Filter :
With the rising conversation about women’s sexual health, a lot of focus of late has been placed on vaginal hygiene as well. Vaginal health is a vital part of healthcare as it is where some of the deadliest transmittable diseases find an ideal breeding place. Sometimes the problems are mostly limited to itching and some amount of manageable discomfort. But other times it can be the stepping stone for a bigger, more difficult-to-deal condition. Vaginitis falls under this category. To know more about this condition and its types, read on…
Table of Contents
Vaginitis is a medical condition that affects a female’s vagina. It is an inflammation that occurs in the vagina which leads to frequent discharge, vaginal itching and sometimes pain. This happens when there is an unusual change in the pH balance or an infection in the vaginal region, which is home to good bacteria that keep the vagina clean. For post-menopausal women, reduced oestrogen levels or some kind of skin disorder can also cause vaginitis.
There are different types of vaginitis that can happen to women. These are:
In this case, there is an overgrowth of the bacteria that is naturally found in your vagina. This leads to a natural imbalance.
These are also a type of vaginitis and the most common form. Here the main cause is Candida albicans, a fungal infection. Candida fungi normally live in the vagina, mouth and digestive tract in all men and women.
These are caused by sexually transmitted parasites. There are three STI Vaginitis variants:
Therefore, vaginitis is an umbrella term that describes various disorders that are linked to infection or inflammation in the female vagina. Meanwhile, vulvovaginitis is the condition where there is an inflammation in the external female genitalia that includes both the vagina and vulva.
The cause of vaginitis will purely depend on the type of vaginitis you have. But when you assess all the variants of vaginitis, the following will be the primary factors that you may want to consider:
The significant symptoms of Vaginitis are:
To summarise, the causes & symptoms of Vaginitis
| S. No. | Major Causes of Vaginitis | Main Symptoms of Vaginitis |
| 1 | Hormonal disbalance due to pregnancy, birth control or menopause | Change in colour, odour or amount of vaginal discharge. |
| 2 | Unsafe sex and STIs or warts due to this | Vaginal itching or irritation |
| 3 | Steroid medication | Painful intercourse |
| 4 | Uncontrolled diabetes | Painful urination |
| 5 | Using too many vaginal hygiene products or damp clothing | Vaginal Bleeding |
The real question is to determine when you need help. The simple answer is whenever you experience vaginal discomfort accompanied by symptoms like:
You Can Also Read: Chlamydia: The Silent STI you didn’t even know about
Good hygiene is the best option to prevent vaginitis and relieve symptoms. Follow these alerts and you might just steer clear of these infections:
While the matter at hand is sensitive, this is one condition where you have to come clean with your Gynaecologist. Make sure you mention these explicitly when consulting your physician. Any or all of these can be a sure-shot indicator for your doctor to take the right course of treatment.
| S.No. | Unpleasant Vaginal Odour |
Vaginal Discharge With Itching |
| 1. |
Sexual Partner with STI |
Recurrence of old infection |
| 2. |
Sudden fever or chills |
Pain in the pelvic region |
| 3. |
Vaginal irritation during sex |
Painful urination or bleeding |
The CK Birla Hospital provides a judgement-free comfort zone for patients to talk freely about their concerns. With compassionate care at its core, our doctors prioritise patient’s comfort and well-being above everything else. To book an appointment with our sexual health expert.
Ans: Some women have vaginal discharge every day, while others experience it less often. Normal vaginal discharge is usually clear or milky and may have a subtle odour that is neither unpleasant nor foul. It’s also important to know that vaginal discharge changes during a woman’s menstrual cycle.
Ans: Vaginal discharge is normal, but to prevent vaginal infections that can begin to abnormal discharge, you can follow these tips:
Ans: Vaginal discharge is a natural and healthy bodily function. It is how the body cleanses and protects the vagina. For example, it is normal for secretion to increase with sexual arousal and ovulation. Exercise, taking birth control pills, and emotional stress can also trigger a discharge.
Ans: Several pregnant women experience vaginal discharge, which is usually not associated with pregnancy. However, most pregnant women discharge sticky, white or pale yellow mucus by the beginning of the first trimester and throughout pregnancy. The increase in hormones and vaginal blood flow leads to vaginal discharge.
Ans: Different colours of vaginal discharge indicate different reasons for the health of a woman including;
Ans: Different types of infections can cause itching or abnormal discharge from the vagina. Abnormal discharge means abnormal colour and smell, which is associated with itching or irritation.
Ans: To stop the excess vaginal discharge, you can do the following things;
Behavioural problems in children are so common nowadays. There are times when they do not behave properly. They can go through different phases and moods as they grow older and become more independent. Several reasons are responsible for behavioural problems in children, like anger, tiredness, overexcitation, or frustration. If behavioural problems in children are causing you or your child to suffer or bother the rest of the family, it is very important to take care of this issue. Understanding the underlying problem will surely help the child’s behavioural issues.
Both toddlers and adolescents go through a lot of changes in their growth phases. As a parent, no not worry about it. These behavioural changes will usually ease as they grow up. When a child starts schooling, the child slowly starts learning different things. These things are how to behave, how to process things, how to react, etc. If the behavioural problems in children continue for a long time and affect the child’s mental health, then asking for external help is a good option.
There are many causes of behavioural problems in children, such as;
Other than these few external things related to the child’s home life and family relations may add to behaviour disorder. These could be,
Sometimes, the child throws tantrums at you or shows destructive or aggressive behaviour- this is usually nothing to worry about. The symptoms to look out for are:
If your child is in these moods throughout the day, and this continues for a long time. Then you could take advice to the best child specialists near you.
