Filter :
Robots have been used in surgery since the late 1980s, and in orthopaedic surgery since 1992. Overtime, the technology has evolved and showed promising outcomes when compared with traditional orthopaedic procedures. Currently these are performed in two modes: haptic and autonomous.
Robotic or Robot-assisted surgery, is taking minimal access surgery to the next level with a plethora of advantages for the surgeon as well as the patient. Currently used in a majority of surgical procedures, it has enabled surgeons to perform common and complex procedures with greater safety and precision. Results of the above have proven to be beneficial from the patient’s as well as the surgeon’s perspective.
Table of Contents
A robot assisted surgery is primarily a robotic system that is controlled by a surgeon. The surgeon operates from a console near the operating table, which controls the arms of the robotic system. The surgeon’s hand and wrist movements are exactly replicated by the tip of the wrist on the robotic arm. This arm has a wide array of movement and flexibility to overcome the limitations of a human wrist.
Due to this robot enabled dexterity, the surgeon can navigate into areas in the surgical space which were previously not accessible in conventional surgical approach. Moreover, the robotic system lends the surgeon a higher depth in perception due to a 3D surgical imaging technique. This vastly increases the accuracy and safety of the surgical procedure.
Some of the key advantages of robotic surgery are:
Robotic systems come with an in-built safety mechanism that is factored in with algorithms of artificial intelligence and machine learning. Most laparoscopic surgeons find the transition to robotic surgery seamless, and adapt easily with a short learning curve. The excellent patient outcomes, increased surgical control over the safety measures and the enhanced accuracy of the procedure are gradually making robotic surgeries the preferred option for healthcare providers far and wide.
The most successful implementation of this technology has been observed in the case of Total Knee Arthroplasty. Let us understand how conventional, navigated and robotic TKA’s compare when choosing the best outcomes in a TKA surgery.
Compared to conventional total knee replacement or arthroplasty, robotic or robot assisted surgical approaches give far better outcomes. Let us understand with a simple comparison.
Clearly there are more problems to this approach which has been reported by patients and observed by specialists over time. To overcome this they moved to a navigated TKA surgical approach.
Navigated TKR fares much better than the conventional approach as it follows a planned prototype approach to eliminate errors.
However, in comparison to both these approaches, the only concern which was still unaddressed was accuracy. This is where Robotic TKA takes the edge above rest.
Here a robotic device helps execute the pre-operative patient-specific plan with a high level of accuracy.
To ensure that the robotic TKA surgery finds maximum success potential for the patients, we at the CK Birla Hospital, also use CUVIS Joint system to ensure that every surgical outcome leads to a more natural recovery and better quality of life.
The advantages of the CUVIS Joint system are mainly attributed to its comprehensive preoperative plan, intraoperative monitoring, patient specific and appropriate intervention by surgeons. These joints contribute majorly to the success of a TKR due to:
Surgeries must not prevent us from leading a healthy regular life, they must ensure that we all get a chance to overcome pain and experience the unlimited joys that life has to offer. At the CK Birla Hospital we ensure our patients get the best surgical outcomes to lead a better life.
By implementing the latest innovations in surgical techniques we not only improve the chances for our patients, but also enable our award winning team of orthopaedic surgeons to keep delivering on the promise of world class healthcare services.
If you are thinking of getting a total knee replacement, now is the time to ensure that you get the best surgical results. For a consultation and more information about this approach, Book an appointment with Dr Ashwani Maichand today.
Having sleepless nights can be a choice for some and a liability for many. To quote the famous words of author F. Scott Fitzgerald, “The worst thing in the world is to try to sleep and not to.” While the whole world regales in the romanticism of sleepless nights, it is a big deal for a person with sleep disorders. Sleep disorder is a broad umbrella term that includes many different medical conditions. It is often the starting point of most mental health issues which gradually surface over time.
So if you can’t get any “shut-eye” despite multiple efforts or are not able to sleep despite everything being “normal”, read on…
Table of Contents
As mentioned earlier, sleep disorder refers to various medical conditions that affect sleep quality & duration, and directly affect the person’s ability to properly function during the day when they are awake. To date, there are 100+ sleep disorders broadly based on the cause, symptoms and physical and psychological effects. But most disorders can be classified under the following:
These are all signs of a disorder that are either physical or psychological and need medical intervention.
