
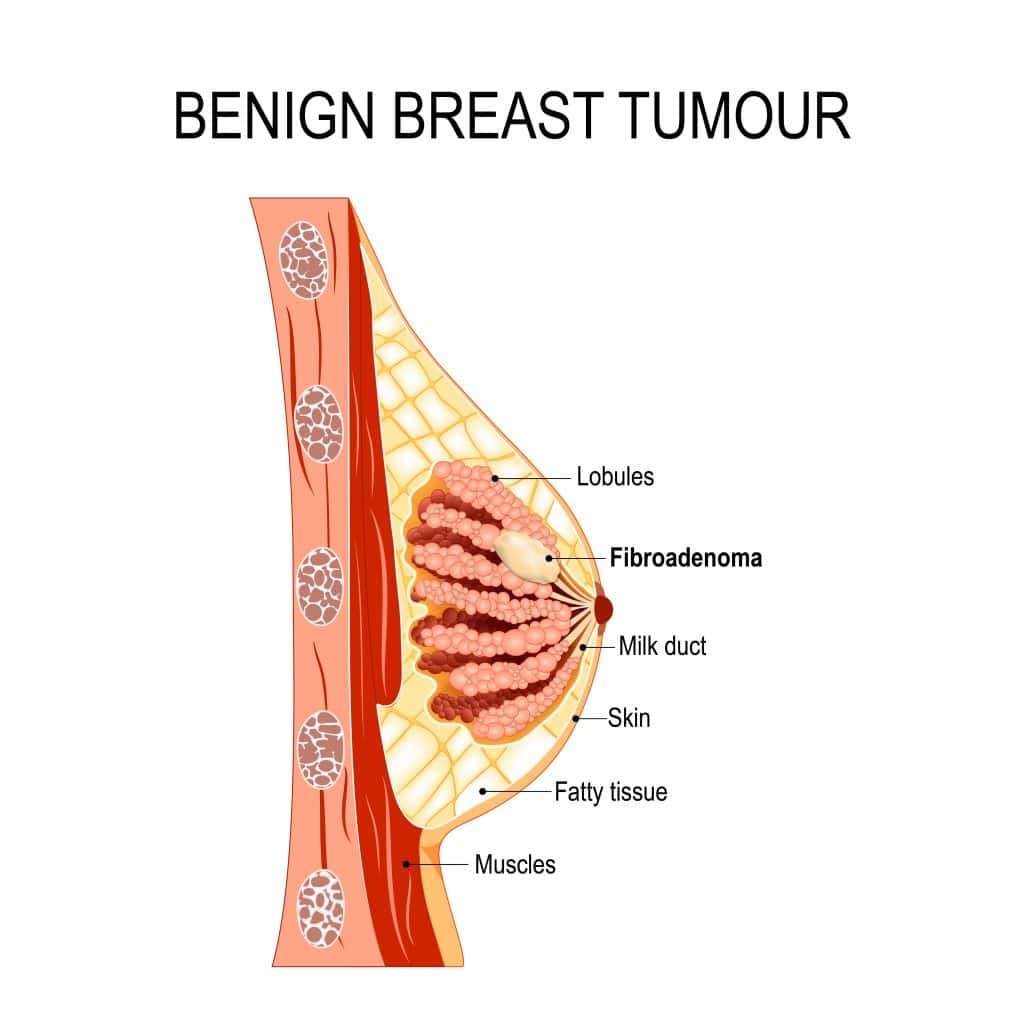
Benign, by definition, means non-malignant aka non-cancerous. Benign breast conditions (also referred to as benign breast disease) are non-cancerous tumours or diseases that affect the breast area.
Human beings have a natural tendency to be health anxious, especially with regards to some areas of our body, for instance, breasts. If you were to wake up with an abnormality in your breast size, shape, touch or appearance, you would most likely assume it to be cancer. And rightly so, considering the high prevalence of breast cancer with nearly 2 million people affected worldwide every year. However, irrespective of the rising incidence, not all breast abnormalities are cancer. Benign breast conditions (also called non-cancerous breast conditions or benign breast disease) are also commonplace and affect millions of women across different age groups.
In this article, Dr Rohan Khandelwal, a leading breast specialist in Gurgaon at the CK Birla Hospital, explains everything there is to know about benign breast conditions.
Benign, by definition, means non-malignant aka non-cancerous. Benign breast conditions (also referred to as benign breast disease) are non-cancerous tumours, growths, or structural changes that affect the breast area.
Noncancerous breast conditions indicate the presence of unusual growths that are not related to cancer cells. These growths appear in the form of breast lumps and are often misunderstood for cancerous tumours. However, about 80% of breast lumps are found to be benign upon diagnosis.
