
Vitamin D keeps our bones healthy and strong. Know more about the symptoms & causes of Vitamin D deficiency and get in touch with our team of experts today.
Vitamin D deficiency is one of the common nutritional deficiencies found among adults and children, as well as it is the common undiagnosed medical condition across the globe.
According to a study, Vitamin D deficiency is prevalent in nearly 76% of Indians.
Vitamin D is also known as the sunshine vitamin that helps in keeping your bones strong. Recent research suggests that Vitamin D protects you from a lot of health problems. As the name depicts, the sunshine vitamin is produced by the body in response to skin exposure to sunlight.
There are a few foods that have vitamin D, like fish, fish liver oils, egg yolks- which fortifies dairy, and grain products. When Vitamin D enters our body, it regulates bone metabolism, calcium, and reduces the risk of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular, malignancies, autoimmune diseases, and infectious diseases.
Vitamin D deficiency is prevalent in everyone in our country and especially in the Northern parts of India. The very first reason is the limited or no sun exposure, generally, in urban areas- people do not prefer going outside, or if they go, they prefer minimum sun exposure.
In this article, Dr. Harshavardhan Hegde, one of the best orthopaedic experts in Gurgaon, will discuss the importance of Vitamin D for children and adults, and everything about Vitamin D deficiency.
Vitamin D deficiency indicates that there is not enough vitamin D in your body. People with fair-skinned and young individuals are more capable of converting sunshine into vitamin D more efficiently than darker-skinned and aged people.
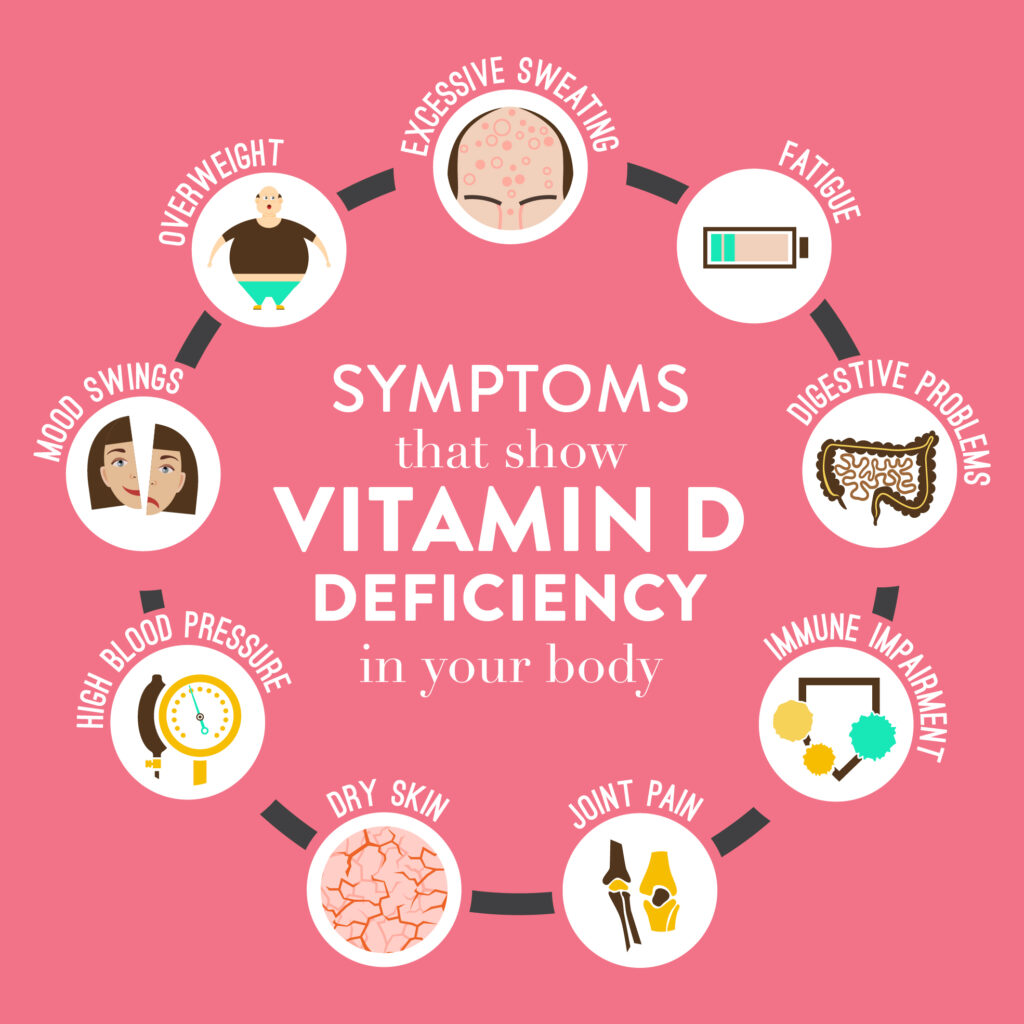
1. Bone and joint pain
2. Fatigue and tiredness
3. Headaches
4. Weight gain
5. High blood pressure
6. Insomnia
7. Cramps in muscles
8. Osteoporosis
9. Rickets in children
10. Depression
11. Becoming More Prone to Infections
12. Impaired Wound Healing
Listed below are a few symptoms that can help you understand that you might have Vitamin D deficiency in your body
There is an established relation between Vitamin D and calcium. Vitamin D is an essential hormone as it helps your body effectively absorb calcium by mediating the transportation of this mineral and supporting bone growth.