Those who get at least a good uninterrupted 8 hours of sleep are normal and do not fall under the category of sleep disorders. But those who might be suffering from sleep disorders get bogged down by:
Once this condition starts, it does not seem to stop and eventually becomes a big roadblock in leading normal day-to-day life. Each of these triggers leaves a negative impact on our energy, mood, concentration, and overall health. The best way out is medical treatment and lifestyle changes.
Experts suggest that prompt diagnosis helps resolve the condition faster as prolonged sleep disorders become deep-rooted with further health complications. Since the conditions are linked to mental health issues they can directly affect
Symptoms of each type of sleep disorder depend on the severity and type of disorder. It will also depend on the severity of any underlying condition. Generally, the notable symptoms are:
Your physician will assess your concerns and suggest one or more of the following tests as per the underlying symptoms.
The results from these tests are vital inputs in determining the proper course of treatment for the patient. Based on the findings lifestyle changes will be suggested to help revive the circadian rhythm of the body. Such as:
Apart from this, the doctor might prescribe medicines like sleeping pills, melatonin supplements, allergy & cold medication, dental guard (teeth grinding), breathing device(sleep apnea), and any other medication as the specialists deem fit. Please note: never opt for medication unless expressly advised by the doctors for any sleep disorder.
The impact of sleep disorders can be disruptive. There will be a point where you will seek immediate relief. But that will only be possible for short-term cases, as old persisting cases take time to heal. But whenever sleeplessness starts interfering in your everyday life it is imperative to seek medical intervention. In case you are facing a similar concern do not hesitate to walk in or call us at (number) to book an appointment with a sleep specialist. You might just be solving a much bigger problem by opting for prompt diagnosis at the CK Birla Hospital. Book an appointment with leading Pulmonologist Now.
.
Sometimes the cause cannot be determined properly. However, most sleep disorders are caused by:
The three most popularly found sleep disorders are:
There can be different treatment approaches, but ultimately these conditions are curable with a little discipline.
Make your oasis to rest and recuperate.
There are many diseases men experience about which they do not open up. The prostate gland in men has multiple functions and each function is very vital. While it manages the excretory system it also manages their fertility. One of the major concerns in men, observed by urologists is prostatitis. Let us understand the condition better to help the men in our lives cope better with this disease.
Table of Contents
The prostate is a key part of the male reproductive system. Its main function is to prepare the fluid that goes into semen. This prostate fluid is therefore vital for male fertility. The prostate gland is a walnut-shaped structure that surrounds the urethra near the bladder. The urethra joins the bladder at its neck forming the lower urinary tract. The prostate has two or more lobes enclosed by a layer of tissue, located in front of the rectum, below the bladder. The urethra carries urine from the bladder to excrete. However, in men, the urethra is also responsible for carrying out semen through the penis.
Now that we understand what a prostate is, let us now understand in the next section, what prostatitis is.
A painful condition of an inflamed prostate gland and inflammation in the adjoining areas of the prostate is called Prostatitis. Based on the location and cause of the condition, prostatitis can be classified into 4 distinct types:
In the case of asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis, the symptoms are not visible and are mainly diagnosed when we are testing for other urinary tract disorders. This variant usually doesn’t cause complications and hence does not need any specific treatment.
Prostatitis is a seemingly common urinary tract-related condition for men aged less than 50 years, but seniors are also susceptible to this in old age but the frequency is lesser. Of all the variants, the highest reported cases belong to chronic prostatitis. Other than this the following have a higher risk of getting prostatitis.
You Can Also Read: The Link Between an Enlarged Prostate and Prostate Cancer
Each type of prostatitis has different symptoms and causes.
Chronic prostatitis or chronic pelvic pain syndrome:
The exact cause is unknown. However, it may be linked to the chemicals or microorganisms in urine, excluding bacteria. Apart from this a weak immune system due to a previous illness such as UTI or traumatic nerve damage might also cause this type of prostatitis.
Acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis:
As the name suggests it has to be a bacterial infection in or around the prostate gland that causes bacterial prostatitis. The acute variant happens suddenly and lasts a short while. Chronic variant develops slowly and last longer, sometimes even up to years. If this is an extension of a bacterial UTI, then the bacteria usually travels from the urethra into the prostate gland.
The symptoms will vary with each type of prostatitis. The range of symptoms varies depending on the cause and the body composition of different individuals.
Symptoms of Chronic Prostatitis:
Symptoms of Acute and chronic Bacterial Prostatitis:
You Can Also Read: Premature ejaculation-causes, symptoms and treatment
While prostatitis is treatable, the more severe condition is caused by a bacterial infection. Hence the commonly observed complications are:
If untreated, prostatitis can become much more severe and can also progress towards prostate cancer and permanent male infertility. So, you must get immediate medical attention when any of the above-mentioned symptoms show up.
