Filter :
Throughout the ages, childbirth has been considered to be one of the most beautiful and life-changing experiences. Many expectant mothers, however, especially first-time mothers dread the infamous labour pains that come along with “the miracle of birth”.
With leaping advances in technology and medical care, women have a number of alternatives to choose from while deciding how to deliver their baby. These birthing techniques adopt different ways to manage labour pain and make childbirth easier for the mother as well as the baby. Here we will explore these birthing alternatives in greater detail, exploring the various pros and cons associated with each.
Benefits of vaginal delivery
Going into labour and opting for a vaginal delivery generally means spending several hours in the labour room, straining to bring your baby into this world. It is a physically gruelling process which involves a lot of hard work and pain.
However, many women opt for vaginal delivery in-spite of the labour pains because of its benefits in the long run. Vaginal delivery usually means significantly shorter hospital stays and recovery times. The mother also avoids life-long scarring that comes with surgical birthing techniques.
Women opting for vaginal deliveries also avoid the risks associated with major surgery such as bleeding, infection, post-op pain and complications due to anaesthesia. As the you would be more aware during vaginal birth (as compared to post surgery), you can start breastfeeding sooner.
Studies also indicate that vaginal birth is beneficial for the baby as it helps in squeezing out fluid from the baby’s lungs as he/she travels through the birth canal. The baby is also exposed to healthy bacteria in the birth canal which in turn boosts his/her immunity.
Risks of vaginal delivery
Even though vaginal delivery is often thought to be the “best” birthing technique, it does involve a number of risks that every expectant mother should be aware of. Today, medical authorities around the world are mandating that every birthing alternative should be discussed with the to-be parents in detail, enabling them to make informed decisions.
Natural vaginal delivery is associated with risks such as tearing, excessive bleeding (haemorrhaging), injury to pelvic floor muscles amongst others. In some cases, the doctor can make a small incision in the perineum (the area between the vagina and anus) to aid the delivery. This procedure is called an episiotomy. Vaginal delivery can also result in injuries to the baby, if the baby is too large or the labour too intensive and long.
Also, read: Normal delivery – tips & preparation
Benefits of caesarean section
Caesarean section is a surgical birthing technique in which the doctor delivers the baby through incisions in the abdomen and uterus. Opting for caesarean delivery often allows the parents to schedule the procedure. In some cases, it can be an emergency procedure or the only suitable birthing technique available. This is especially true for high risk pregnancies, pregnancies with complications such as gestational hypertension, preeclampsia etc.
Caesarean section is the safest option for mothers if there are any concerns about her health or her baby’s. This surgical birthing method reduces the risk of painful labour, vaginal injuries, heavy bleeding, loss of bladder control, pelvic organ prolapse etc. It also offers the doctor better control of the delivery.
Risks of caesarean section
Like all surgical procedures, caesarean section involves the risks of bleeding, infection, blood clots, surgical injury and complications from anaesthesia. Caesarean section is usually not recommended for first time mothers who want to have more children, as this procedure can cause complications in subsequent pregnancies. These complications include placenta previa, preterm birth etc.
The recovery time for patients who underwent caesarean section is also longer. They are usually kept under observation in the hospital for a few days, post which they can continue recovering at home.
Read: Caesarean section delivery – What to expect
Benefits of assisted vaginal delivery
When vaginal delivery is aided by forceps or a vacuum device to pull the baby out, it is called an assisted vaginal delivery. In some cases, such as when the mother becomes too tired to push, forceps or vacuum is used to help her deliver the baby. In case of a forceps assisted delivery, the forceps are inserted into the vagina to gently hold the baby’s head which is then pulled out of the birth canal while the mother is pushing. A vacuum assisted delivery is similar with the exception of a suction cup being used instead of forceps.
Assisted vaginal delivery is usually done if there are any concerns about the baby’s heart rate, if the mother is too tired, the baby is not moving forward in the birth canal and if the mother has any medical condition which limits her ability to push safely.
The main benefit of assisted vaginal delivery is that it helps avoid the need for a caesarean section and the risks involved in the same.
Risks of assisted vaginal delivery
Risks associated with assisted vaginal delivery are very similar to those of normal vaginal delivery. These include injury to the vaginal tissues, perineum and anus. It can also cause injury to the pelvic floor muscles. For the baby, there is an extremely small risk of injury due to improper use of forceps and suction.
Benefits of water birthing
This birthing technique has been around for centuries however, the past few years has seen an exponential rise in the popularity of water birthing. Simply put, it is the process of giving birth inside temperature-controlled water. Some women choose to give birth to their baby while immersed in water, while some women may choose to step out of the birthing pool before giving birth to the baby.
There are numerous benefits of water birthing. Reduction of labour pains is one of the most well-known benefits of water birthing. Many women also say that they felt calmer and more in control while they were immersed in water. They also had a greater sense of privacy. The warm water helps in making the perineum more elastic and relaxed, reducing the risk of injury or tear during birth.
Water birthing is also thought to be less stressful for the baby as he/she enters an environment similar to the womb (amniotic sac).
Risks of water birthing
Like every medical procedure, water birthing has a few risks as well. In case of emergencies such as a baby in distress or increased labour pains, it can become difficult to get the mother out of the birthing pool. Another disadvantage of water birthing is that fetal monitoring is not possible. Water birthing also limits the usage of pain management techniques such as epidurals. Due to such reasons, water birthing is recommended only for healthy non-complicated pregnancies.
There is also a risk of infection if the baby passes stool during delivery. However, these are extremely rare cases.
Today, there are a number of birthing options available to women. Many factors such as personal opinion, maternal and fetal health, pregnancy complications etc have to be considered while deciding which birthing technique to opt for. Remember to have this discussion with your maternity doctor early on in the pregnancy so you can start preparing mentally and physically for childbirth.
Also, read: Water Birth: The Most Natural Form of Normal Birth
Ques 1: Can I have normal delivery after caesarean?
Ans: Yes, these deliveries are termed as VBACs (Vaginal delivery after caesarean section). You can consult an obstetrician who specialises in VBACs to find your suitability for this procedure.
Ques 2: Can my baby be injured during normal vaginal delivery?
Ans: There are a few risks for the baby during normal vaginal delivery. This process is quite painful and long for many women. They can get tired mid labour, causing the baby to get stuck in the birthing canal, the baby can also get hypoxia if he/she gets stuck in their umbilical cord etc. While choosing a maternity hospital, make sure the team is experienced in handling pregnancy emergencies. In such cases, the doctor usually aids the delivery with forceps or vacuum suction cups.
Ques 3: Can caesarean section make it tougher for me to get pregnant again?
Ans: Caesarean sections are known to make future pregnancies difficult, hence it is not recommended for first-time mothers or for women desiring to have more children.
Read: Normal Vaginal Delivery – What Should ‘Mothers-to-Be’ Expect
For years diet and exercise were the only two methods of tackling obesity. Even today, they are essential for healthy weight loss and maintaining a healthy body weight.