If you have noticed that your child is facing some behavioural issues, you can discuss them with a child specialist. A medical professional can evaluate the child by performing functional behavioural assessments based on different strategies and techniques to identify and address any behavioural issue in the child.
Hardly, a child below the age of five can be diagnosed with a behavioural disorder. They may, though, show early warning signs of the following:
Sometimes, behavioural problems in children can be manageable at home. As a parent, there are a few things that you can do to address these problems.
Practice those habits which you want your child to follow. If you do something which you do not believe in probably will not work with your child. Children notice their parents when they do not mean what they are saying.
As a parent, tell your child that if they have decided to do something, continue to do it until you achieve it.
Kids need consistency. If you react to your kid’s behaviour differently on different days, you create confusion for them. Everyone close to the child must treat the child in the same way.
When your child is doing annoying things on repetition, your frustration and anger can build up. But try to stay relaxed, and make your child understand the issue and switch to other things where you can both enjoy or feel good about it.
Sometimes, kids have mixed thoughts, and they are afraid to talk to their parents. Consider talking to them about their day to day life and what is going around it, such as new school, friends, and their likes & dislikes. Try to ask them why they are annoyed or behaving a certain way, and work with them to overcome the problem.
Hitting or giving punishment may stop your kid for that moment. This action will not have a positive effect on the child’s mind. Kids always learn from examples so, if you hit the child, you’re showing them that hitting is acceptable for every bad behaviour.
When a child’s behaviour is challenging, and they do not understand their mistakes. Discuss it with your child and correct your child. Try to make them understand both the positive and negative side of it.
Rewarding for good behaviour can switch your child’s behaviour from doing something wrong. For example, offer them their favourite food or cartoon show for good behaviour. When your kid behaves well, tell them how you are feeling and praise them.
When something happens in a child’s life, they find it difficult to understand the situation. For example, changing schools, a new baby born in the family, relocating to a different city, or something similar to these things.
Children always remember how their parents are reacting to their behaviour in the past. If you make them a habit of taking bribes, they will expect the same every time for everything.
Sometimes kids show tantrums to get attention. The child may disturb you while you’re having a conversation with someone, or the child will start crying while playing or cuddle you and need your company. Try to address them whenever you think it is good to appreciate them.
Children do understand when their parents are not in a good mood. In this situation, try to talk to your child about the problem in an easy way. So they do not feel left alone. Try to cheer up in front of them.
If your child is having behavioural problems, then do not sit back, just ask your doctor to help it out. In most cases, child counselling is the best way to resolve behavioural problems. For more information on behavioural problems in children, you can book an appointment with the best paediatric specialists at the CK Birla Hospital.
The size of a breast tumor can give doctors an idea of the severity of a breast cancer case. Staging cancer based on this information, the condition of the lymph nodes, and metastases are essential for determining the disease extent, treatment options, and prognosis. Other factors which help to plan the cancer treatment include the tumor’s location, whether it has spread outside the breast, the appearance of cancer cells, and the presence of hormone receptors.
Let us discuss breast cancer tumor size and stages through the tumor size chart in this article and also how tumour size can affect cancer staging? We will also highlight other factors contributing to cancer staging, its treatment, and a person’s outlook.
TNM is the most popularly used staging system for breast cancer, where;
• T = the size of the primary tumor
• N = if cancer has spread to close neighbouring lymph nodes
• M = if the cancer is metastatic (cancer has spread to distant parts of the body)
T=Tumor Size
To measure the tumor size before surgery, doctors rely on imaging examinations.
Standard breast imaging methods are:
• Mammogram: It is the film mammography used to image breast tissue. If you’ve been postmenopausal, have fatty breast tissue, or have been pregnant, this can be much accurate. With dense breast tissue, digital mammography is more reliable.
• Breast ultrasound: Ultrasound used to help diagnose breast lumps or other abnormalities. In ultrasound imaging, sound waves produce pictures of the breast. It is deemed less accurate than mammography.
• Breast MRI: A breast MRI is needed to measure if the breast tissue is dense or if your biopsy shows the mass is extensive than expected. Although MRI can give a clear picture of your tumor, it tends to exaggerate its actual three-dimensional size.
After analysing imaging examinations, a breast surgeon can approximate the tumor’s size. In some breast cancer cases determining the tumor’s size can be easy, but it can be more challenging in others. Not all breast tumours are easy and circular in shape. For example, the tumor could be in a potato shape, with hard to see all the dimensions. Some even have more irregular edges making it hard to estimate the total diameter.
| T-1 | 0 to 2 cm |
| T-2 | 2 to 5 cm |
| T-3 | Bigger than 5 cm |
| T-4 | The tumour can be of any size which is growing into the chest wall. This category covers inflammatory breast cancer. |
N=Lymph Node Status
Because cancer can get into your lymphatic system, the lymph nodes closest to your tumor must examine for cancer and micrometastasis.
Your surgeon can check your lymph nodes by palpating (touching) the skin just above the lymph node and noting what they notice.
| N-0 | Can not feel swollen nodes. |
| N-1 | Can feel some swelling that can be cancerous nodes. |
| N-2 | The lymph nodes are lumpy, swollen, and bunched together. |
| N-3 | Swollen lymph nodes are close to the collarbone. |
M=Metastasis
Metastasis indicates that cancer spreads to a different body part from where it started and further affects cancer stages.
| M-0 | A sample of the lymph nodes was surgically removed and analyzed, and they are cancer-free. |
| M-1 | Nodes contain cancer cells or micrometastases. The tumour has lost cells beyond its original location, and cancer is found in other parts of the body. |
Tumour size
Through biopsies and imaging examinations, a surgeon can identify the approximate measurement of the tumor. It is necessary to have the actual tumor size to make the best treatment decisions.