Bladder issues, prostate pain and hyperplasia can also signal prostate cancer in the early stages. Therefore men must seek immediate medical help when they notice problems like
A urologist will examine your symptoms and conduct a physical test. Then you will be asked to do a urine sample test which will reveal if there is any bacterial intervention, if yes then the bacteria will be identified with a urine culture report.
Then to check your flow of urine, a uroflowmetry test will be performed where the doctor will check the pressure of your urine. Finally, the doctor will inquire about any family history of prostate-related issues.
Depending on the outcomes of initial tests, the urologist may suggest further blood tests, cystoscopy, transrectal ultrasound, sample biopsy, etc. if he has anything which suggests that the symptoms are early signs of prostate cancer.
To summarise, prostatitis is not a fatal disease or condition. However, it might be an indication of a bigger concern that may be brewing underneath. So it is always safe to get regular prostate exams, at least annually to ensure that you keep conditions like prostatitis at bay. But if you have a family history of this condition or are experiencing any of the aforementioned symptoms it is best to reach out or book an online appointment with our award-winning team of urologists at the CK Birla Hospital.
These are some of the common reasons which might make your urologist suspect that you might have prostatitis.
But always get checked and tested under the guidance of a urologist before self-diagnosing yourself.
Prostatitis is often caused due to unexplained inflammation and bacterial infection. Therefore it is not something that can be passed on through sexual intercourse. However, in some cases, it is seen that a sexually transmitted infection might be the cause of Prostatitis symptoms.
Practise safe sex and always consult an experienced specialist in case of any discomfort.
Prostatitis is caused by a bacterial infection. UTI is also caused by bacterial infection. And the symptoms for both are the same. In the case of Acute or Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis, it acts in the same manner as a UTI infection. Always get an experienced urologist’s opinion to ensure you get prompt and timely treatment.
Did you know that diabetes is genetic? That means if anyone in your family has diabetes, there are very high chance that you have inherited it too, from the day you were born! International Diabetes Federation says that as of this day in 2022, India has 77 million people suffering from Diabetes and it is one of the most prevalent kinds of inherited disorders people suffer from worldwide. But type 1 & 2 diabetes is just one of the many congenital and inherited metabolic disorders that people suffer from. What other metabolic disorders are passed on from generation to generation? Let’s find out.
Table of Contents
To understand what inherited metabolic disorders are, first we need to understand metabolism and metabolic disorders.
When these disorders become congenital and are seen to develop naturally in the next generation, it is called an inherited metabolic disorder.
So now that we understand metabolism and metabolic disorders, let us identify the causes of inherited metabolic disorders.
As the name indicates, the disorder has to develop in humans congenitally. Some of these disorders are so deep-rooted that they are typical for a specific racial profile as well. For instance, a person can be born with a malfunctioning pancreas or liver and over time it rapidly deteriorates. These further depend on factors like:
Further another cause can be a mutation of genes passed down through generations in families. Based on racial profiling these are some of the most observed genetic metabolic disorders:
Research suggests that a man with type 1 diabetes is likely to have a child with diabetes in 1 out of 17 cases. For women, if the child is born before 25 years, the probability will be 1 in 25 but for delayed pregnancy, the odds go down to 1 in 100.
Further, your child’s risk is doubled if you develop diabetes before age 11. If both you and your partner have type 1 diabetes, the risk is between 1 in 10 and 1 in 4.
As enumerated above, inherited metabolic disorders can be highly diverse in their origin and cause as it affects the body in a lot of different ways. But the most common signs are:
Since the origin is congenital it is more likely to be spotted at the time of birth. However, if the problems are triggered later in life the usual process is:
To summarise, it is not easy to live with an inherited metabolic disease and in most cases these cannot be cured. However, they can be managed through proper management to prevent fatality. If your family has a history of metabolic disorders it is essential for you to regularly check for symptoms and get a full body checkup done annually to keep the problems at bay. You can reach out to our specialist in endocrinology by booking an appointment or simply walking into the nearest CK Birla Hospital.
You reach out to an endocrinologist and get yourself assessed for any kind of symptoms mentioned above. The doctor will suggest you some blood tests to understand the kind of metabolic disorders you may have. Sharing your family’s medical history helps immensely.