However, in some cases, losing weight is not as simple as increasing one’s physical activity and decreasing their daily calorie intake. This is when weight loss surgery or bariatric surgery comes into the picture.
In earlier times, obesity was not considered a medical condition. People struggling with obesity were often judged harshly. This increased the psychological impact of the condition. Today, we know that obesity is the result of a complex interplay of factors including genetic, environmental and lifestyle.
Obesity is linked to a wide range of chronic and acute health conditions such as heart disease, type II diabetes, hypertension etc. For people who are suffering from serious weight related conditions and have a BMI (body mass index) greater than 35, weight loss surgery or bariatric surgery is a good option.
Table of Contents
Bariatric surgery is a surgical procedure that aids in weight loss. In this procedure, changes are made to the digestive system.
Bariatric surgery is used in combination with lifestyle and dietary changes to effectively treat obesity. People who are obese and have serious health conditions such as type II diabetes or sleep apnoea (due to their weight) are considered for bariatric surgery.
Weight loss surgery can be broadly classified into two categories:
In open bariatric surgery, the doctor makes a single large cut in the abdomen to make the necessary changes in the digestive system. In laparoscopic procedures, the surgeon inserts thin surgical tools including a small scope into the abdomen through several small incisions. Laparoscopic procedures are preferred as it is associated with lower risks, post-op pain and recovery time.
Furthermore, bariatric surgeries can either be malabsorptive or restrictive. In restrictive bariatric surgery weight loss is achieved by limiting the food intake while in malabsorptive, it is achieved by limiting the absorption of nutrients and calories.
The different types of weight loss surgeries are:
Of these, gastric bypass (Roux-en-Y) and sleeve gastrectomy are the most common procedures.
In Roux-en-Y, the surgeon makes a direct connection between the stomach and the small intestine. This enables the consumed food to bypass most of the stomach and the first half of the small intestine, hence limiting absorption of nutrients and calories.
In sleeve gastrectomy, the surgeon takes out a part of the stomach to make the stomach smaller. This decreases the amount of food that can be held in the stomach hence limiting the intake of food.
The amount of weight lost after undergoing bariatric surgery depends on the patient’s health as well as the type of bariatric surgery performed. Studies show that patients who have had the Roux-en-Y shed around 70% of their excess body weight while patients who underwent a sleeve gastrectomy loose up to 60% of their excess body weight.
Bariatric surgery is an effective way to reduce body weight when exercise and diet are not effective enough. It helps in preventing a wide spectrum of health conditions which are linked to obesity. These include:
Patients also claim that their weight loss has improved their quality of life as well as their psychological health.
Every surgery has some or the other risks associated with it. Before opting for any type of bariatric surgery, it is essential that you understand the procedure and the risks it involves. The short-term complications that may arise after any weight loss surgery is similar to the risks associated with any abdominal surgery. These include:
Bariatric surgery can also lead to complications that may arise later in life. The long-term risk of weight loss surgery includes:
Bariatric surgery is no magic solution to obesity. Medical professionals believe that a multi-disciplinary approach is the best way to ensure long term results. After getting weight loss surgery, exercise and diet are key to avoid gaining weight again. You can get tailored exercise regimens with a physiotherapist. Dieticians and nutritionists can help you come up with a diet that suits your body’s requirements.
Obesity can also have a severe psychological impact. Psychologists can help patients overcome psychological barriers, improve self-control and regain their confidence.
Patients generally discharged 2-5 days after the surgery, if complications do not develop. Once the hospital stay is over, you can resume mild exercise to improve blood circulation, prevent blood clots and hasten to heal. Consult your doctor before you perform any type of physical activity.
Remember, any type of weight loss surgery does not guarantee that you will not regain the weight. Bariatric surgery may not be the magic solution to stubborn and dangerous weight but it certainly is an important ingredient.
क्या आपके पीरियड्स मिस हुए हैं? यदि इसका उत्तर हाँ है तो यह आपकी प्रेगनेंसी का एक शुरूआती लक्षण हो सकता है। वैसे तो प्रेगनेंसी की जाँच के लिए मार्किट में बहुत सारे प्राथमिक टेस्ट उपलब्ध हैं, किन्तु कुछ लक्षण ऐसे होते हैं जिनको देखकर आप पता लगा सकती हैं की आप गर्भवती हैं या नहीं।

यद्धपि हर महिला भिन्न भिन्न तरह के लक्षणों को महसूस कर सकती हैं, किन्तु कुछ लक्षण सभी महिलाओं में समान होते हैं जो प्रेगनेंसी के प्रारम्भिक लक्षणों के रूप में जाने जाते हैं।
डॉ अरुणा कालरा, गायनेकोलॉजिस्ट एवं आब्सटेट्रिक्स (Gynecology and Obstetrics), सी के बिरला हॉस्पिटल, के अनुसार अक्सर मिस्ड पीरियड को प्रेगनेंसी का प्रारम्भिक लक्षण माना जाता है। इसके अलावा आप अपने ब्रेस्ट में दर्द, मॉर्निंग सिकनेस, जी मिचलाना इत्यादि भी महसूस कर सकती हैं।
यहाँ हमने कुछ प्रेग्नेंट होने के लक्षण दिए हैं जिन्हे देखकर आप पता लगा सकती हैं की आप गर्भवती हैं या नहीं।
इसे भी पढ़ें: प्रेगनेंसी के पहले महीने में क्या क्या होता है?