After the lumpectomy or mastectomy process, combine the removed breast tissue with the biopsy tissue to examine the actual size of the lump. The pathological measure of the tumor is the standard for tumor size. Your post-operative pathology report summarizes your complete diagnosis of breast cancer.
1. Hormone receptor status
While breast cancer staging, doctors examine tumor cells for the presence of hormone receptors. Receptors are proteins that respond to the estrogen and progesterone hormones. Doctors describe breast cancer as estrogen receptors (either estrogen receptor-positive or ER-positive). They also refer to breast cancer as progesterone receptors (either positive progesterone receptors or PR positive). Hormone therapy is usually the most effective treatment for cases with hormone receptors.
2. HER2 status
The next factor to include in breast cancer staging is HER2 status. The human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) gene could play a role in breast cancer development.
HER2 receptors protein helps in controlling the growth, division, and repair of healthy breast cells. Doctors test HER2 status to see if this receptor is above normal levels and then call it HER2 positive cancer. Targeted therapies generally work best in such cases.
3. Cancer cell appearance
How the cancer cells appear or differentiate is another factor in cancer staging. Under the microscope, doctors group cancer cells according to their appearance to noncancerous cells. Those cancer cells that are close to matching healthy cells are considered low grade. These cancer cells grow more slowly. Cancer cells that appear very different from normal cells are acknowledged as a high grade, and they tend to grow faster.
Tumor size is an essential factor to determine the breast cancer stage. Despite this factor, doctors also consider several other factors, including:
• Age
• General health
• Personal preferences when suggesting treatment options
Early breast cancer diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve a person’s outlook. However, different people have different experiences with breast cancer.
Breast cancer tumor size is one of the most important determining factors for breast cancer staging. Early diagnosis of breast cancer helps your doctor to prepare more efficient and effective treatment for you. If you have any further queries related to signs or symptoms of breast cancer, book an appointment with our Breast cancer Doctors or call us at +91 124 4882248.
Diabetes occurs when your body cannot absorb the glucose (sugar) in your cells and use it for energy, leading to a build-up of extra glucose in the blood. Poorly controlled diabetes can have serious outcomes and damage different organs and tissues in the body, including the heart, kidneys, eyes and nerves. Diabetes has multiple long-term complications that develop gradually over a period of time. The longer a person is diabetic and the lesser control he has on his blood sugar, the higher is the risk of complications.
In this article, Dr Tushar Tayal, one of the best diabetologists/Critical care specialists at CK Birla Hospital, will discuss serious and long term complications of diabetes mellitus and how to prevent complications of diabetes?
Following your diabetes treatment plan requires constant commitment. But your efforts are worth it. Careful diabetes care can reduce the risk of serious and even fatal complications.
There are a few things that are related to type 1 diabetes complications, including;
There are a few things that are related to type 2 diabetes complications, including;
There are several kidney complications of diabetes (diabetic nephropathy) that may develop gradually over months or years. These kidney complications of diabetes may include:
Older people are more likely to have other health problems that affect their diabetes and make it more difficult to control. Some conditions such as high blood pressure, heart disease, and peripheral vascular disease.
Older people with diabetes are likely to have high blood sugar for a longer period, which leads to more damage and complications to their blood vessels.
Older people with diabetes are more affected by complications, and complications can be more difficult to manage.
Being less mobile and less active can make it difficult for older people to adopt healthy lifestyle measures to help manage their diabetes. Likewise, other medical conditions such as arthritis can affect an older person’s ability to cook healthy meals or be physically active.
Unfortunately, diabetes makes older people more prone to eye damage, kidney disease, and the risk of needing an amputation.
A doctor advised that, for adults, at least once a year checkup is necessary for the following complications of diabetes mellitus:
It is important to consult your doctor right away whenever you feel you show any signs or symptoms of diabetes complications. For more information on long term complications of diabetes mellitus or any personal enquiry with Dr. Rajeev Gupta, you can book an appointment or call at +91 1244882248.
The gallbladder is a small pouch-like, a pear-shaped organ found just under the liver and on the right side of your abdomen. This small organ is responsible for storing bile juice produced by the liver. Bile juice is useful for the process of digestion. The gallbladder, however, is highly susceptible to being affected by cancer cells. Gallbladder cancer is one of the most common cancers in India with nearly 10% of the global burden.
In this article, with insights from Dr Vinay Samuel Gaikwad, a leading surgical oncologist in Gurgaon, we will explore everything you may need to know about gallbladder cancer.
Table of Contents
Gallbladder cancer occurs when the cells in the gallbladder mutate and spread at an abnormal rate. The cancer cells may remain in the organ or even spread outside the gallbladder.
The outer wall of the gallbladder is made up of four layers of tissue:
Cancer begins to grow in the inner layer, that is, the mucosal layer and spreads through the outer layers. This cancer can further spread through your tissues, lymph nodes or blood.
This cancer is not usually detected in its stages due to its asymptomatic character. However, common symptoms include:
Some of the above-given symptoms may overlap with symptoms of other digestive conditions. Hence it is important to consult a healthcare provider at the earliest for a thorough and accurate diagnosis.
Gallbladder cancer progresses through five stages:
Stage 0: When the cancer is confined to the inner layer of the gallbladder
Stage 1: When cancer has spread to the muscle layer
Stage 2: When the cancer cells have spread to the connective tissue
Stage 3: When cancer has metasised to the nearby organs and lymph nodes
Stage 4: When the cancer has advanced to the lymph nodes and organs located far from the gallbladder
The most common type is adenocarcinoma. Adenocarcinoma is a type of cancer that starts in the glandular cells of your body.