Poor metabolism leads to hormonal imbalance affecting the thyroid causing weight gain. It can also restrict the production of insulin used to break down carbs in the body leading to weight gain. There can be some unexplained weight gain that is also linked to this condition.
Since a lot of the problems are on enzymes and hormones it is effectively looked into by an experienced endocrinologist. Apart from this, a paediatric surgeon can identify problems spotted at birth.
If you have it then a lifelong commitment to a healthy lifestyle may save your next generation from inheriting it.
It’s the Great Indian Wedding season. You are home, stuck enduring unlimited loops of the party anthem of the year, playing at the wedding next door. You just want the song to stop. You plug a finger in each of your ears and hope for the ordeal to be over with. Finally, the song ends. You remove your fingers and another problem now irritates you more than the song did. Your ears have blocked and now you hear everything at a lower volume. You try undoing the damage but in vain.
This kind of situation happens to everyone at some point of time in their lives. Ear blockage can be very irritating and the causes may be multiple. Sometimes it is a simple air pocket that releases on its own. While at other times it might be a symptom of something more severe like anxiety or Meniere’s disease. So what causes ear blockage? What are the symptoms and treatment for ear blockage? For all these queries and a lot more awareness read on…
Table of Contents
When you start hearing less and when loud voices also start sounding muffled, your ears might be clogged or plugged up. Multiple reasons can lead to ear blockage. Common ear wax is the primary reason for the blockage, but sometimes there could be nothing in your ear canal and the blockage still exists.
Let us understand the various causes of ear blockage in the next segment.
While the reasons are not always apparent, the most common causes behind ear blockage are:

Our ear’s self-protective measure is earwax. The stickiness of ear wax acts as a lubricant for the middle ear canal, traps dirt & pollutants, and helps clean out the ear canal like a natural cleaning agent when it falls off the ear by itself. But when the ear wax becomes impacted, it directly affects your hearing ability.
How to know if your blockage is due to impacted ear wax? Here are the symptoms
Never try to poke your ear or extract wax with a cotton swab, peroxide or baby oil. This will make matters worse and might end up affecting your eardrums.
When the fluid gets stuck in the middle ear it can lead to ear blockage. This can also happen in several ways. Such as:
A stuffy nose, blocked ears and tenderness on the face are the outcomes of sinus pressure. These symptoms can also lead to a temporary hearing loss. This is because the sinus is located beside the ear canal. So when the sinus cavity experiences inflammation, it results in the swelling of Eustachian tubes closing the connection between your throat and your ear. This makes clogged ears feel much worse. But if the inflammation grows more severe it can lead to temporary hearing loss.
Barotrauma or aeroplane ear condition is another cause of ear blockage. When you are on a flight, your ears cannot properly adjust to the changing air pressure.
Noise is the biggest cause of hearing loss in people. Exposure to loud noises, explosions and blasts can lead to people experiencing blocked ears.
Ear blockage can be due to various other underlying health causes also. Such as anxiety or panic disorder. This can cause fullness, pressure and pain in the ears due to some triggering event. During these episodes, You have a constant urge to pop your ears to relieve the stress and feel better.
The most severe cause is linked to Meniere’s disease. This inner ear condition is often accompanied by tinnitus, dizziness and hearing loss. This makes our bodies lose their balance over time.
Trauma or injury to the head can cause ringing and aural fullness of the ear. This makes you feel as if your ears won’t ever pop.
Sometimes children put small things in their ears which can cause blockage. An insect worm or any foreign object inside the ear can also create problems.
Unclogging your ears at home is a welcome option for all of us since the experience of a clogged ear can be frustrating. However, we need to understand what is good or bad in terms of home remedies that will not impact the overall well-being of our ears.
| What not to do for earwax blockage? | What to do for earwax blockage? |
Any invasive means of cleaning is not advisable:
|
Find only the minimally invasive means of cleaning and maintaining the hygiene of your ears. |
Now let us understand the various treatment options available to us in case of an earwax blockage.
In addition to these, you can always use the humble hair dryer to easily dry out all the water after a bath and keep the ear dry.
You Can Also Read: Ear Bleeding – Causes and Treatment
The ears are very delicate parts of our body. Blocked ears can make you very distracted from your daily work. However, in case this comes along with symptoms like fever, pain or earache, do not waste time seeking medical help.
As a preventive measure, one can always get their ears assessed by a specialist who will evaluate their hearing to set a good benchmark for your healthcare provider to use in an emergency.
