms of lung cancer, when combined with any of these risk factors, is a cause for concern, and should be diagnosed by a qualified medical professional.
Once you recognise the early signs and symptoms of lung cancer, along with the risk factors of lung cancer, you should visit an oncologist (cancer specialist).
After a physical examination, the oncologist would suggest a few tests to get a clearer view of the abnormal growth.
Imaging tests like X-rays, MRIs, CT scans, and PET scans detect the exact location and size of the growth of abnormal cells. Imaging tests don’t need any special exercises like fasting. The tests are quite simple, and you get the results within minutes.
Sometimes, the results of imaging tests are not sufficient for accurate lung cancer diagnosis. In such cases, the oncologist may recommend sputum cytology. In this test, the phlegm of the patient is studied to analyse the existence of cancerous cells.
If the results of these tests show a positive outcome for cancer, the tissue is further studied by doing a biopsy. A biopsy is when a sample of infected tissue is taken from the patient to be analysed.
A needle biopsy entails inserting a narrow, hollow needle into the lungs to collect the required sample. If the samples collected are not enough, the doctor might do a core biopsy, i.e., the doctor uses a larger needle to collect samples from the lungs.
Samples from a core biopsy provide the doctors with a larger tissue to conduct tests on. CT scans and X-rays are used to direct the needle to the affected cells.
A bronchoscopy test uses a bronchoscope, which is a long instrument made of a fibre-optic, flexible material, that holds a camera and light source at the end. The bronchoscope is inserted into the lungs through the mouth or nose. It allows the doctor to examine the inside of the lungs and airways.
This is a more advanced test to check the spread of lung cancer. Similar to a bronchoscope, a thoracoscope is also a flexible tube containing a camera and light source. Thoracoscopy is done to check the area between the lungs and the chest wall to see if the cancerous cells have spread. Any fluid is also collected to analyse for cancer cells.
If the warning signs of lung cancer are checked, and these tests are performed, the chances of recovery will increase in case the patients test positive for the disease.
For the prevention of lung cancer, consider getting screening tests once a year, even if you are healthy. These tests rule out lung cancer if you are at risk due to any mitigating factors.
No matter how small an early sign of lung cancer is, there is no harm in reaching out to your medical service provider to get the correct diagnosis.
Also, read: How Chemotherapy Works Against Cancer
If you’re diagnosed with hip dysplasia, you’re not alone. It is the most common form of hip arthritis before the age of 50. Let’s learn about this condition before moving on to hip dysplasia treatment.
Table of Contents
More than half of your body weight rests on your hips. They allow smooth movement of your upper legs so that you can walk, run, climb or sit with ease. Moreover, the hip joint is the biggest, ball, and socket joint in the body. Any problem in this joint can negatively affect your daily life.
Hip dysplasia is a condition wherein the socket of the hip bone is shallow and doesn’t completely cover the ball on the upper thigh (femoral head). It often results in instability and hip displacement (the bone slides out of place) of the hip joint.
If left untreated for long, the joint may become painful and develop osteoarthritis. As the condition progresses, hip dysplasia can damage the cartilage, the tissue that cushions these bones in the joint, known as a hip labral tear. According to the American Family Physician, about 1 in every 1000 babies is born with hip dysplasia.
Most people diagnosed with hip dysplasia are born with this condition. It is also called DDH- Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip. It is a form of congenital dislocation of the hip which is caused by abnormal formation of the hip joint during the baby’s early stages of fetal development
Your doctor may do a physical examination gently applying pressure and rotating your baby’s legs in different positions to check for any abnormality. Your child may have:
An ultrasound scan helps diagnose hip dysplasia in babies less than six months old.
Mild cases of this condition do not show any signs until a person has reached teenage or adulthood. As per the International Hip Dysplasia Institute, diagnosis of nine out of ten cases of hip dysplasia happens during adolescence or adulthood.
Your doctor will require imaging tests like X-ray and MRI to evaluate your condition correctly, during this time. These tests will help your doctor in assessing the extent of damage to the cartilage and the severity of dysplasia.