Other types of gallbladder cancers include papillary adenocarcinoma, adenosquamous carcinomas, squamous cell carcinomas, and carcinosarcomas. These types, however, are extremely rare.
The exact reason why gallbladder cancer occurs is yet unknown to medical science. Researchers and doctors believe that healthy cells inside the gallbladder mutate in their DNA and begin to multiply abnormally leading to the growth of cancer.
Though the precise reason for gallbladder cancer is undefined, we do know that some people are more vulnerable to developing this cancer than others.
Gallbladder cancer is more prevalent in women as compared to men. Other risk factors for why gallbladder cancer occurs include:
Gallbladder cancer, popularly termed as ‘an Indian disease’, is highly prevalent in the northern parts of India. The incidence of gallbladder cancer in India is reported at 9/100000 in women.
The probable cause for this alarming incidence is the prevalance of gallstones. Gallstones and cancer have found to be interrelated. It has been noted that nearly 95% gallbladder cancer patients have suffered from gallstones. Researches believe that the chronic irritation caused by the stones leads to the eventual development of cancer.
It is, thus, suggested that in case a person suffers from large gallstones, the treatment protocol should include the removal of the gallbladder in order to avoid the probability of cancer.
Another reason for this cancer, especially in the Indian population, is the sedantary and unhealthy lifestyle habits that includes nutrient deficient diet and a lack of physical activity.
Due to it asymptomtic nature, this cancer is not diagnosed early on. In most cases, this cancer is identified on the onset of gallstones or other disorders.
In order to diagnose your condition, your oncologist will perform the following gallbladder cancer test:
Your oncologist may also administer other lab tests such as Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) assay and CA 19-9 assay.
In addition to the above gallbladder cancer test, your oncologist may order overall physical health checks, endoscopic ultrasound, biopsy and diagnostic laparoscopy to diagnose cancer.
The treatment protocol will depend on the type of cancer, stage of cancer, if the cancer has spread, your overall health and the severity of your symptoms. You will receive treatment through a multidisciplnary care team which will include surgical oncologist, medical oncologist, gastrenterologist and radition oncologist.
In most cases, more than one treatment protocols are used in a combination for effective outcomes. Listed below are some common treatment methods for gallbladder cancer:
It is not highly likely to prevent gallbladder cancer. However, you can take cautious steps to decrease your risk. Some expert-approved tips include:
The disease burden of gallbladder cancer is uncommon. Nonetheless, its incidence in India is preferably high. It is important for patients to understand that timely detection can help in seeking timely and effective treatment in the long run.
If you have higher risk for gallbladder cancer or if you are experiencing bothersome symptoms, visit the CK Birla Hospital, best hospital for gallbladder cancer in India.
Ques: How fast does gallbladder cancer grow?
Ans: If the cancer is not addressed in its early stages, it can grow at an alarming speed.
Ques: Can stage 4 gallbladder cancer be cured?
Ans: Gallbladder cancer only be cured if it has not spread beyond the primary organ. Stage 4 can, thus, can be effectively treated.
Ques: How long can a person live with gallbladder cancer?
Ans: The survival rate depends on the type, stage and spread of cancer as well as patient’s overall health.
Hormonal imbalances sometimes develop female breasts like chest enlargement in men. This condition is known as gynecomastia or commonly known as “man breasts.” Gynecomastia is due to the swelling of the breast tissue in men. Regular exercise can slightly reduce the gynecomastia condition, but to have a chiselled chest area, you need to be patient to see the results naturally. However, if you want to see results quickly, you can opt for gynecomastia surgery.
Male breast reduction (gynecomastia surgery) is a cosmetic procedure designed to aid men in breast enlargement by creating a more feminine-looking chest area. Gynecomastia surgery is a popular plastic surgery procedure performed across the globe to shrink male breast tissue in men struggling with the condition.
In this article, Dr Anmol Chugh, plastic & cosmetic surgeon at CK Birla Hospital in Gurgaon, will discuss gynecomastia surgery scars, the benefits of gynecomastia surgery, and how to reduce scar tissue after gynecomastia surgery?
Gynecomastia is an overdeveloped or enlarged breast condition in men that can appear at any age. This condition can be the result of hormonal changes, heredity, obesity, or the use of certain medications. Gynecomastia can cause emotional stress and affect a man’s self-confidence.
There are two types of gynecomastia: true gynecomastia, in which the main component is the enlargement of the glandular tissue, and pseudogynecomastia, in which the breasts grow due to the deposition of fat in the chest area.
A man who can opt the gynecomastia surgery are;
Most men seeking surgical treatment for gynecomastia may be concerned about the location and size of the incision and the visibility of the scar after the procedure. Depending on the severity of each case, gynecomastia surgery may require large incisions to remove more significant amounts of excess breast tissue and fat. Some of the techniques used in male breast reduction surgery are no different from those used in female breast reduction procedures. While a total reduction of scars is quite impossible with any surgical procedure, the natural contours of the man’s chest area help hide gynecomastia scars for optimal results. For male patients with small amounts of fat or breast tissue, liposuction may be an option that requires small incisions, which are almost unnoticeable once they have fully healed.
The goal of gynecomastia surgery is to give men a flatter and masculine chest. Typically, most male patients can return to work within a week and resume normal activities within a few weeks, suggested by their surgeon. This highly effective cosmetic surgery for men offers almost instant results once the post-operative swelling reduces in the second week. Men with gynecomastia will appreciate their new, more masculine looks and feel confident about their looks.