To summarise, a blocked ear or ears can be a huge inconvenience, and worse, a health risk. When a blockage happens out of the blue, you are left preoccupied with trying to relieve yourself of it. To help you in the long run, consult a professional ENT specialist who will be able to regularly keep your ears clean and monitor your ears for any kind of problems. At the CK Birla Hospital, we urge all our patients to get into the habit of regular checkups to stay ahead of any kind of health hazards. Think you might want to start now? Then walk in or book an appointment here with the leading ENT Doctor at CK Birla Hospital.
The ear blockage depends on a lot of conditions. But primarily the ear with more accumulated ear wax will have a greater tendency to get clogged or blocked. This can also be due to the existence of a fungal or bacterial infection in the middle ear. The ENT will usually clean out the infection through professional ear drainage and prescribe a course of antibiotics to overcome the infection.
Sometimes in very rare cases, a blocked ear may be due to a benign growth inside the middle ear. This might take a serious turn if the benign growth goes rogue. A blocked ear can also indicate harm and cuts to the ear canal or the ear drums. Since the area of the ear is very small a blockage, though usually harmless, must be given due importance if it does not disappear on its own.
Passive techniques and activities to open up your eustachian tubes such as yawning, chewing gum, gulping frequently, saltwater gargling and drinking water may ease ear clogging naturally.
Apart from this, you can always take steam with essential oils like peppermint or tea tree which will help ease out the blockage.
Sometimes an ear blockage might be due to an air pocket stuck between ear wax. Sometimes it tends to resolve on its own without any intervention. A blocked ear can last a few minutes to even months depending on the underlying cause.
If you are undergoing your periods it is very common to think that when you pass urine you are passing blood with it. The source of the blood is not the same as the source of the urine. However, in cases other than this if you notice red or pink urine it might be a warning sign from your body about an underlying disease waiting to surface. What does this mean? What are the possible diseases it might indicate? To know all about this,
Table of Contents
In medical terms, the condition where you get blood in your urine is called Hematuria. There can be several different causes of hematuria or blood in the urine. It can range from rare blood disorders to cancer or kidney disorders. But don’t be alarmed, sometimes the blood is visible and other times it might be present in such small quantities that it’s not even seen by the naked eye. Mainly hematuria is of two types:
But no matter what the reason or amount, any signs of blood in urine is a sign of a serious health problem, which is why ignoring hematuria is never a good idea. This might just be a symptom of a fatal disease like prostate cancer or kidney failure, hence it is important that it is promptly treated.
You Can Also Read: Hematospermia (Blood in the Semen)
While there are multiple causes, in some cases, the blood may be coming from a different source. So first one must confirm the source of the blood, this is because in the following cases it may show up when you urinate:
When it is none of the above and the blood is in your urine, then these may be the possible causes:
Apart from diseases, blood in urine can be due to blunt trauma to the prostate or Kidney area.
While this can happen to anyone, there are some who are at greater risk of getting blood in their urine.
| Risk Factor of Hematuria Explained |
| Age Factor | Men above the age of 50 are at higher risk due to the chances of an enlarged prostate gland. This risk is similar in cases of prostate cancer. |
| UTI (across ages) | Men, women and children get blood in urine whenever they contract UTI. |
| Inherited Problem | A family history of kidney diseases can be a high risk factor. |
| Medication Side-effects | Blood thinners, pain medication, antibiotics etc., taken in a frequent manner can trigger hematuria-like conditions too. |
| Hardcore Exercise | Contact and high-performance sports can also cause this problem. It is very commonly seen in marathon runners. |
It is advisable to consult a urologist for the blood in the urine. They will assess the amount of blood you find during urination, your frequency of urination, the pain you feel and the medications for any other existing comorbidities you’re currently on.
After that, you will have a physical examination and a urine sample will be collected for testing and urine culture. The analysis will confirm the presence of blood and detect the cause of the infection. The doctor will also suggest blood work in case there is any symptom that might indicate cancer. If the CA 125 blood test suggests cancer, an imaging test like a PET CT scan will be done to isolate cancer.
Apart from this, your doctor might suggest a cystoscopy, where a small tube is sent up the urethra with a camera to examine the insides of your bladder to isolate the cause of the blood in your urine.
Simply put the treatment will not be directed towards blood in urine, but instead towards what is causing this.
Sometimes athletes who undergo rigorous aerobic training can also end up with slight bleeding in their urine. So the best way to treat the problem is by treating the underlying disease that caused it.