Symptoms of hip dysplasia vary with age. Some prominent signs and symptoms include:
There is no exact, specific cause of this condition. However, some common causes and risk factors are listed below:
The reason why early diagnosis is crucial to hip dysplasia treatment is its potential to cause debilitating complications later in life. Over time, this condition can result in:
As with all progressive ailments, hip dysplasia also has better treatment potential if found out in the early stages. Hence, it is advisable to consult an orthopaedist as soon as you notice any signs. Untreated hip dysplasia is most likely to develop arthritis later.
Hip dysplasia treatment varies with age and the extent of damage to the hip joint.
Congenital hip dysplasia treatment includes soft braces such as a Pavlik harness that holds the ball of the joint securely in its socket for a few months. This treatment moulds the socket to the shape of the ball and is ideal for babies less than six months old.
For babies older than six months old, your doctor may use a full-body cast that holds the bone into its proper position for several months.
The primary goal of doctors is to preserve your hip for as long as possible or opt for a minimally invasive procedure. Periacetabular Osteotomy (PAO) is a surgical procedure performed by your doctor in which the bone is cut around the hip socket to correct the condition.
Periacetabular is a medical term that means “around the hip socket,” and osteotomy refers to a procedure in which the bone is cut. PAO is ideal for patients whose hips haven’t yet become arthritic.
If the condition is detected later in life and osteoarthritis has already established your doctor may suggest a total hip replacement surgery. It is also referred to as “arthroplasty” and uses simulated parts to replace the damaged joint.
Mild hip dysplasia with mild symptoms or where the hip is too damaged for surgery, your doctor may go for non-operative treatments. These are best suited to reduce hip dysplasia pain and manage your daily life. Your doctor’s advice shall include:
Hip dysplasia is a progressive condition that worsens with time. For this reason, early diagnosis and considering different treatment options play an important role. Surgery is usually the most preferred method to treat hip dysplasia in teenagers and adults.
Most people go on to live healthy lives after treatment without hip dysplasia pain. You may require rest for six weeks to three months after surgery before you can resume regular activities. However, it is vital to visit your doctor regularly to keep a check on the hip joint and to see that the condition doesn’t return.
Also, read: Your comprehensive guide to joint pains and their treatment
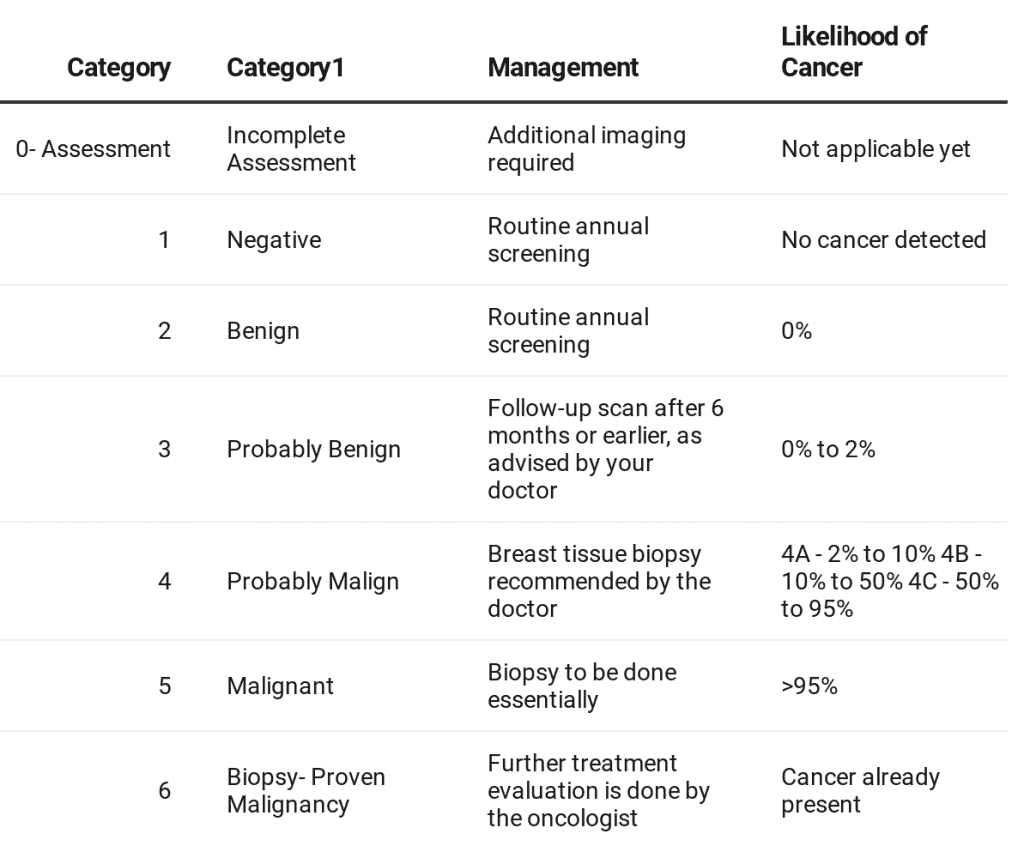
BI-RADS refers to Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System. It is a standardized system developed by the American College of Radiology (ACR) for radiologists to categorize their findings of the mammogram. A mammogram is an X-Ray of the breast and is used to detect early signs of breast cancer.
The BI-RADS score helps radiologists communicate the results of the mammogram clearly to your doctor, along with assessment and follow-up recommendations.