Table of Contents
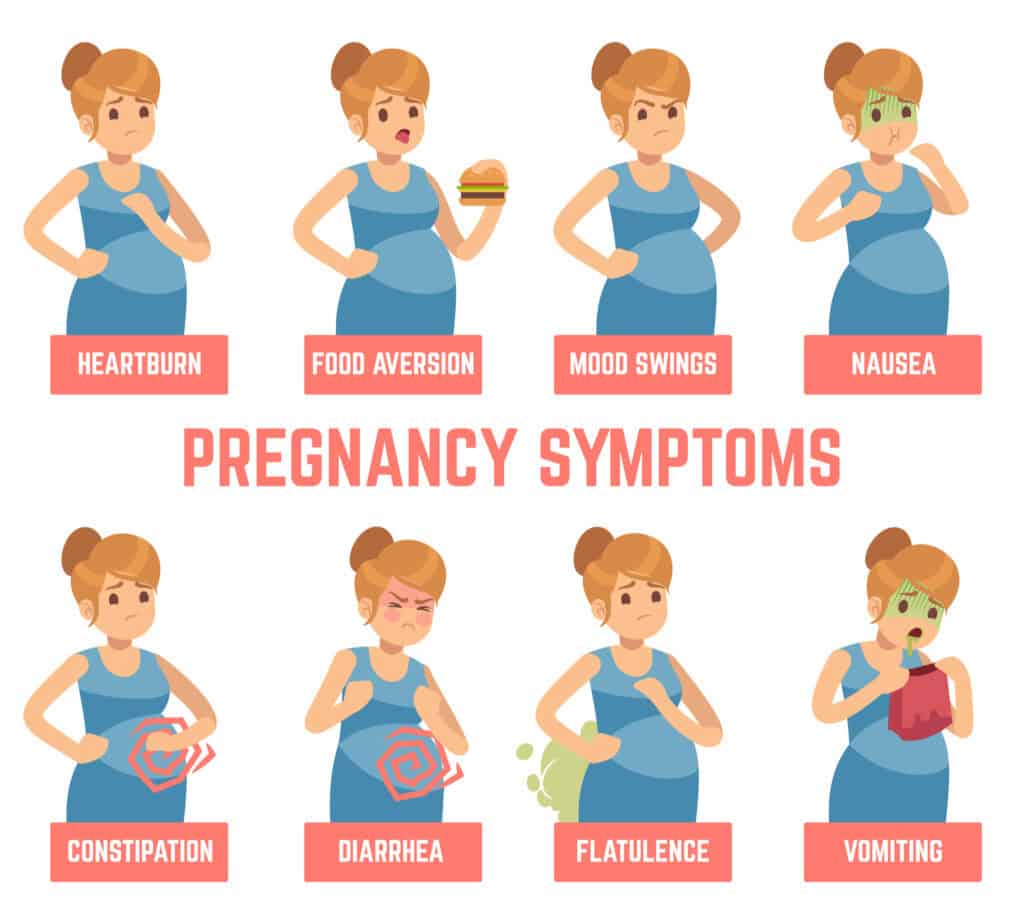
यदि आप कन्सीव करने की कोशिश कर रही हैं और उस दौरान आपके पीरियड्स मिस हो जाते हैं तो आप प्रेगनेंट हो सकती हैं। डॉक्टर के अनुसार भी आपके पीरियड्स का मिस होना प्रेगनेंसी का प्रारम्भिक लक्षण माना जाता है।
किन्तु कभी कभी अन्य स्वास्थ्य समस्याओं के कारण भी आपके पीरियड्स मिस हो सकते हैं अतः पीरियड्स मिस होने पर प्रारम्भिक प्रेगनेंसी टेस्ट करें या अपने डॉक्टर से तुरंत सलाह लें।
कुछ महिलाओं को गर्भधारण के तुरंत बाद जी मिचलाने और चक्कर आने की समस्या महसूस हो सकती है किन्तु आवश्यक नहीं की यह समस्या सभी महिलाओं को हो।
वैसे तो इस समस्या के होने का कोई स्पष्ट कारण नहीं होता लेकिन डॉ अरुणा कालरा के अनुसार यह समस्या गर्भावस्था के दौरान हार्मोन के घटने बढ़ने के कारण हो सकती है।
जब भ्रूण पहली बार गर्भाशय में जाता है, तो यह रक्त वाहिकाओं (ब्लड वेसल्स) को बाधित करता है और रक्तस्राव का कारण बनता है, जिसे “इम्प्लांटेशन ब्लीडिंग” के नाम से जाना जाता है।
इस हल्के रक्तस्राव को अक्सर भूलवश पीरियड्स की शुरुआत मान लिया जाता है, लेकिन आमतौर पर पीरियड्स के खून का रंग थोड़ा अलग होता है। यह फर्टिलाइजेशन के दस से चौदह दिन बाद हो सकता है।
डॉक्टर के अनुसार यह गर्भावस्था के शुरुआती संकेत के रूप में जाना जा सकता है, हालांकि, यह सभी महिलाओं को नहीं होता है।
गर्भावस्था के शुरुआती लक्षणों में थकान महसूस होना भी बहुत सामान्य होता है। प्रारंभिक गर्भावस्था के दौरान, हार्मोन प्रोजेस्टेरोन का स्तर बढ़ जाता है जिससे आप थकान अनुभव कर सकती हैं जिससे आपको अधिक नींद भी आ सकती है।
मॉर्निंग सिकनेस को भी प्रेगनेंसी के मुख्य लक्षणों में से एक माना जाता है जो दिन या रात किसी भी समय हो सकती है, अक्सर आपके गर्भवती होने के एक महीने बाद यह लक्षण दिखाई देना शुरू होता है।
हालांकि, कुछ महिलाओं में यह कुछ पहले भी शुरू हो सकता है, क्योंकि प्रत्येक महिला के लक्षण भिन्न भिन्न हो सकते हैं।
गर्भावस्था के शुरुआती दिनों में हार्मोनल परिवर्तन के कारण आपके ब्रेस्ट या स्तनों में आप संवेदनशीलता और निप्पल्स में दर्द महसूस कर सकती हैं। कुछ महिलाओं में निप्पल्स में संवेदनशीलता के साथ साथ ब्रेस्ट में दर्द भी अनुभव किया जा सकता है।
यह असुविधा कुछ हफ्तों के बाद कम होने लगती है क्योंकि समय के साथ आपका शरीर हार्मोनल परिवर्तनों को अपने में समायोजित कर लेता है। इसके अलावा आपके निप्पल्स का रंग भी भूरे से काले रंग में परिवर्तित होने लगता है।
गर्भावस्था के शुरूआती लक्षणों में मूड में उतर चढ़ाव आना भी अहम् भूमिका निभाता है। प्रेग्नेंसी के बाद एक महिला बिना कारण हँसना, रोना और असामान्य रूप से भावनात्मक व्यवहार का अनुभव करती है ऐसा उसके शरीर में हार्मोन के कारण होता है। यह लक्षण अक्सर सभी महिलाओं में उनकी गर्भावस्था के समय काफी आम हैं।
प्रेग्नेंसी के शुरुआती दिनों में आप सिर दर्द का अनुभव कर सकती हैं जो गर्भावस्था के शुरूआती दिनों में शरीर में बढ़ते रक्त परिसंचरण और (निश्चित रूप से) बढ़ते हार्मोन के स्तर के कारण हो सकता है। बहुत बार तेज़ सिर दर्द के साथ आप अत्यधिक थकान का भी अनुभव कर सकती हैं।
बार बार टायलेट जाना भी प्रेगनेंसी के मुख्य लक्षणों में जाना जाता है। यदि आप आपनी ओवुलेशन प्रक्रिया के बाद गर्भधारण कर लेती हैं तो आप एक दिन में सामान्य से अधिक बार पेशाब के लिए जा सकती हैं ऐसा इसलिए होता है क्योंकि गर्भावस्था के दौरान आपके शरीर में रक्त की मात्रा बढ़ जाती है, जिससे आपकी किडनी अधिक मात्रा में तरल पदार्थ निकालने लगती है जो हैं जो पेशाब की सहायता से बाहर निकलता है।