Any surgical treatment to correct gynecomastia requires incisions. After the surgical treatment, most of the cut lines are within natural contours, some may be visible as a part of the surgical procedure.
Following are some methods to reduce gynecomastia surgery scars caused by surgery:
Apart from physical appearance, other benefits of gynecomastia surgeries are-
Gynecomastia surgery is one of the best treatments to reduce male breast because it is so effective and offers many benefits. Based on the severity of your gynecomastia, medical history, and current health status, our expert will create a personalised treatment plan for you. To determine if this procedure is right for you, contact CK Birla Hospital in Gurgaon today to schedule your initial consultation.
1. How long does it take to heal from gynecomastia surgery?
The initial recovery time for gynecomastia surgery is around 1 to 2 days on average. During this time, patients have to relax and avoid strenuous activities to aid healing and to avoid complications.
2. Can gynecomastia grow back after surgery?
Yes, gynecomastia can come back after a male breast reduction surgery. The most common causes of recurrence of gynecomastia could be-
3. What are the side effects of gynecomastia surgery?
There are several side effects of gynecomastia surgery, including;
4. Do gynecomastia surgery scars go away?
Over time, scars can lose their colour and even shrink. Your doctor may recommend using a scar gel once the wound has healed. For scar gels to work, you need to use them every day until you get the results you want. It can take several months.
If you have an urge to pass urine more often than usual, you might be dealing with the problem of frequent urination. Frequent urination may occur day and night, or more noticeable only during the night. Frequent urination can affect your sleep, general well-being, and work.
In the digestive system, gas is a part of the normal process of digestion. It’s normal to get rid of excess gas through burp or flatus (passing gas). Sometimes, in the digestive system, the gas is trapped or not moving well that develops gas pain in the abdomen area. An increase in gas pain or gas may result from eating foods that produce more gas. Usually, simple changes in eating habits can reduce bothersome gas. Certain digestive system disorders, such as celiac disease or irritable bowel syndrome, may cause an increase in gas or gas pain.
Table of Contents
Frequent urination can be due to diseases affecting the urinary tract. The urinary tract consists of kidneys, ureters (tubes that connect the kidneys to the bladder), bladder, and urethra (the tube through which urine flows from the bladder to the outside of the body).
Several reasons may link to frequent urination, such as:
Some other diseases or conditions of frequent urination include:
Depending on the causes of the frequent urination, you may encounter other urinary problems, like:
Gas in the digestive tract (the stomach, oesophagus, small intestine, and large intestine) comes from the following two sources:
Belching, or burping, is how most of the air you swallow, containing nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide, leaves the stomach. The remaining gas enters the small intestine, where it is partially absorbed. A small amount enters the colon for release through the rectum.
The body does not digest or absorb all of the carbohydrates (sugar, starch, and fibre found in many foods) in the small intestine due to a lack of certain enzymes. This undigested food then travels from the small intestine to the large intestine. In the large bowel, normal, harmless bacteria break down food and produce carbon dioxide, hydrogen, and methane (in few people). Eventually, these gases exit through the rectum.
Foods that produce excessive gas in one person may not cause symptoms in another. Some bacteria found in the colon can destroy the hydrogen produced by other bacteria. The balance between the two types of bacteria can explain why some people have more gas than others. In addition, most people with symptomatic gases do not have more gas than others but are more sensitive to the symptoms caused by that gas.
Most carbohydrate food can cause more gas as compared to fats and proteins.
Sugar such as raffinose, stachyose, lactose, sorbitol, and fructose can cause gas.
Most starches such as corn, noodles, potatoes, and wheat produce gas. These starches are broken down in the colon (large intestine).
Food also contains soluble and insoluble fibre. Soluble fibre easily dissolves in water and forms a soft, gel-like texture in the intestines. Mainly found in oat bran, peas, beans, and most fruits. Insoluble fibre produces little gas, such as wheat bran and vegetables.
If you are experiencing frequent urination more than usual or if you have the following conditions, then make an appointment with your doctor:
Seek immediate medical help if you have frequent urination along with any of these symptoms:
Urinary tract disorders may cause the above symptoms, along with other serious diseases. Contact your doctor to find out the causes of frequent urination and how you can treat it.
Talk to your doctor if your gas is so persistent or severe and impacts your daily life. Gas accompanied by other symptoms may indicate more serious conditions. Seek doctor’s help if you experience any symptoms:
Seek immediate attention if you experience:
After knowing what causes frequent urination and excessive gas in your body, you must take careful actions to limit these incidences. However, if frequent urination and excessive gas are affecting your daily life, seek medical attention. You can book an appointment with our consultants, or you can reach us at +91 124 4882248.
Being a parent is always a tough job, be it a mother or a father. A lot of things change when you welcome your newborn baby into your life. Sometimes when a premature baby is born due to any complications related to a baby’s health, a doctor will advise you to the neonatal intensive (noeontal intensive doctors) care unit (NICU). Now, as a parent, you must be worried and want to know what to expect when your baby is in the NICU. Let us discuss what CK Birla Hospital’s neonatology & paediatrics department has to offer you?
While a NICU is rarely part of a birth plan. But, knowing what neonatal services are available at the place where you are going to deliver can put you at ease. For example, it is much easier for the neonatal team to communicate with obstetricians and maternal-fetal medicine doctors a lot before the baby is born. This communication continues as the baby receives care from many specialists in the hospital, and then follows the infant after being released from the hospital, easing the transition of care from medical specialists to the baby’s new paediatrician.