While a benign breast lump may not be directly associated with cancer, certain conditions may increase the risk of developing breast cancer in the future. Medical experts therefore classify benign breast diseases based on their cancer risk.
Therefore, benign breast lumps classification includes three categories:
Also called non-proliferative breast lumps, these are typically associated with no future risk of breast cancer.
Examples include:
The risk of cancer with such conditions is minor, but they may require regular monitoring.
Examples include:
Other conditions include juvenile papillomatosis and peripheral intraductal papillomas.
Also called “atypical ductal hyperplasia” or “atypical lobular hyperplasia”, this condition involves unusual-looking cells dividing excessively. It increases the lifetime risk of breast cancer by 3 to 5 times.
The treatment may include removal of cells around that area as well as paying closer attention to breast health.
The symptoms of a benign breast lump and breast cancer often overlap. You may feel overwhelmed and scared after discovering the initial symptoms. However, mostly, these atypical growths are diagnosed as benign. Benign breast conditions are so common that up to 50% of all women experience one such disease once during their lifetime.
There are several different types of benign breast diseases that affect every person uniquely. Only a qualified medical professional can diagnose these diseases correctly. Some common signs and symptoms of benign breast disease include:
You must consult a breast specialist even when a single symptom is seen. All of the above signs and symptoms require further testing and investigation.
Benign breast conditions can affect a person in the form of various conditions. Some common diseases include:
Since there is a wide range of benign breast diseases, there are multiple reasons why they occur. Some common reasons for the development of non cancerous breast conditions are:
Anyone can be affected by non cancerous breast conditions. However, some people are at a greater risk than others. You are more likely to have a benign breast disease, if:
It is common to mistake a benign breast lump for breast cancer. It is important that you seek urgent clinical help upon discovering any of the above-mentioned symptoms. The diagnosis of a benign breast disease starts similar to the diagnosis of breast cancer.
Your healthcare provider will order a variety of tests to eliminate the possibility of cancer and identify the type of benign disease. Some common tests include:
Other diagnostic tests may also be ordered if your doctor suspects the need for them or a suspicious lump in breast ultrasound appears.
Your treatment plan for a benign breast disease depends upon its type and severity of symptoms. Most of the benign breast diseases do not require any treatment and do not cause any painful symptoms. These conditions tend to subside on their own.
If you are wondering about breast lump when to worry, you may consult our Breast Cancer Doctor upon experiencing extreme pain or discomfort. Your doctor may offer relevant treatment, accordingly.
As mentioned above, most breast lumps shrink on their own without causing any pain or discomfort. However, you can speed up the treatment of breast lumps naturally.
Here listed are some home remedies that can help to cure breast lumps.
Please note, you should consult with your healthcare provider before applying any of these measures.
Benign breast tumor, by description, are non-cancerous. A majority of benign breast diseases do not turn malignant, that is, cancerous. However, some of them may increase your risk of developing cancer cells.
Simple and fibrosis cysts can be treated if they are causing pain or discomfort. The fluid in these cysts can be drained by inserting a thin and hollow needle in the cyst.
Benign breast conditions are highly common in women across all ages. However, these diseases are not a cause for concern.
If you detect any symptoms that may signal a problem, seek immediate health care. Frequent breast exams and timely treatment will help doctors address complications in time and suggest corrective measures.
For more information on what is benign breast disease, book an appointment with Dr Rohan Khandelwal, the best breast cancer specialist in Gurgaon at the CK Birla Hospital.
Also, watch Dr Rohan Khandelwal, Breast cancer specialist at the CK Birla Hospital sheds some more light on this condition:
Ques: Do benign breast tumours need to be removed?
Ans: If your doctor suspects an abnormality in benign breast tumour along with severe symptoms and pain, they may suggest to surgically remove it.
Ques: Can a benign breast lump turn into cancer?
Ans: No, most benign breast lumps do not turn into cancer.
Ques: What happens if you have a benign breast lump?
Ans: Benign breast lumps are non-malignant and do not usually require clinical intervention.
Ques: What does a benign breast lump feel like?
Ans: Benign breast lumps are soft and usually have smooth edges. These lumps can be moved slightly when pushed.
Ques: Is it necessary to remove benign breast lumps?
Ans: Most often, a benign lump does not need treatment. Surgery may be done if you experience pain, discomfort or other symptoms.
Ques: Are benign breast conditions & cancer common in men?
Ans: Men are at a much lower risk of breast cancer or breast conditions than their female counterparts, although they can develop similar breast conditions, too.
Written and Verified by:

Similar The Breast Centre Blogs
Request a call back