Table of Contents
When your radiologist interprets a mammogram, he/she assigns a numerical value from 0 through 6 to BI-RADS. This score further enables your doctor to assess your breast cancer risk.
Some people wrongly assume this score to be the breast cancer stage. Since this confusion brings unnecessary worry, patients need to be aware of the BI-RADS system of assessment.
Let’s learn about what each BI-RADS value on your mammography or ultrasound report means.
This category is indicative of insufficient imaging information, which means the study is not yet complete. It usually happens when your radiologist finds difficulty in reading the images that may be cloudy or not distinct. It may be due to dense breasts or a technical issue.
In such a case, follow-up imaging is necessary for proper evaluation. The extra imaging is also compared with the previous mammography to check stability.
If you have a BI-RADS 0 score, it is important to get additional imaging done through mammography views, ultrasound or MRI.
When there is no noticeable abnormality in the scan obtained, it is assigned a BI-RADS score of 1. It is a negative report implying that the report is normal and there is no evidence of a lesion or mass.
This report is good news for you as there is no obvious sign of cancer in the mammogram at present. In this case, you can continue with your routine annual screening of the breasts.
The mammography scan in BI-RADS 2 category suggests a benign, i.e. non-cancerous mass. It may include a cyst, calcification or fibroadenomas. These lumps have a 0% risk of turning malignant, i.e. cancerous and do not need a biopsy of the breast tissue for further evaluation.
In this case, too, the doctor usually suggests a routine breast examination.
When the imaging report suggests lesions or masses that probably appear benign, it is put in the category of BI-RADS 3. In comparison to BI-RADS 2, these lumps have a chance of 0 to 2 per cent of turning malignant. These include non-palpable, incidental and complicated cysts.
A 6-month follow-up scan is usually suggested in this category, and there is no need for a biopsy. However, your physician may ask you to follow up earlier than 6 months if you have a family history of breast cancer.
The lumps or lesions found in this category have a greater chance of turning cancerous than the scan in BI-RADS 3. Depending on your case, your doctor may perform a biopsy of the breast tissue to establish a proper diagnosis. BI-RADS 4 is further sub-divided into:
In the BI-RADS 5 category, the scan suggests a lump that has more than 95% risk of turning cancerous. Since the risk of breast cancer is the highest in BI-RADS 5, your doctor will conduct a biopsy to further check your case.
As a side note, certain benign breast conditions like mastitis can also appear cancer-like in the mammogram report. Thus, do not immediately panic and let your doctor provide the correct understanding of the score.
A BI-RADS score of 6 suggests a mammogram of someone who has a known biopsy-proven malignancy. The doctor may recommend the scan for further treatment evaluation or to check the breast cancer stage.