Every parent’s experience in the NICU is different. One thing that mothers recall from their NICU days when they started the journey. They didn’t know what to expect once they got there. Some tests that the parents might notice their baby undergoing are the bilirubin test, oxygen level tests, sugar level tests, blood tests, and urine tests. Even though these tests can be daunting to parents, try and remind yourself that they are necessary for your baby’s advancement and proper growth. Infants get measured every day.
Following are some of the equipment you will see when you enter the NICU:
Infant warmers: These are small beds with heaters to keep babies warm while being monitored.
Incubators: They are small beds surrounded by clear, hard plastic. The temperature in the incubator is under control so that the baby’s body temperature stays where it should be. Doctors, nurses, and other caregivers treat babies through the holes in the sides of the incubator.
Phototherapy: Some newborn babies are born with jaundice, which causes the skin and whites of their eyes to turn yellow. Phototherapy helps in treating jaundice. During the treatment process, infants lie on a special light therapy blanket and have lights attached to their incubator. Most babies only need light therapy for a few days.
Monitors: With the help of monitors, doctors and nurses can easily keep track of your baby’s vital signs – temperature, heart rate, and breathing – from anywhere in the NICU.
The monitors include:
Feeding tubes: Breastmilk can often help babies that are born early. Sometimes mothers whose babies are in the NICU are not yet strong enough to nurse, but mothers can still pump milk and have their babies consume it. The hospital usually has staff who can help new mothers pump milk or even try nursing if their NICU babies seem healthy enough. Some NICU units also have a milk donation centre where other mothers donate their breastmilk to tiny infants in need of power.
Intravenous Catheter (IV): An intravenous catheter is a thin, flexible tube inserted into a vein to deliver fluids and medicines. Almost all babies in the intensive care unit have an IV. Infusions give some medications in small amounts 24 hours a day instead of injecting your baby every few hours. Intravenous treatment can refer to as a “drip” or “infusion”.
Lines: Some babies need more fluids and medicine than an intravenous catheter can give. Sizeable tubes called midlines placed in a large vein in the chest, neck, or groin. Doctors place arterial lines in the arteries instead of veins. They are used to monitor blood pressure and blood oxygen levels.
Ventilators: Babies in the intensive care unit sometimes need extra help with breathing. Babies who have been in intensive care for a long time (several months in a row) may have a tracheostomy (a plastic tube in the windpipe) connected to the ventilator at the other end.
Oxygen hood or nasal cannula: Some infants do not need a ventilator but need an extra oxygen supply. Babies who can breathe on their own can get oxygen from nasal cannulas ( a plastic tube inserted in their noses) or from an oxygen hood worn over the baby’s heads.
Also, read: What makes kids picky eaters and what may help them get over it
Following are some of the tests performed in NICU, including
In the worst cases, doctors go for specialized testing like computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to examine the brain, radiographs to look for problems with the gastrointestinal tract, and echocardiograms to see the functioning of the heart.
Mothers can breastfeed their babies or offer formula in a bottle in the NICU.
Babies in the intensive care unit have a feeding schedule. Your baby’s nurse can tell you when to feed and sleep your baby. The more time you spend with your baby, the more you learn about:
NICU doctors and nurses play an important role in monitoring the baby’s growth and development. The Neonatal Care at the CK Birla Hospital provides expert neonatologists to ensure that the treatment is as comfortable for the baby as possible. Research has shown that babies nursed with the Development Care approach are healthier, develop faster and go home earlier. Consult top neonatologists at the Department of Neonatology & Paediatrics to learn more.
Vitamin D deficiency is one of the common nutritional deficiencies found among adults and children, as well as it is the common undiagnosed medical condition across the globe.
According to a study, Vitamin D deficiency is prevalent in nearly 76% of Indians.
Vitamin D is also known as the sunshine vitamin that helps in keeping your bones strong. Recent research suggests that Vitamin D protects you from a lot of health problems. As the name depicts, the sunshine vitamin is produced by the body in response to skin exposure to sunlight.
There are a few foods that have vitamin D, like fish, fish liver oils, egg yolks- which fortifies dairy, and grain products. When Vitamin D enters our body, it regulates bone metabolism, calcium, and reduces the risk of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular, malignancies, autoimmune diseases, and infectious diseases.
Vitamin D deficiency is prevalent in everyone in our country and especially in the Northern parts of India. The very first reason is the limited or no sun exposure, generally, in urban areas- people do not prefer going outside, or if they go, they prefer minimum sun exposure.
In this article, Dr. Harshavardhan Hegde, one of the best orthopaedic experts in Gurgaon, will discuss the importance of Vitamin D for children and adults, and everything about Vitamin D deficiency.
Table of Contents
Vitamin D deficiency indicates that there is not enough vitamin D in your body. People with fair-skinned and young individuals are more capable of converting sunshine into vitamin D more efficiently than darker-skinned and aged people.