गर्भधारण के बाद एक खास लक्षण होता है जो अधिकतर सभी महिलायें अनुभव अवश्य करती हैं, वह है आपके स्वाद में परिवर्तन, कभी किसी भोजन को खाने की बहुत इच्छा होना या मनपसंद भोजन से चिड़न होना।
नई गर्भवती महिलाओं में अक्सर भोजन की गड़बड़ी विकसित होती है, प्रेगनेंसी से पहले उनके पसंद किए जाने वाले व्यंजन इस दौरान पसन्द नहीं आते।
इसके अलावा आपको किसी खास भोजन को खाने का मन बार-बार हो सकता है, इसे गर्भावस्था में भोजन की क्रेविंग के रूप में जाना जाता है।
गर्भधारण करने के बाद आपकी पाचन क्रिया थोड़ी कमजोर पड़ सकती है जिस कारण आप कुछ पाचन सम्बन्धी समस्याओं जैसे पेट फूलना, कब्ज, उल्टी आना इत्यादि सामना कर सकती हैं। ये सभी समस्याएँ भी प्रेगनेंसी के शुरूआती लक्षणों के रूप में जानी जाती हैं।
गर्भावस्था के दौरान, पाचन क्रिया धीमी होने के कारण भोजन पाचन तंत्र में सामान्य से अधिक लंबे समय तक रहता है जिस कारण कई गर्भवती महिलाओं को अपनी गर्भावस्था में गैस या ब्लोटिंग की समस्या काफी पहले अनुभव होने लगती है। इसके अलावा कब्ज की शिकायत भी काफी आम है।
प्रोजेस्टेरोन का उच्च स्तर न केवल पाचन प्रक्रिया को धीमा करके गैस और ब्लोटिंग का कारण बनता है, साथ ही ये पाचन तंत्र की विभिन्न मांसपेशियों को भी धीमा कर देते हैं, जिस कारण कब्ज की समस्या भी उत्त्पन्न हो जाती है।
प्रेगनेंसी की पहली तिमाही में महिला को पेट में हल्का सूजन अनुभव हो सकता है। हालाँकि, यह कुछ सप्ताह के भीतर अपने आप दूर भी हो जाता है। सूजन के कारण प्रेगनेंसी के शुरुआती लक्षण में पेट में दर्द की शिकायत भी हो सकती है। अधिक परेशानी होने पर डॉक्टर से परामर्श करना चाहिए।
प्रेगनेंसी में महिला के स्तनों में सूजन होना और निप्पल्स का रंग बदलने के साथ-साथ स्तनों का आकार भी बढ़ता है। यह भी प्रेगनेंसी के शुरुआती लक्षणों में शामिल है।
इसे भी पढ़ें: जानिए प्रेगनेंसी में संबंध बनाना चाहिए या नहीं ?
जब एक महिला गर्भधारण करती है तो उसकी योनी से ब्लीडिंग डिस्चार्ज होने के साथ-साथ पेट में गैस और ऐंठन की शिकायत भी होती है। यह भी प्रेगनेंसी के लक्षण में से एक है।
गर्भवती महिला के शरीर में हार्मोनल असंतुलन होता है जिसके कारण महिला को सामान्य से अधिक मात्रा में भूख और प्यास लगती है। गर्भावस्था के दौरान महिला को बार-बार भूख और प्यास लगना सामान्य है। यह गर्भधारण के शुरुआती लक्षण में शामिल है।
गर्भधारण करने के बाद एक महिला का खुद में कमजोरी और सुस्ती अनुभव करना सामान्य है। यह भी गर्भावस्था के शुरुआती लक्षणों में से एक है।
गर्भावस्था के दौरान महिला को गैस की समस्या होती है जिसके कारण उसके सीने में जलन की समस्या पैदा हो सकती है। इसे दूर करने के लिए डॉक्टर आमतौर पर डाइट में कुछ बदलाव लाने का सुझाव देते हैं।
प्रेगनेंसी के शुरुआती लक्षणों में महिला को सांस लेने में तकलीफ होना भी शामिल है। गर्भधारण करने के बाद महिला का साँस फूलना, थकान और कमजोरी महसूस करना सामान्य है। हालाँकि, अधिक परेशानी होने पर तुरंत डॉक्टर से मिलना चाहिए।
गर्भावस्था के कारण शरीर में हार्मोनल परिवर्तन होने के कारण महिला की सूंघने की क्षमता में बदलाव आता है और उसके सूंघने की क्षमता बढ़ जाती है। प्रेगनेंसी के शुरुआती लक्षण पहले महीने के शुरुआत में अनुभव हो सकते हैं।
यदि आप उपरोक्त दिए सभी लक्षण महसूस कर रहे हैं तो आप गर्भवती हो सकती हैं, किन्तु कुछ भी स्पष्ट करने से पहले प्रेगनेंसी टेस्ट अवश्य करायें या तुरंत अपने डॉक्टर से सलाह लें। हम समझते हैं कि किसी भी महिला के लिए प्रेगनेंसी एक खास होती है अतः किसी भी निष्कर्ष पर पहुँचने से पहले अपने डॉक्टर को दिखाएँ और अपनी प्रेग्नेंसी की पुष्टि करें।
इसे भी पढ़ें:जानिए क्या और कब होता है ओवुलेशन?