Vitamin D deficiency can hence affect your bone and joint health causing a variety of symptoms including pain. Inadequate levels of vitamin D can lead to the development of bone and joint disorders such as arthritis and osteoporosis.
Several studies show that a deficiency of Vitamin D in your blood can impact your energy levels and sleep quality. Individuals living with Vitamin D deficiency often complain of fatigue and tiredness.
Low levels of Vitamin D can cause delayed sleep and even shorter sleep duration. Poor quality of sleep can hence cause daytime sleepiness and tiredness.
Vitamin D can cause different types of headaches including migraine. It is because decreased levels of vitamin D may be responsible for bone pain and swelling which can further aggravate and sensitise your nervous system causing headaches.
A comparatively recent study has shown people with a higher BMI and excess fat especially around the waistline are more likely to have low levels of Vitamin D.
Vitamin D deficiency is related to heart health. Individuals with low levels of vitamin D are more likely to experience high blood pressure (hypertension).
As discussed above, vitamin D deficiency can impact your sleep. Besides hindering the quality of your life, it can also trigger insomnia by affecting your sleep schedule. People living with low levels of vitamin D are seen to have daytime sleepiness and drowsiness.
Vitamin D is responsible for maintaining the strength and functioning of your musculoskeletal system. A significant decrease in these vitamin levels can cause pain, discomfort, spasms and cramping in your muscles.
Osteoporosis is a condition in which your bones become weak and brittle. It is because in this condition, your body is unable to produce new bone tissues to replace the new ones.
Vitamin D helps your body absorb calcium and phosphorus, rightly. If there is a lack of these nutrients, you are likely to develop osteoporosis.
Rickets is a condition that hinders bone development in children. It primarily occurs as a result of inadequate vitamin D levels causing the softening and weakening of bones.
Several types of research have shown that vitamin D deficiency can lead to mood disorders and mental health issues including depression and anxiety. It has been seen that increasing the consumption of vitamin D can help improve the symptoms of depression.
Your immune system determines how well you are able to fight off bacteria and viruses. Vitamin D is an anti-inflammatory hormone that has diverse effects on your immune system.
It directly interacts with your immune system cells that fight the above-mentioned infections. A vitamin D deficiency can affect this ability and make you more prone to contracting infections.
Vitamin D is a contributing factor in the development of new skin on wounds as it increases the production of components leading to the skin layer growth. It is, thus, an important aspect in a person’s healing journey after a surgery, injury or infection.
Vitamin D deficiency can occur in your body due to various reasons, listed below are a few of them.
Vitamin D deficiency can be caused as a result of insufficient intake of vitamin D. You may have the above-given symptoms if you are not able to consume the recommended levels of the vitamin over a long time, especially if you follow a strict vegan diet. If your diet excludes most of the natural sources for Vitamin D like fish, beef, egg yolks, you may behave vitamin D deficiency.
Sunlight is a natural source of vitamin D. A restricted or low exposure to sunlight can cause a deficiency of vitamin D.
Melanin is a pigment in your skin that provides its colour. Dark-skinned people have more melanin than light-skinned people. Melanin also protects your skin from UV rays. An increased amount of melanin reduces your ability to synthesise Vitamin D from the sun, thus, impacting its effectiveness and causing an insufficiency.
Obesity and vitamin D deficiency are highly correlated. People with a BMI of 30 or more than 30 often have low Vitamin D levels.