1. Bone and joint pain
2. Fatigue and tiredness
3. Headaches
4. Weight gain
5. High blood pressure
6. Insomnia
7. Cramps in muscles
8. Osteoporosis
9. Rickets in children
10. Depression
11. Becoming More Prone to Infections
12. Impaired Wound Healing
Listed below are a few symptoms that can help you understand that you might have Vitamin D deficiency in your body
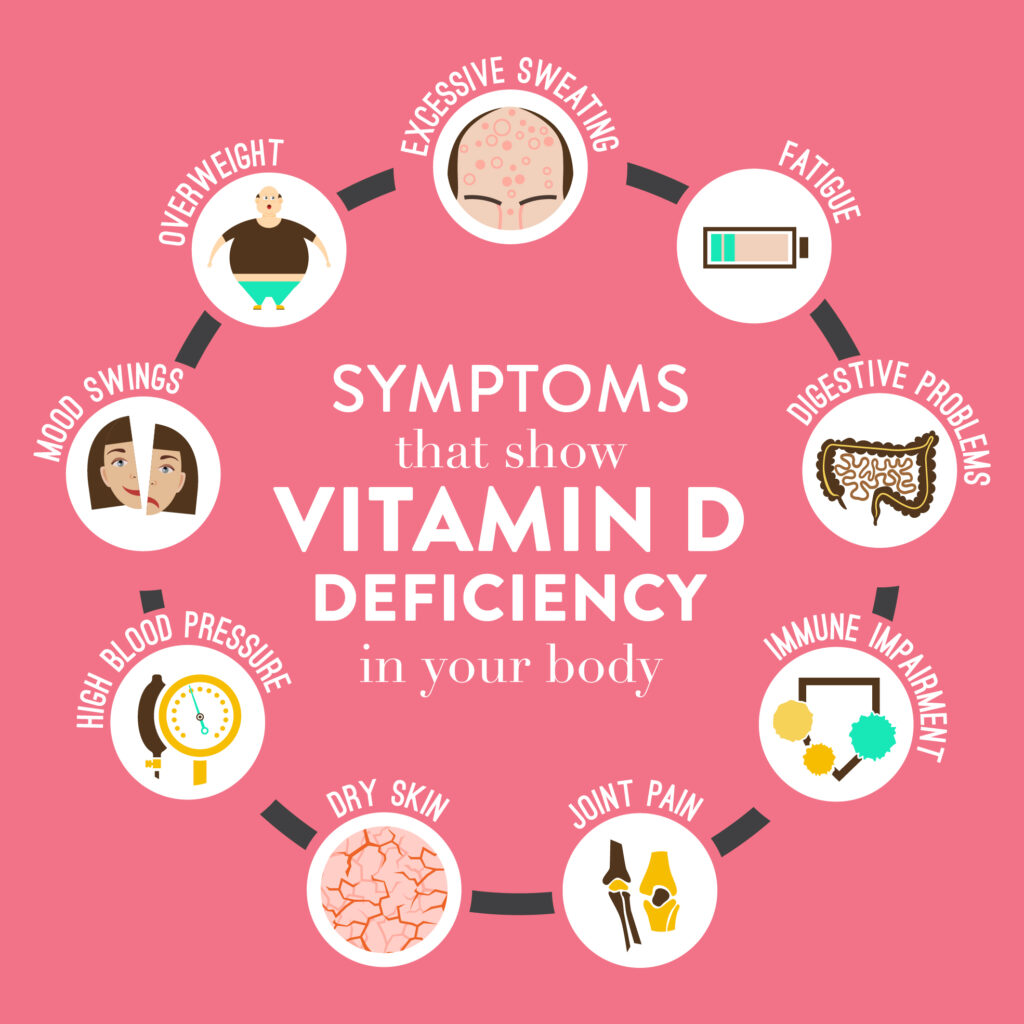
There is an established relation between Vitamin D and calcium. Vitamin D is an essential hormone as it helps your body effectively absorb calcium by mediating the transportation of this mineral and supporting bone growth.
Vitamin D deficiency can hence affect your bone and joint health causing a variety of symptoms including pain. Inadequate levels of vitamin D can lead to the development of bone and joint disorders such as arthritis and osteoporosis.
Several studies show that a deficiency of Vitamin D in your blood can impact your energy levels and sleep quality. Individuals living with Vitamin D deficiency often complain of fatigue and tiredness.
Low levels of Vitamin D can cause delayed sleep and even shorter sleep duration. Poor quality of sleep can hence cause daytime sleepiness and tiredness.
Vitamin D can cause different types of headaches including migraine. It is because decreased levels of vitamin D may be responsible for bone pain and swelling which can further aggravate and sensitise your nervous system causing headaches.
A comparatively recent study has shown people with a higher BMI and excess fat especially around the waistline are more likely to have low levels of Vitamin D.
Vitamin D deficiency is related to heart health. Individuals with low levels of vitamin D are more likely to experience high blood pressure (hypertension).
As discussed above, vitamin D deficiency can impact your sleep. Besides hindering the quality of your life, it can also trigger insomnia by affecting your sleep schedule. People living with low levels of vitamin D are seen to have daytime sleepiness and drowsiness.
Vitamin D is responsible for maintaining the strength and functioning of your musculoskeletal system. A significant decrease in these vitamin levels can cause pain, discomfort, spasms and cramping in your muscles.
Osteoporosis is a condition in which your bones become weak and brittle. It is because in this condition, your body is unable to produce new bone tissues to replace the new ones.
Vitamin D helps your body absorb calcium and phosphorus, rightly. If there is a lack of these nutrients, you are likely to develop osteoporosis.
Rickets is a condition that hinders bone development in children. It primarily occurs as a result of inadequate vitamin D levels causing the softening and weakening of bones.
Several types of research have shown that vitamin D deficiency can lead to mood disorders and mental health issues including depression and anxiety. It has been seen that increasing the consumption of vitamin D can help improve the symptoms of depression.
Your immune system determines how well you are able to fight off bacteria and viruses. Vitamin D is an anti-inflammatory hormone that has diverse effects on your immune system.
It directly interacts with your immune system cells that fight the above-mentioned infections. A vitamin D deficiency can affect this ability and make you more prone to contracting infections.