खान पान हर रोग के इलाज के बाद बहुत ज्यादा महत्वपूर्ण साबित हो सकती है। गर्भावस्था के पहले महीने में आपके बच्चे के विकास के लिए आवश्यक पोषक तत्वों की आपूर्ति करना महत्वपूर्ण है। इस समय के दौरान बच्चे का दिल, मस्तिष्क और अन्य महत्वपूर्ण अंगों का निर्माण शुरू हो जाता है। गर्भावस्था के पहले महीने के डाइट में निम्नलिखित खाद्य पदार्थों को शामिल ज़रूर करना चाहिए –
फल और सब्जियां विटामिन, खनिजों और फाइबर का एक अच्छा स्रोत है। यह सारे पोषक तत्व आपके बच्चे के विकास के लिए बहुत ज्यादा आवश्यक है।
होल ग्रेन फाइबर, विटामिन और खनिजों का एक अच्छा स्रोत है। इसके द्वारा आपके शरीर को ऊर्जा मिलती है, जिससे बच्चा स्वस्थ रहता है।
स्वस्थ वसा, जैसे कि ओमेगा-3 फैटी एसिड, आपके बच्चे के मस्तिष्क और आंखों के विकास के लिए आवश्यक है।
प्रोटीन का कार्य बच्चों के ऊतकों और अंगों का निर्माण है, इसलिए इसका सेवन भी बहुत ज्यादा अनिवार्य है।
अपने आहार में इन खाद्य पदार्थों को शामिल करने के अलावा, आपको नियमित रूप से पानी पीना चाहिए। इससे शरीर में पानी की कमी नहीं होती है जिसके कारण शरीर में प्रेगनेंसी से संबंधित कोई समस्या भी नहीं होती है।
ये भी पढ़े: गर्भावस्था में उल्टी की समस्या के लिए कारगर घरेलू उपाय
प्रेगनेंसी के पहले महीने में शिशु के विकास की प्रक्रिया बहुत ज्यादा खास होती है। उस दौरान मां के मन और स्वास्थ्य में बहुत बदलाव आते हैं। निम्नलिखित चरणों में प्रेगनेंसी के पहले महीने में शिशु का विकास होता है –
इस समय आपके बच्चे को एक कोशिका के रूप में निषेचित किया जाता है। निषेचित अंडा गर्भाशय की दीवार में प्रत्यारोपित होता है।
इस समय, आपके बच्चे के दिल का निर्माण शुरू हो जाता है। शिशु का सिर और रीढ़ की हड्डी भी बनने लगती है।
पहले महीने की शुरुआत में शिशु का चेहरा आकार लेने लगता है। इस दौरान आंख, मुंह, नीचे का जबड़ा और गले का निर्माण भी शुरू हो जाता है। इसके साथ साथ रक्त प्रवाह भी शुरू हो जाता है। पहले महीने के अंत तक भ्रूण का आकार चावल के दाने से भी छोटा होता है।
ये भी पढ़े: लिकोरिया (Likoria) का कारण, लक्षण और उपचार
आमतौर में प्रेग्नेंसी के शुरुवाती लक्षण 6 से 14 दिनों में दीखते हैं। इन लक्षणो में शामिल हैं शरीर का तापमान बढ़ना, ब्रेस्ट में सूजन, ज्यादा थकावट महसूस होना, ज्यादा नींद आना, ऐंठन और पेट संबंधी दिक्कते।
यदि आपके पीरियड मिस (Missed Periods) हुए हैं तो यह सुरुवाती संकेत हो सकते हैं| पीरियड मिस होने के 10 से 12 दिन बाद आप घर पर प्रेगनेंसी टेस्ट किट का उपयोग करके या आप डॉक्टर से टेस्ट करवाकर भी प्रेगनेंसी की पुष्टि करवा सकते हैं।
प्रेगनेंसी के पहले हफ्ते में निम्न लक्षण दिखाई देते हैं:
दरअसल पीरियड के कितने दिन बाद गर्भ ठहरता है ये महिलाओं के ओवुलेशन पर निर्भर करता हैं, यदि कोई महिला पीरियड के करीब 12 से 14 दिन बाद अपने पार्टनर के साथ संबंध बनाती हैं तो गर्भ ठहरने की संभावना बढ़ जाती है।
प्रारंभिक गर्भावस्था के लक्षणों में मिस्ड पीरियड्स, मतली और उल्टी, स्तन परिवर्तन, थकान और बार-बार पेशाब आना शामिल हैं। इनमें से कई लक्षण तनाव या बीमारी जैसे अन्य कारकों के कारण भी हो सकते हैं। अगर आपको संदेह है कि आप गर्भवती हो सकती हैं, तो अपने डॉक्टर से परामर्श करें।
कुछ महिलाएं गर्भाधान के एक या दो सप्ताह बाद गर्भावस्था के पहले शुरुआती लक्षणों को नोटिस करना शुरू कर सकती हैं, जबकि अन्य गर्भधारण के बाद चार या पांच सप्ताह के करीब लक्षणों को महसूस करना शुरू कर देंगी। कुछ महिलाओं को तब तक लक्षण महसूस नहीं हो सकते हैं जब तक कि उनकी अवधि काफी देर से न हो, या गर्भावस्था में आगे भी।
गर्भावस्था के दौरान पेट के निचले हिस्से में दर्द सामान्य है और यह 18 से 24 सप्ताह के बीच सबसे आम है। आपका बढ़ता हुआ गर्भाशय उन मांसपेशियों को खींच रहा है और उन पर दबाव डाल रहा है जो इसे सहारा देती हैं। आप तेज दर्द महसूस कर सकती हैं या बस एक हल्का खींचने वाला सनसनी महसूस कर सकती हैं। यह अक्सर तब होता है जब आप खांसती हैं, छींकती हैं, कड़ी होती हैं, बैठती हैं, करवट बदलती हैं या यौन संबंध बनाती हैं।
कुछ महिलाओं को ओव्यूलेशन के 4 दिन बाद से ही हल्के लक्षणों का अनुभव होना शुरू हो सकता है, लेकिन आपको कुछ सप्ताह इंतजार करने की आवश्यकता होगी। गर्भावस्था के शुरुआती लक्षणों में शामिल हैं: पेट के निचले हिस्से में ऐंठन।
आपकी गर्भावस्था के सप्ताह आपके अंतिम मासिक धर्म के पहले दिन से शुरू होते हैं। इसका मतलब यह है कि पहले 2 हफ्तों में, आप वास्तव में गर्भवती नहीं हैं – आपका शरीर हमेशा की तरह ओव्यूलेशन (आपके अंडाशय में से एक अंडा जारी करना) की तैयारी कर रहा है। आपका “गर्भवती होना” समयरेखा है: दिन 1: आपकी अवधि का पहला दिन।
लाइट स्पॉटिंग गर्भावस्था के पहले लक्षणों में से एक हो सकता है। आरोपण रक्तस्राव के रूप में जाना जाता है, यह तब होता है जब निषेचित अंडा गर्भाशय की परत से जुड़ जाता है – गर्भाधान के लगभग 10 से 14 दिन बाद। प्रत्यारोपण रक्तस्राव उस समय के आसपास होता है जब आप मासिक धर्म की अवधि होने की उम्मीद करेंगे।
आपकी पहली तिमाही के दौरान, जो कि 12वें सप्ताह तक है, आप अनुभव कर सकती हैं:
हां, आप अपनी अवधि याद आने से पहले गर्भवती महसूस कर सकती हैं। कुछ लोगों का कहना है कि गर्भधारण के एक सप्ताह के भीतर उन्हें गर्भावस्था के लक्षण महसूस हुए हैं (पीरियड मिस होने से लगभग एक सप्ताह पहले)।
महिला के गर्भधारण करने के 6-14 दिनों के भीतर प्रेगनेंसी के शुरुआती लक्षण दिखने लगते हैं। इसमें मुख्य रूप से पीरियड्स नहीं आना शामिल है।
गर्भधान करने के एक से दो सप्ताह के अंदर महिला खुद में प्रेगनेंसी के लक्षणों को अनुभव करना शुरू कर सकती है। अगर आप यह जानना चाहती हैं की गर्भ ठहरने के शुरुआती लक्षण क्या है तो हम आपको बता दें की प्रेगनेंसी के शुरुआती लक्षणों ब्रेस्ट में सूजन आना, पीरियड्स मिस होना, मतली और उल्टी होना, थकान महसूस करना और बार-बार पेशाब करने की आवश्यकता होना आदि शामिल है।
Every year, more than 11 lakh new cancer cases are reported in India. Of these, bladder cancer is one form of cancer which is seen predominantly in men. In this article, we will explore bladder cancer in further detail including types of bladder cancer, early warning signs of bladder cancer, lifestyle changes that can help reduce the risk of developing bladder cancer and what to do after getting diagnosed with bladder cancer.