If the underlying disease stays untreated, then the body might develop complications associated with hematuria. If it is a symptom of cancer, ignoring it will lead to the formation of new tumours and if it is a symptom of a UTI then it might lead to kidney failure. Basically, it will reach a point of no return. Hence prompt diagnosis is the best way forward.
You Can Also Read: Guide to identifying UTI and managing its risk
Preventing blood in urine will require preventing the underlying causes. Hence each situation will need to be dealt with accordingly.
Runners are most often affected, although anyone can develop visible urinary bleeding after an intense workout. If you see blood in your urine after exercise, don’t assume it’s from exercising. See your doctor.
To summarise, it is never a good sign to spot blood in the urine. So if this is ever a problem you find yourself in, reach out to our team of award-winning urologists and get prompt treatment before conditions worsen. Book an appointment with a leading urologist at the CK Birla Hospital, today.
A polycystic kidney is a congenital disorder where one has a tendency to develop multiple cysts in the kidneys. In case any of these cysts burst, one will find blood in the urine. Over time unless properly managed, polycystic kidneys lead to kidney failure or cancer. So it is better to get diagnosed early on and live a better life.
Yes. This means that you are undergoing gross hematuria. You should immediately seek help from an experienced urologist who will diagnose the cause of the blood. In case you experience painful and frequent urination or pain in the pelvic region with pink urine it is a clear sign of a major problem in your kidneys.
When we pass our first urine of the day or we don’t urinate for long hours our urine resembles a reddish-hay colour. This is because urine also contains blood which is not visible to the eye. The normal range of blood in this situation is 4 RBCs under the microscope. Anything more is a cause for concern.
Anxiety and urination are well-linked. We always urinate more before any major event where we are stressed or anxious. Similarly, bloody urine and anxiety can also be linked to each other. When we are anxious, the mucosal defences of our body are lowered which might lead to bloody urine.
Yes. It may come and go. However, it is always safe to consult a specialist for this. Especially if you are nauseous, feverish and have pain in the lower back or abdomen. Seek emergency support if you start seeing blood clots in your urine.
Every morning, after you wake up there are two things you need- a hot cup of tea or coffee and a clean gut. There is no bigger satisfaction than a clean gut and a refreshed mind to make your day productive. But every day might not be the same. While some days are sunny, others days might be cloudy. Similarly, on days your system does not clear up, you feel bogged down, preoccupied and simply constipated. Now imagine if this happened for prolonged periods. Constipation is relatively common, but chronic constipation could last several weeks making it difficult for the body to function properly.
So how can we avoid this? What are the ways in which we can ensure proper bowel functions every day? To know about this in detail, read on…
Table of Contents
When your regular bowel movement is restricted to less than thrice a week, you are having constipation. This is common and often tends to interfere with your ability to go about your day-to-day tasks. However, when this stretches out for several weeks or more, it turns into chronic constipation.
Chronic constipation causes people to strain excessively in order to force a bowel movement. But in most cases, constipation is the symptom of an underlying cause, most of which do not reveal any clear answers.
You Can Also Read: Facing Frequent Abdominal Pain: Know the Causes & Treatments
Constipation changes your bowel habits and messes with your daily routine. When constipation is prolonged, it becomes chronic. But how to tell whether matters are getting worse? Look for the following signs:
When any of these symptoms keep happening for a prolonged period of time, it is advisable to seek medical help.
As per a recent Gut Health Survey carried out by a healthcare giant, approximately 22% of the Indian adult population suffers from constipation. The survey also suggested that this was not an age-related problem, anybody can suffer from constipation.
Source: https://www.abbott.in/media-center/press-releases/indian-adults-suffer-from-constipation.html
The intestines in our body are the organs responsible for bowel movements. Constipation commonly occurs when the excretory waste or stool moves very sluggishly through the digestive tract. So much that it cannot be eliminated effectively from the rectum. This leads to the stool becoming hard and dry. To get a better understanding let us first explain the digestion to excretion path, step by step:
During constipation, the stool stays in the colon for much longer, giving it time to absorb water to a bigger extent leading to a dry and hardened consistency of stools that are difficult to push out.
Chronic constipation follows the same internal mechanism where it seems that the stool is stuck and refuses to budge.
The main cause of chronic constipation, therefore, is a blockage in the rectum. This slow or restricted stool movement can be due to the following reasons:
While constipation on its own is nothing major, a few lifestyle changes can make the problem non-recurring.