Vitamin D is a contributing factor in the development of new skin on wounds as it increases the production of components leading to the skin layer growth. It is, thus, an important aspect in a person’s healing journey after a surgery, injury or infection.
Vitamin D deficiency can occur in your body due to various reasons, listed below are a few of them.
Vitamin D deficiency can be caused as a result of insufficient intake of vitamin D. You may have the above-given symptoms if you are not able to consume the recommended levels of the vitamin over a long time, especially if you follow a strict vegan diet. If your diet excludes most of the natural sources for Vitamin D like fish, beef, egg yolks, you may behave vitamin D deficiency.
Sunlight is a natural source of vitamin D. A restricted or low exposure to sunlight can cause a deficiency of vitamin D.
Melanin is a pigment in your skin that provides its colour. Dark-skinned people have more melanin than light-skinned people. Melanin also protects your skin from UV rays. An increased amount of melanin reduces your ability to synthesise Vitamin D from the sun, thus, impacting its effectiveness and causing an insufficiency.
Obesity and vitamin D deficiency are highly correlated. People with a BMI of 30 or more than 30 often have low Vitamin D levels.
Medical problems like Crohn’s disease, cystic fibrosis and celiac disease can affect your intestine’s ability to absorb Vitamin D through food that you eat.
With ageing, kidneys are unable to convert Vitamin D into an active form which increases the risk of being Vitamin D deficient.
The following are at risk for Vitamin D deficiency
There are several reasons to consider Vitamin D as an essential vitamin for the human body, including;
1. Supports Bone Health (Calcium & Phosphorous Absorption)
Vitamin D helps your intestines absorb calcium and phosphorus, essential minerals for strong, healthy bones. Without enough vitamin D, bones can become soft or brittle, leading to osteomalacia, osteoporosis or loss of bone density, in adults and rickets in children, and increasing the risk of fractures and osteoporosis.
2. Boosts Immune Function
Vitamin D plays a key role in your immune system. Immune cells have vitamin D receptors, and adequate levels help your body fight infections more effectively, reducing the frequency and severity of illnesses.
3) Maintains Muscle Strength
Vitamin D affects muscle fibre performance and coordination. Low levels can cause muscle weakness, poor balance, and a higher risk of falls, especially in older adults.
4) Regulates Cell Growth and Repair
Vitamin D acts like a hormone in the body, influencing how cells grow, mature, and repair themselves. This function supports healthy tissues and proper cell function throughout the body.
5) Reduces Inflammation
Vitamin D helps control inflammatory processes in the body. Adequate levels may reduce chronic, low-grade inflammation, which is linked to many health problems including heart disease, diabetes, and autoimmune conditions.
Getting enough vitamin D plays an important role in keeping you healthy by protecting against diseases or conditions, these conditions can include:
The 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] test is the best indicator of vitamin D status.
Typical interpretation (ng/mL):
Conversion: 1 ng/mL = 2.5 nmol/L. Ranges can vary slightly by lab and clinical context.
Vitamin D (the sunshine vitamin) is important to maintain overall health. You can easily and effectively boost your vitamin D levels by taking the following measures.
The best way to get the sunshine vitamin is through sunlight. Increasing your exposure to sunlight is one of the best ways to increase your vitamin D consumption. You should consider the duration, time, skin tone and sensitivity to decide how much sunlight exposure is adequate.
Seafood such as fatty fish, tuna, and shrimp are rich in vitamin D. For those who prefer vegetarian options, egg yolks, fortified milk, fortified cereals, fortified orange juice, and UV-exposed mushrooms are excellent sources. Including a variety of these foods can help maintain healthy vitamin D levels.
Another way to up your vitamin D intake is through nutritional supplements. You can consult your healthcare provider about the type of supplement ideal for you.
Obesity can make you more prone to developing vitamin D deficiency. You should aim to achieve and attain your ideal body weight by proper diet and physical activity.
Outlook
If you have any queries related to Vitamin D or how to boost the level of Vitamin D in the body, get in touch with our team of experts to get your Vitamin D levels checked.
Vitamin D is naturally present in only a few foods. Here is a list of the top foods that contain it.
| Food | Category | Key notes |
| Cod liver oil (1 tsp) | Natural | One of the richest natural sources |
| Salmon (wild/farmed) | Natural | Fatty fish; baked, grilled or steamed |
| Sardines (canned in oil) | Natural | Convenient pantry option |
| Trout | Natural | Freshwater fish, naturally rich |
| Tuna (canned, light) | Natural | Check mercury advisories if pregnant |
| Egg yolks | Natural | D is in the yolk, not the white |
| UV-exposed mushrooms | Natural/UV | Look for “UV-treated” on the label |
| Fortified milk/plant milks | Fortified | Check label: cow’s, soy, almond, oat |
| Fortified cereals/orange juice | Fortified | Varies by brand; read nutrition panel |
Tip: Labels for fortified foods will list vitamin D per serving (IU or mcg). Use these along with fish/eggs to diversify sources of vitamin D.
Your skin can make vitamin D from UVB rays.
This is a practical way to increase vitamin D alongside diet. Supplements may be considered if your test shows low levels only as advised by your clinician.
Q. How long does it take to recover from vitamin D deficiency?
Based on your treatment and proactive measures, you may take nearly 3-6 months to recover.
Q. Can low vitamin D cause neurological symptoms?
Yes, low levels of vitamin D can cause certain neurological symptoms such as tremors and depression.
Q. Can low vitamin D cause dizziness and headaches?
Yes, vitamin D can sensitise your nervous system leading to dizziness and headaches.