Table of Contents
The bladder is a small muscular sac which is a part of our urinary system. It is responsible for storing urine in the body before eventually passing it out. The bladder is lined by a layer of urothelial cells. These cells are also found inside the kidneys and ureters (tubes connecting the kidneys to the bladder). Bladder cancer occurs if the urothelial cells change or start multiplying rapidly causing a mass to grow (called a tumour). If left unchecked, these cells can spread to other parts of the body (metastasis).
Depending on which type of bladder cell is determined as the starting point of the cancer (which type of bladder cell starts multiplying uncontrollably), bladder cancer is classified into the following types:
Urothelial carcinoma is the most common form of bladder cancer, accounting for almost 90% of all reported bladder cancers. It is also sometimes referred to as “transitional cell carcinoma” (TCC). Urothelial carcinoma can be traced back to the urothelial cells which form the lining of the bladder and other parts of the urinary tract including the kidneys, ureters and the urethra. While TCC can occur in these parts of the urinary system as well, it is most common in the bladder.
This type of bladder cancer is linked to chronic irritation of the bladder. This can occur due to any underlying infection or from long term use of a urinary catheter. It is a relatively rare form of bladder cancer.
Adenocarcinoma is an extremely rare form of bladder cancer. It originates in cells that form the mucus-secreting glands in the bladder.
This form of bladder cancer stems from the neuroendocrine cells. Small cell carcinoma grows rapidly and often requires chemotherapy similar to the one used for small cell carcinoma of the lung.
Sarcomas originate in the muscle cells of the bladder. It is an extremely rare form of bladder cancer and is treated similarly to TCC (transitional cell carcinoma).
Based on how far the bladder cancer has spread into the wall of the bladder, it is also classified into the following two categories:
Bladder cancer is also classified as papillary carcinomas (grows in slender finger-like projections from the inner surface of the bladder toward the hollow centre) and flat carcinomas (does not grow towards the hollow part of the bladder). This type of classification is done based on how the cancer spreads/grows in the body.
For almost all types of cancer, early detection and timely treatment offer the best chances of complete recovery. For bladder cancer as well, knowing the early symptoms is important especially for individuals who are at a greater risk of developing bladder cancer.
In the early stages of bladder cancer, bleeding can occur with little or no pain. Blood in the urine can also be caused due to benign conditions. To rule out bladder cancer, get yourself screened if you notice any change in the colour, frequency or consistency of your urine.
If the bladder cancer has penetrated through the bladder lining and has spread into the surrounding layers of tissue and muscle or other parts of the body, it is considered to be in an advanced stage. The symptoms of advanced bladder cancer are:
If cancer has spread to other parts of the body, the symptoms might be specific to that type of cancer such as bone pain or frequent fractures if cancer has spread to the bones.
Read: Common causes of frequent urination in men
While the risk of bladder cancer cannot be eliminated entirely, making some lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk of developing bladder cancer. Some of these steps are
Consumption of tobacco in any form has been linked to a wide range of cancers including lung cancer, cancers of head and neck etc. Smoking is also one of the leading causes of bladder cancer.
Certain chemicals are known to increase the risk of bladder cancer. There is a higher risk of exposure to such chemicals for people working in industries using leather, rubber, printing materials, textiles and paint. People working in salons are also at risk to these chemicals.
Studies suggest that increasing fluid intake can also reduce the risk of developing bladder cancer.
Following a healthy diet rich in vegetables, fresh fruits, lean protein etc and limiting your intake of empty carbohydrates and fat can help you lead a healthier life. Some studies do suggest that it can lower the risk of bladder cancer, however, there are no conclusive evidence to prove the same.
While controlling risk factors of bladder cancer such as age, gender, ethnicity and family history is not possible, the aforementioned factors are still in our control. As we grow older, the risk of developing bladder cancer also increases. Regular screening and health check-ups are vital to staying ahead of any health problems that may arise with age. For more information regarding your risk factor, you can reach our experts at the CK Birla Hospital, Gurgaon.
Every year approximately 96,922 women are diagnosed with cervical cancer of which more than 60,000 women succumb to the disease. This is majorly due to late diagnosis and lack of regular screening. It is considered to be the 2nd most common cancer detected amongst women of 15-44 years of age.
Table of Contents
Cervical cancer is defined as a type of cancer that develops in the cells of the cervix. The cervix is the lower part of the uterus which connects to the vagina.
The cervix is divided into two parts, namely; the endocervix (opening of the cervix which leads to the uterus) and the ectocervix (outer part of the cervix which is visible in a speculum exam). Both these parts are made of different types of cells (glandular cells and squamous cells respectively). The area where these two regions meet is called the transformation zone. Most cervical cancers begin here itself.
This, however, is a gradual process. The normal cells present in the cervix first develop abnormal changes. These pre-cancerous changes are also referred to as cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN), the squamous intraepithelial lesion (SIL) and dysplasia. Pre-cancerous changes can be detected in a Pap test.
While the exact causes of cervical cancer are still unclear, HPV or human papilloma virus is known to play a role. Not all women with HPV develop cervical cancer.
Lack of awareness, overlooking the need to routine gynecological screening and lifestyle changes have all contributed towards the increasing occurrence of cervical cancer. Dr Anjali Kumar (Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology at the CK Birla Hospital) explores the various warning signs of cervical cancer to watch out for, its risk factors and the need for routine screening.
Similar to almost all other forms of cancer, early detection offers the best chance of complete recovery from cancer. Some of the early symptoms of cervical cancer include:
These symptoms don’t necessarily mean cervical cancer but you must seek the opinion of a gynaecologist.
Read: Ways to Get Rid of Period Cramps
Cervical screening (which is also called a smear test) involves taking a small sample of cells from the surface of the cervix. This is then sent to the laboratory to see if there are any abnormal cells which can turn into cancer if left untreated.
Cervical cancer screening is done with Pap testing (LBC- liquid base cytology) and/ or HPV testing.
Connect with one of our top gynaecologists today to speak about scheduling a screening, receiving the HPV vaccination, or to discuss your symptoms. Book an appointment at the CK Birla Hospital now.
One of the most important risk factors for cervical cancer is infection by HPV or human papilloma virus. HPV is a group of 150 viruses and can cause a type of growth called papilloma. It can affect cells on the skin, lining the genitals, anus, mouth and throat.
HPV spreads via skin-to-skin contact and any type of sexual intercourse. Most types of HPV are considered low risk type, they rarely cause cancer. The HPV types that cause cancers of the cervix, vagina, penis, anus, mouth and throat are called high risk HPV.
Smoking has also been shown to increase the risk of developing cervical cancer amongst other health conditions. Other risk factors include chlamydia infection, long term use of oral contraceptives, multiple full-term pregnancies, unhealthy diet and becoming pregnant at a very young age.