In conclusion, it is essential that you pay attention to your diet and lifestyle to avoid constipation. Patients undergoing treatments that lead to constipation should get a proper diet chart and follow the same to help their recovery and avoid further complications from chronic constipation. Those who are undergoing nerve-related issues or diabetes need to get a proper diagnosis from their physicians and follow up with the proper medication to avoid constipation. If things look bad, always reach out to a doctor for proper medical support to relieve this constipation. Our team of experts are ready to help. Book an appointment with CK Birla Hospital.
If you don’t pass stools regularly, find problems in pushing it out of your rectum, or have passed stools less than 3 times a week for over 2 weeks you need help getting your intestines cleared out. When you experience discomfort, drink water and healthy fluids except dairy products to assist your intestines to push out the stools.
When the digested food residue lies in the large intestine for longer than it is supposed to then the stool starts getting hard and it becomes difficult to excrete it. So the problem does not lie in eating the food but the kind of food you eat will decide how long your body will take to push it out of your system.
Food which is not fibre or roughage rich like vegetables, beans, bran, etc. takes longer to leave the system. Roughage from fibre acts like a lubricant for your intestines to help smooth the blockage. So eat fibre-rich food and hydrate with ample fluid intake to relieve constipation.
Food which is not fibre or roughage rich like vegetables, beans, bran, etc. takes longer to leave the system. Roughage from fibre acts like a lubricant for your intestines to help smooth the blockage. So eat fibre-rich food and hydrate with ample fluid intake to relieve constipation.
When your poop is stuck in the rectum for too long it starts developing gas and you will pass gas even when you’re constipated. If you don’t hydrate enough then the gas will build up causing abdominal pain too.
Bananas have a medium glycemic index and are high in fibre which helps prevent and relieve constipation. However this applies to normal constipation and might not help with chronic constipation. Bananas when ripe have soft soluble fibre that absorbs water, helping the stools stay large and soft. Also, the enzymes in bananas act as a lubricant to improve the movement of stool through your digestive tract.
Constipation is largely caused by to lack of water in your stools. So it will not go away on its own unless you do something.
When a newly pregnant woman gets her first sonogram the doctor shows her a small little blip growing inside her womb. This is by far the most emotional moment for her, as it is the first time she sees her baby. In the first trimester, the baby is just a foetus, ready to grow into an infant and start a new life. This entire process of a foetus turning into a baby is called foetal development. This is a critical part of the entire pregnancy journey and needs proper monitoring by an experienced maternity team comprising the doctor and the ultrasound technicians who will be able to track the growth of the foetus inside the womb.
As an informed parent-to-be, it helps to know how your baby is supposed to develop. This is the time when all the organs and the body of the baby develop with which it will arrive into this world. Different growth trends can be noted in some babies so the timelines depend on each baby. Having said that, to know how a foetus usually grows, read on…
You Can Also Read: A Guide to Increasing Baby Weight When 9 Months Pregnant
At an average of two weeks from your last menstrual period, your egg will fertilise, and you will conceive. Within the first 24 hours of fertilisation, cell division begins on the fertilised egg. Then it moves down the fallopian tube as a blastocyst, develops into an embryo and simultaneously the link between your cervix and birth canal is sealed by a layer of mucus. By the 8th week of pregnancy, the embryo evolves into a foetus. At this time the hormone human chorionic gonadotrophin (HCG) will start showing up in your blood works confirming your pregnancy.
An average full pregnancy takes about 40 weeks which is divided into 3 trimesters of roughly 12-13 weeks/ 3 months each.
You and your foetus undergo a lot of changes throughout each trimester and your maternity team will be able to monitor the growth on a weekly basis. Depending on the calendar months you are pregnant, the entire pregnancy can last from 9 to 10 months which is normal.
The closer you get to the end of your pregnancy, the more critical it becomes to track the changes in the baby’s growth. The last few weeks of pregnancy are vital because babies born before full term have a higher risk of breathing, hearing or learning issues than babies born in the full term.
The last few weeks of pregnancy are divided into 4 groups, each showing the first number as the number of weeks a.k.a. Gestational age, followed by days in a week. So 6/7 means the 6th day of the week.
| Term of pregnancy | Time Period of Human Gestational Age |
| Early term | 37 0/7 weeks to 38 6/7 weeks. |
| Full term | 39 0/7 weeks to 40 6/7 weeks. |
| Late-term | 41 0/7 weeks to 41 6/7 weeks. |
| Post-term | 42 0/7 weeks and on |
This will last for 3 months or 12 weeks. The fertilised egg will evolve from a cell to a blastocyst, then an embryo and finally a foetus that starts developing the baby’s features.