Breast density affects the mammogram report and thus, also the imaging assessment. Dense breasts have less fatty tissue and are twice as likely to develop breast cancer. They also make it difficult for mammograms to detect cancer. BI-RADS and Breast Density
Naturally, a breast cancer diagnosis is hard to accept. However, it is also important to note that early detection is the key to managing breast cancer effectively. For this, you must undergo regular screenings and pay attention to the warning signs.
Your BI-RADS score on the mammography report, indeed, is an important tool for your doctor to assess your breast cancer and suggest further follow-up action. But remember, all breast lumps aren’t cancerous.
So whatever your BI-RADS score, make sure to consult your doctor to rightfully diagnose your condition. Your doctor may additionally ask you to take some tests before any final assessment.
Also, read: Worried about an underarm lump? Find out what it means
Are you finding that you need to go to the bathroom more frequently than normal? Or are you exhaling much more gas than usual? It’s possible that your body is producing too much gas and that you are urinating a lot.
You may experience stress as a result of these upsetting circumstances, but you may also control them with the appropriate strategy. You may stop the regular annoyance of frequent urinating by finding its source.
To treat the underlying issue effectively, this article offers a glimpse into the primary reason for excess gas and urine.
Table of Contents
If you need to urinate more than usual, it may be a cause of worry. The issue can occur with men, women and even children but certain conditions enlarge its possibility in some people.
A normal person pees for up to 8 times a day. Anything more than that can be termed as frequent urination. It could be related to the kidneys, bladder, or urethra, which together form the urinary tract.
Any irritation, injury, disease or infection in the bladder can cause the urge to pee. This effect on the bladder can also result from changes related to nerves and tissues in the urinary tract.
Excessive peeing can be caused by certain diseases, such as:
You may want to consider these additional conditions which can cause excessive urination.
But sometimes, an external factor tends to cause these bladder issues. The use of diuretics which remove extra salt through urine from the body could trigger increased urine production. Even the consumption of excessive caffeine and alcohol could be the reason for frequent urination.
Depending on the reason, you could face one or more symptoms which can indicate the presence of a serious medical condition in your body.
If you notice any of these red flags, you should seek immediate medical attention:
If you have a family history of diabetes and experience excessive thirst along with frequent urination, you should get your symptoms checked out.
Seek a doctor’s advice for frequent urination if:
To prevent frequent urination, consider the following tips:
You Can Also Read: Heartburn: Causes, Symptoms & Medication
You will have to consider the intake of any medicines, amount of fluid intake and consumption of caffeine and alcohol before deciding if it is a case of frequent urination.
If you still face difficulties with urination, you can always take a test to determine the same. Once you have identified what causes excessive urination, you will be able to control it to some extent, without medical interference.
In general, it is recommended to follow these tips to avoid putting unnecessary pressure on your bladder:
Have you been feeling a bloated sensation in your body and wondering why you have so much gas building up inside it? There are reasons for excessive gas which can cause severe discomfort in the body, if not released in the same proportion as it is produced.
Excessive gas can result from:
Disorders such as:
Eating foods such as beans, lentils, bran, dairy products, fructose, carbonated beverages, cabbage, cauliflower, sprouts, etc. can also lead to gas buildup.
While it feels uncomfortable and embarrassing around other people, the release of gas from the body is merely a sign of proper functioning of the digestive system in your body. But if you are farting more than 15 times a day, it is a sure sign of excessive gas formation in your body.
On its own, it is rare for intestinal gas to cause any major problem in the body. It’s normal to experience a sharp pain in the stomach every once in a while. However, if you find that the pain is unbearable, you should seek medical attention.
Seek a doctor’s advice for excessive gas if:
You Can Also Read: Constipation common causes & treatment explained by best Gastroenterologist
To prevent excessive gas, consider the following tips:
Certain changes, such as the inclusion of exercises and yoga, can help in limiting the blockage of gas in the body and help release it. At the same time, changes in dietary habits can be beneficial for the body to reduce the formation of gas. Severe persistence of gas in the body warrants seeking medical advice, though.