Medical problems like Crohn’s disease, cystic fibrosis and celiac disease can affect your intestine’s ability to absorb Vitamin D through food that you eat.
With ageing, kidneys are unable to convert Vitamin D into an active form which increases the risk of being Vitamin D deficient.
The following are at risk for Vitamin D deficiency
There are several reasons to consider Vitamin D as an essential vitamin for the human body, including;
1. Supports Bone Health (Calcium & Phosphorous Absorption)
Vitamin D helps your intestines absorb calcium and phosphorus, essential minerals for strong, healthy bones. Without enough vitamin D, bones can become soft or brittle, leading to osteomalacia, osteoporosis or loss of bone density, in adults and rickets in children, and increasing the risk of fractures and osteoporosis.
2. Boosts Immune Function
Vitamin D plays a key role in your immune system. Immune cells have vitamin D receptors, and adequate levels help your body fight infections more effectively, reducing the frequency and severity of illnesses.
3) Maintains Muscle Strength
Vitamin D affects muscle fibre performance and coordination. Low levels can cause muscle weakness, poor balance, and a higher risk of falls, especially in older adults.
4) Regulates Cell Growth and Repair
Vitamin D acts like a hormone in the body, influencing how cells grow, mature, and repair themselves. This function supports healthy tissues and proper cell function throughout the body.
5) Reduces Inflammation
Vitamin D helps control inflammatory processes in the body. Adequate levels may reduce chronic, low-grade inflammation, which is linked to many health problems including heart disease, diabetes, and autoimmune conditions.
Getting enough vitamin D plays an important role in keeping you healthy by protecting against diseases or conditions, these conditions can include:
The 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] test is the best indicator of vitamin D status.
Typical interpretation (ng/mL):
Conversion: 1 ng/mL = 2.5 nmol/L. Ranges can vary slightly by lab and clinical context.
Vitamin D (the sunshine vitamin) is important to maintain overall health. You can easily and effectively boost your vitamin D levels by taking the following measures.
The best way to get the sunshine vitamin is through sunlight. Increasing your exposure to sunlight is one of the best ways to increase your vitamin D consumption. You should consider the duration, time, skin tone and sensitivity to decide how much sunlight exposure is adequate.
Seafood such as fatty fish, tuna, and shrimp are rich in vitamin D. For those who prefer vegetarian options, egg yolks, fortified milk, fortified cereals, fortified orange juice, and UV-exposed mushrooms are excellent sources. Including a variety of these foods can help maintain healthy vitamin D levels.
Another way to up your vitamin D intake is through nutritional supplements. You can consult your healthcare provider about the type of supplement ideal for you.
Obesity can make you more prone to developing vitamin D deficiency. You should aim to achieve and attain your ideal body weight by proper diet and physical activity.
Outlook
If you have any queries related to Vitamin D or how to boost the level of Vitamin D in the body, get in touch with our team of experts to get your Vitamin D levels checked.
Vitamin D is naturally present in only a few foods. Here is a list of the top foods that contain it.
| Food | Category | Key notes |
| Cod liver oil (1 tsp) | Natural | One of the richest natural sources |
| Salmon (wild/farmed) | Natural | Fatty fish; baked, grilled or steamed |
| Sardines (canned in oil) | Natural | Convenient pantry option |
| Trout | Natural | Freshwater fish, naturally rich |
| Tuna (canned, light) | Natural | Check mercury advisories if pregnant |
| Egg yolks | Natural | D is in the yolk, not the white |
| UV-exposed mushrooms | Natural/UV | Look for “UV-treated” on the label |
| Fortified milk/plant milks | Fortified | Check label: cow’s, soy, almond, oat |
| Fortified cereals/orange juice | Fortified | Varies by brand; read nutrition panel |
Tip: Labels for fortified foods will list vitamin D per serving (IU or mcg). Use these along with fish/eggs to diversify sources of vitamin D.
Your skin can make vitamin D from UVB rays.
This is a practical way to increase vitamin D alongside diet. Supplements may be considered if your test shows low levels only as advised by your clinician.
Q. How long does it take to recover from vitamin D deficiency?
Based on your treatment and proactive measures, you may take nearly 3-6 months to recover.
Q. Can low vitamin D cause neurological symptoms?
Yes, low levels of vitamin D can cause certain neurological symptoms such as tremors and depression.
Q. Can low vitamin D cause dizziness and headaches?
Yes, vitamin D can sensitise your nervous system leading to dizziness and headaches.
Written and Verified by:

Similar Orthopaedics Blogs
Request a call back