The most effective way to prevent cervical cancer is to get screened regularly. Visit your gynaecologist for routine HPV screening, pap smear and general health check-up. If you are sexually active, you should also get screened for STDs once in a while. Those with weak immune systems or those suffering from human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) will be more likely to contract cervical cancer and hence, should take additional precautions against it.
HPV Vaccine can also be taken to prevent cervical cancer. It is available at the CK Birla Hospital. Connect with Dr Anjali Kumar, expert gynaecologist at the Department of Obstetrics & Gynaecology to learn more.
The ongoing coronavirus pandemic has made us fear the words “fever”, “cough”, “sore throat” and other symptoms associated with COVID-19. Earlier, fever was not an immediate cause of concern, unless it was related to other conditions such as fever in a surgical patient. Today, however, even a mild fever can result in panic and quarantine. In this article, we will look closer at “fever”, measuring it and how to understand if it is harmless or indicative of something far more serious.
Table of Contents
A fever (or hyperthermia) is defined as a temporary increase in your body temperature. Fever is not a condition on its own, in fact, it is one of the first symptoms that indicates something amiss in your body. A body temperature above 98.6℉ is considered to be a fever. While fever is uncomfortable in adults, in most cases, it need not cause concern unless it crosses 102℉.
Based on what condition is causing the fever, you may also experience other symptoms such as:
Fever should be taken more seriously if it manifests in infants and children between the ages of 6 months to 5 years as even a slightly elevated temperature may indicate a serious infection.
There are several types of thermometers available to help measure temperature. These are oral, rectal, tympanic (ear) and forehead thermometers.
Doctors recommend the use of rectal thermometers for infants. Hence, if you are reporting your baby’s temperature to your doctor, do mention how you recorded it as well.
The following steps can help you measure your temperature more accurately.
Usually, fevers should not immediately be a cause of alarm. Seek medical attention in the following cases.
Fevers are considered to be more serious in babies and young children. Take your child to the doctor if
You need not worry about your child having mild fever if he/she is responsive to you, ie: making eye contact, speaking etc. Consult your child’s pediatrician if:
Adults need to seek medical attention in the following cases:
Also Read: Ivy Gourd: Benefits & Side Effects
Fever can be caused due to a number of reasons. Some of the most common reasons are
In some cases, the cause of fever might not be evident. In such cases, the diagnosis is defined as “fever of unknown origin”.
As fever is a symptom, the focus is placed on minimising the risk of developing conditions that can cause fever. This includes reducing your exposure to infections and maintaining proper personal hygiene. The following steps can help reduce the risk of developing fever both in adults and children
The table below can help you identify fever associated with COVID-19. However, this is only for reference, if you are experiencing a fever with or without any other symptoms of COVID-19, please practice self-quarantine until recommended otherwise.
You can consult Dr Tushal Tayal, the best internal medicine specialist in Delhi NCR, at the CK Birla Hospital – Gurgaon.
Also read: What is Coronavirus: symptoms | how it spreads | how to avoid it
Did you know that almost every child is born with flat and flexible feet? During the first year of their life, they grow exponentially fast. However, the arches of their feet might fully develop only after they are 3-4 years old, even though they started walking and running much sooner. This article offers valuable insight into this condition for parents looking to learn about flatfeet.
Table of Contents
The reason behind every child being born with flat feet is that their muscles, bones and ligaments are yet to develop fully. One usually starts noticing the formation of the main arch of the foot (medial longitudinal arch) after the child reaches 3 years of age. This arch keeps developing until the child reaches 10 years of age. In many cases, the mature arch foot isn’t developed till the age of 7.
Basically, don’t be alarmed if your child has flatfeet before they are 3-4 years old, this is completely normal. The condition generally corrects itself with age as the muscles become stronger.
In medical terms, flatfoot is referred to as “Pes Planus”. It means a fallen arch of the foot has made the individual come in full contact with the surface they are standing on. People with flatfeet are further classified as symptomatic and asymptomatic. One common characteristic of asymptomatic and symptomatic flatfeet is the partial or total collapse of the arch.
Many parents become concerned about this condition. It is important to note that for most cases, this condition isn’t problematic and does not require any primary treatment.
As mentioned earlier, paediatric flatfeet are classified as symptomatic or asymptomatic (showing no symptoms). Understanding this distinction helps in deciding the best course of action to manage and treat this condition.
Also, read: All You Need to Know About Flat Feet
Flatfeet requires medical intervention only when it causes pain or is impacting the child’s daily life and play. Some of the common signs that indicate the need for treatment include:
Flatfeet can be caused by a number of reasons. Some of which are extrinsic while some in some cases, it is caused by underlying conditions. Some of the common reasons that can contribute to this condition are:
Read: Clubfoot or Congenital Talipes Equinovarus (CTEV)
These are two forms of foot deformities that can be present at birth (congenital deformity) and result in Flatfeet. These conditions are named after the “Talus” – a small bone that sits in the ankle and connects the foot with the lower leg.
Congenital oblique talus is a less severe form of vertical talus. In the latter (vertical talus), the talus points towards the ground, resulting in a stiff foot with no arch. This condition is also called “rocker bottom foot”. In oblique talus, even though the foot is pointing towards the wrong direction, it can be aligned normally whenever it is put down. A foot affected with congenital oblique talus looks more severe as compared to a normal foot, however, it looks less severe than a foot affected by vertical talus.
Both these conditions are treatable with surgical and non-surgical treatment methods which will be discussed in the following sections.
Based on the symptoms experienced by your child and the physical appearance of the foot, the condition is classified as:
This is the most common manifestation of Flatfeet which isn’t associated with any functional problems or pain. In this condition, the arches of the feet are only seen when you lift the feet off the ground. The arch completely disappears when the foot is placed flat on the surface. In most cases, this condition does not require any support or treatment.
However, in some rare cases, if medical intervention is deemed necessary, the focus is placed on finding the root cause of the deformity and treating that. The deformity itself is addressed later.
This is a rarer manifestation of Flatfeet which can create complications and impact normal functioning. This is due to the abnormal development of the foot with time. However, it is important to note that this deformity is more likely to develop in adults than children.
If not addressed and treated on time, this condition can worsen resulting in extreme pain, swelling and even arthritis.
Rigid Flatfeet requires surgical treatment. The most common reason for rigid flatfeet is a tarsal coalition – a state in which two or more bones are connected in an abnormal manner.
It can be treated with a resection surgery that is aimed at reducing pain and preserving the normal foot.
Depending on the severity of the condition and symptoms, flatfeet can be treated both surgically and conservatively.
Physical therapy
There are several exercises that are designed to treat Flatfeet by strengthening the muscles involved. These include heel chord stretching, gold ball roll, arch lifts and calf raises.
Lifestyle changes
This is especially relevant if Flatfeet is caused due to factors such as obesity. Patients are recommended to follow a healthy diet and exercise routine to bring their weight under control. The patients would also be required to switch to recommended footwear.