The incidences of excessive gas and frequent urination in your body can be limited in most cases by taking precautionary measures. However, some unforeseeable situations can demand medical attention in some severe cases. It is always advisable to seek medical help from an experienced urologist. Timely care and help can ensure an appropriate diagnosis and treatment of your condition.
At the CK Birla Hospital, we ensure patients get holistic medical support which includes treatment in a compassionate environment. This patient-centric approach not only helps patients heal better but also ensures they are aware of the preventive measures as well. In case you need to consult a gastroenterologist, reach out to us, or book a direct appointment at the CK Birla Hospital.
You may be urinating excessively all of a sudden for several common, controllable reasons. The most common reason for frequent urination is an illness that affects the urinary system.
The causes of excessive farting can include intolerance to certain food items or underlying conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome. Identifying the cause of excess gas is key to solving the underlying issues.
Excessive gas may indirectly lead to urinary discomfort due to increased abdominal or stomach pressure. It can create a sensation of frequent urination. However, persistent or severe issues should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
Yes, urinating every 2 hours can be normal, especially if you’re well-hydrated. However, frequency can vary based on factors like fluid intake, bladder capacity, and underlying medical conditions.
Knee replacement surgery or arthroplasty of the knee is performed when there is severe pain that doesn’t respond to medicine, mobility issues or considerable damage to the knee.
Some common reasons why your doctor may recommend knee arthroplasty:
There may be additional reasons why your Orthopedic doctor might suggest knee replacement surgery depending on your lifestyle, symptoms, and condition.
Before getting ready for knee replacement surgery, it’s best to understand how the procedure works. Knee replacement surgery consists of resurfacing the knee with metallic and plastic polymer parts or prosthetic implants that help support the joint. This enables mobility and reduces pain in the damaged area.
There are two types of knee replacement surgery:
From the fear of pain to the doctor’s recommendation, there could be multiple reasons for delaying surgery. Hence it is necessary to make an informed decision when doing so. Most doctors initially go with alternatives to knee replacement. If non-surgical methods fail, surgery is recommended.
Following are some of the dangers of delaying knee replacement surgery:
Also, read: Knee pain – when to see a doctor?
While the hip and knees work in close coordination and support body weight, in the short term, delaying total knee arthroplasty is unlikely to have damaging effects. However, over the years, there could be some pain in the hip due to odd postures and movements. This may happen as the knee balances off-centre loads and may not do so efficiently.
Knee joint replacement surgery may be delayed due to underlying conditions or individual circumstances. Here are some tips to help manage the pain:
Depending on individual cases, along with avoiding the above risks, patients may have the following benefits:
Taking care of your knees may help prevent or delay the onset of problems.
The benefits of arthroplasty of the knee are evident as they provide relief from pain and return mobility. Opting for knee surgery too soon without considering alternatives might lead to minimal benefits and revisions. However, one must note symptoms and approach a doctor before the condition worsens.
While the doctors decide options based on your age, scans, joint function, and intensity of pain, the choice of having knee surgery lies with the patient. So, depending on the discomfort and how much your knee affects day to day life, knee replacement surgery could prove to be of great benefit.
Also, read: Quality of life after Total Knee Replacement Surgery
Pregnancy is a fascinating process that involves a lot of changes in a woman’s body. From the fertilisation of the egg to the delivery, several steps occur in the reproductive system.
In a normal pregnancy, the fertilised egg travels through the fallopian tubes and attaches itself to the uterus. However, if you have an ectopic pregnancy, the fertilised egg starts growing outside the uterus, somewhere else in the belly. It is also referred to as extra-uterine pregnancy.
As the fertilised egg grows, the fallopian tube may rupture, causing heavy internal bleeding and severe blood loss. Also, the blood can lead to scar tissue formation, which can further cause problems with future pregnancies. According to an NCBI report, ectopic pregnancy affects one or two in a hundred pregnancies.