Choosing the right insole
Using the right insole in your shoes can significantly improve the functionality of Flatfeet and reduce pain. In recent times, with the development of 3D printing, customised insoles offer great support and comfort for people affected with flatfeet. The main thing to remember while choosing insoles is to opt for a low arch with maximum support.
Arch support
Even though arch support cannot treat flatfoot, it can help in reducing the symptoms associated with it. These are orthotic devices that are curated to provide support to flatfeet. They can be designed according to the contours of your feet.
Surgical treatment for Flatfeet is usually considered as the last resort. Even though surgery is considered after other forms of treatment, it does result in a positive outcome. Based on the problem that is causing the Flatfeet, your orthopaedic surgeon will try to correct it via surgical methods such as creating a false arch, repairing the tendons, or fusing the bone and joints in place.
To conclude, Flatfeet in children is not necessarily a cause of alarm. Consult a paediatric orthopaedic doctor if this condition is limiting your child’s play or causing excessive pain etc. For more information, you can consult Dr Gourav Jandial, the top paediatric orthopaedic surgeon in Delhi NCR at the CK Birla Hosptial Gurgaon.
Also, read: Finding the permanent solution for clubfoot
In recent years, a lot of effort has been placed on increasing awareness about breast cancer and the steps you can take to minimise its impact. This is largely due to the fact that today, breast cancer is the most common cancer to affect women around the world. It is also easily treated in its early stages. Regular breast cancer screenings and awareness about risk factors can go a long way in minimising the impact of breast cancer.
Breast density is one of the risk factors that is detected on a mammogram. But what does it mean to have dense breasts? Does it really increase the risk of breast cancer? What should be done after being diagnosed with dense breasts? In this article, we will explore the answers to some such questions related to breast density.
Table of Contents
Before we define breast density, let us look more closely into the structure of the breasts. Breasts are made up of three types of tissue. These are:
Breast density is the amount of fibrous and glandular tissue in the breasts compared to the amount of fatty tissue.
Based on the mammogram report, breast density is categorised into the following grades:
Women with heterogeneously dense or extremely dense breasts are considered to have dense breasts.
Dense breast tissue cannot be felt in a physical or self-examination. It is detected only on a mammogram. The dense tissue appears white on a mammogram while fatty tissue appears dark.
The factors which contribute to dense breasts are still unclear. However, some of the causes that can increase the chances of having dense breasts include:
Watch the video as Dr. Rohan Khandelwal, Breast Cancer surgeon in CK Birla Hospital, Gurgaon talks about the relationship between Breast Density and Breast Cancer.
Breast density is an important part of managing your breast health as well as developing your breast cancer screening plan.
Breast density makes it harder for the radiologist to detect anomalies or signs of breast cancer in the mammogram. This is because early cancers, which show up as white dots or masses in the mammograms are masked by the dense breast tissue (which also appears white). Studies show that mammograms can miss almost half of the cancers in women with dense breasts. Women with dense breasts are also more likely to be detected with cancer after getting a normal mammogram report (after other symptoms of breast cancer start appearing such as lumps).
Apart from this, dense breasts are also associated with a higher risk of breast cancer. The reasons for this are still unclear. For women in category C of breast density, the risk of breast cancer is almost 1.5 times that for women with mostly fatty breasts. For women in category D, the risk of breast cancer is almost double that of women who have a mix of dense and fatty breast tissue.
Read: Worried about an underarm lump? Find out what it means
It is important to remember that dense breasts does not necessarily result in breast cancer. Breast cancer is often caused by a complex interplay of risk factors.
The most important steps to keep in mind if you are diagnosed with dense breasts are:
Follow lifestyle recommendations to minimise the risk of breast cancer such as maintaining healthy body weight, limiting your consumption of alcohol, not smoking and exercising regularly.
While breast density is out of our control, the above steps can help you minimise other risk factors. For more information about breast cancer and to assess your risk, you can consult Dr Rohan Khandelwal, one of the best breast cancer specialist in Delhi NCR.
Book an appointment with Dr Rohan Khandelwal.
Read: Breast cancer: warning signs and how do you minimise your risk?
Mood swings, depression, irritability, food cravings etc. are all some of the classic signs of the infamous “PMS”. PMS or premenstrual syndrome affects most women at some point of their lives. Several factors contribute to the severity of the symptoms women experience.
Lifestyle and dietary changes can help manage PMS symptoms to a large extent according to Dr Anjali Kumar, one of the best gynecologists in Gurgaon. With our increasingly busy lifestyles, we often opt for the easy way out, popping pills to manage cramps and other symptoms rather than focusing on healthier alternatives. Medication should always be the last resort. They are more useful for women who have extremely severe PMS symptoms, especially if they have underlying conditions such as PCOS.
Dr Anjali Kumar, Obstetrician & Gynecologist at the CK Birla Hospital, which is known to be one of the best hospitals for gynecology in Delhi NCR, gives us a few lifestyles and dietary tips that can help us breeze through our PMS phase every month.
Regular physical activity goes a long way in alleviating your mood, controlling your bloating and making you calmer during PMS. You should aim to complete atleast 45 minutes of low-medium intensity exercise three or four times per week. Try walking to do your chores rather than driving or climb stairs instead of using the elevator.
What is life without seasoning? Bland is definitely not good, but too much seasoning can be far worse for our body. If you face problems with bloating, breast tenderness/swelling, swollen hands etc every month in sync with your menstrual cycle, you should consider decreasing your salt intake. Try using more of other seasonings such as herbs or spices and with time your body would get used to having less salt.
Make it a point to drink at least 3 litres of water in a day regardless of whether you feel thirsty. Increasing your water intake during PMS can help you reduce symptoms of bloating and indigestion. If wish to make things more interesting, you can flavour the water with ginger or turmeric etc for additional health benefits.
Read: Why is it important to maintain menstrual hygiene
Try avoiding processed food by consuming more whole grains. This will not only help your health in general but also help in managing mood swings, depression and anxiety with is triggered by PMS by reducing the serotonin levels in your body.
Women, especially of the menstrual age are more prone to iron deficiency anemia. This results in them feeling more tired, irritated, bloated etc especially when they are going through PMS. Include iron-rich food in your diet such as whole leafy vegetables, apricots, dates, eggs, chicken, fish etc. If required, consult your doctor for vitamin supplements.
As we grow older, we need to increase our calcium intake. For women, this micronutrient can greatly help in reducing the symptoms of PMS. Increasing calcium intake by having more nut milk, yogurt, sesame seeds, ragi etc.
Always remember that the more you rely on medical intervention for PMS, the more you will need it. Rather train your body and understand its requirements when it comes to dealing with PMS. Exercise to regulate your mood and appetite. Reduce aches and pains by applying a warm compress. And follow healthy eating habits for long term benefits.
Also, read: A quick understanding about Menstrual Cramps