Table of Contents
There are two different types of ectopic pregnancy, depending upon the location:
In most of the ectopic pregnancy cases, the egg implants in the fallopian tube, known as tubal pregnancy and starts growing in it. More than 90% of ectopic pregnancy cases happen in the fallopian tubes.
Related read: Tubal ectopic pregnancy
Nearly two percent of all ectopic pregnancies establish in other areas like the ovary, the cervix or the abdominal cavity.
In the initial phase of ectopic pregnancy, you experience the same typical pregnancy symptoms like missed period, nausea, sore breasts. Typically, after six weeks of pregnancy, you may experience some abnormal pregnancy signs.
Some early signs of ectopic pregnancy to look out for, are:
It is vital to get medical advice if you experience any of the above signs of ectopic pregnancy. If delayed, it has the potential to cause life-threatening complications for the mother.
Certain factors can increase your chances of ectopic pregnancy:
However, it is important to note that it is possible to have ectopic pregnancy without any of the above risk factors. About a third of women in such cases had none of the ectopic pregnancy risk factors.
Your doctor uses a blood test to confirm your HCG (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin) levels. In an ectopic pregnancy, the HCG levels remain low while in a normal pregnancy, the levels double-up every 48 hours in the initial weeks. In this way, regular blood tests give your doctor an idea of the possibility of developing an ectopic pregnancy.
A transvaginal ultrasound can also confirm an ectopic pregnancy after a few weeks of conception. The radiologist places a wand-like tool into your vagina to produce images of the uterus through sound-waves and evaluate the pregnancy.
However, it is difficult to detect pregnancy with ultrasound in the initial few weeks so your doctor may go for blood tests to monitor your condition from early on.
At present, there is no technology to move an ectopic pregnancy to the uterus, and unfortunately, your doctor cannot save it. Depending on your case, an ectopic pregnancy treatment plan includes both surgery and medication.
Laparoscopy, also called key-hole surgery, is usually performed to remove the ectopic tissue. It involves a tiny incision on the pelvic skin to remove the pregnancy. The recovery time for an ectopic pregnancy surgery is the least in laparoscopy, making it a preferred option.
In a tubal pregnancy, the best effort is made to leave the fallopian tube intact for higher chances of a healthy pregnancy in future. However, in some instances, depending on the extent of damage, a portion of the fallopian tube requires essential removal.
If the scar tissue is massive and the internal bleeding is severe, your doctor may perform laparotomy, requiring a larger incision.
You may or may not experience any side-effects after ectopic pregnancy surgery. However, it is essential to take care of the incisions after surgery to avoid any sort of infection. Make sure to keep them clean and dry till they heal completely.
When the pregnancy is detected at an early stage, your doctor may use drug therapy for ectopic pregnancy treatment. Methotrexate is a common drug which stops ectopic tissue cells from growing and dissolves the existing cells. The doctor gives this medication as an injection and performs regular blood tests to monitor its effectiveness.
This method saves you the risk of fallopian tube damage that comes with ectopic pregnancy surgery.
Ques 1: Is there always pain with ectopic pregnancy?
Ans: Usually, there are signs of pain and discomfort in an ectopic pregnancy. You may experience vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain on one-side, and shoulder tip pain after around six weeks of pregnancy.
Ques 2: Can a baby survive in an ectopic pregnancy?
Ans: Unfortunately, the embryo can’t develop to term anywhere other than the uterus. Hence, such pregnancies must be removed by the doctor as early as possible to avoid serious complications.
Ques 3: Can women get pregnant after an ectopic pregnancy?
Ans: Most women can have healthy pregnancies after an ectopic one. Even if one fallopian tube is damaged during your pregnancy, the egg can still fertilise as usual in the other one.
Ques 4: How can I prevent an ectopic pregnancy from happening again?
Ans: It might be difficult for you to fully prevent an ectopic pregnancy. But you can still try to minimise some of the risk factors associated with it by making some lifestyle changes.
Although it’s challenging to cope with a lost pregnancy, do not lose hope. The next time you get pregnant, call your obstetrician right away. Your doctor can monitor your pregnancy from the start for any possible abnormality or complication.