At this stage, the risk of miscarriage has dropped by half, morning sickness is gone and you feel much more comfortable now. The baby’s facial features are starting to develop and the foetus is able to flip and turn.
You are in the endgame now! The final leg of your pregnancy can make you anxious as the foetus gains weight quickly with body fat that will help the baby grow after birth. The duration of the last trimester can last up to 10 months, which is completely normal. In case you pass your due date without spontaneous labour, your doctor might induce your labour through medication. Make sure your maternity team is well prepared for the main event.
To summarise, this is how your baby develops in your womb and the whole experience of feeling the kicks and the hiccups can be extremely emotional for the parents-to-be. At this precious time in your lives, it is essential that you have a maternity team ready to be by your side at every beck and call to ensure a smooth and complication-free delivery. If proper monitoring is done then the baby and the mother can be saved from multiple fatalities at birth. Our team at the Mother & Child Department of the CK Birla Hospital is prepared to handle any sudden requirements that may crop up to assist you in your pregnancy journey. Book an appointment Now.
When planning and undergoing pregnancy, nobody is more excited than the expectant parents, for the baby’s arrival. Counting days is normal in this state of euphoria. But it’s not just you but also your doctor who has to count the days to understand how the little blip in your womb is growing and developing before it arrives healthy and happy.
This concept of counting days in medical terms is called a gestation period. It is a vital part of your pregnancy, not just for you but also for your OB-GYN. So let us understand what is the significance of a gestational age as we read ahead.
Table of Contents
The time period between conception and childbirth is called the Gestation period. This is the period during which the baby develops inside its mother’s womb. Therefore, gestational age is commonly used to describe how far along the pregnancy is at that given point in time. Usually, it is measured in weeks.
Pregnancy has to be carefully monitored to help keep it smooth and free from complications. This is why the gestational age becomes a vital piece of information needed by doctors. It helps them identify the right time to perform various tests and assessments of the baby and the mother’s health at different points throughout the pregnancy.
The thumb rule is: we start from the first day of the expectant mother’s last menstrual cycle to the date on which we are currently prior to the delivery. The gestational age ends with childbirth, however, it can be determined before or after birth.
A normal pregnancy tenure lasts between 38 to 42 weeks. This is why gestational age is also measured in weeks. A child born before the completion of 37 weeks, is considered premature. And if they are born after the 42nd week, they are considered postmature.
Gestational age before birth can be ascertained through ultrasound imaging, where your healthcare partner will measure the baby’s size, especially that of its head, abdomen, and thigh bone. This gives a clear indication of the baby’s fetal development in the womb.
Gestational age can be measured after birth by physically examining the newborn’s weight, length, head circumference, vitals, reflexes, posture, muscle, skin and hair. When the baby’s gestational age equals its calendar age, then the baby is said to be Appropriate for Gestational Age (AGA). These children have lower mortality rates than those who are born too small (SGA) or large (LGA) for their gestational age.
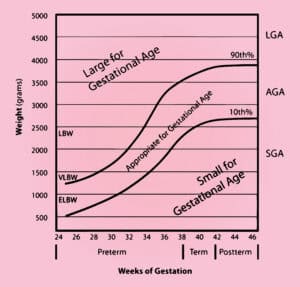
Source: Gestational age chart, how to calculate gestational age & corrected age (healthjade.net)
Over the years ultrasound has emerged as an accurate method of assessing gestational age, especially through transvaginal and transabdominal probe assessments. Transvaginal USG is preferred during the first trimester of pregnancy. Here are some of the sonographic methods of evaluating gestational age:
USG within the first 13 weeks and 6 days gives the best estimate of gestational age. Here, the transvaginal approach often provides a more clear and more accurate view. The gestational sac and yolk sac are the first visible markers, but sometimes they don’t really correlate with gestational age.
If it is not determined within the first trimester, then the crown-to-rump measurement of the foetus is considered a good way to assess the development during the second trimester as the baby is bigger and more palpable to USG imaging.
This is an old but proven method where postnatal gestational age is determined on a point-scoring pattern based on physical and neurologic assessments of tone, patterns, reflexes, movements, abnormalities, and behaviours. Higher scores translate to greater maturity.
This is an improved postnatal scoring system used for premature babies. It assesses 6 physical maturity components: skin, lanugo, plantar creases, breast, ear/eye, and genitals. And six neuromuscular components: posture, wrist, arm recoil, heel to ear, etc.
However, there are other non-sonographic methods also used to measure gestational age.
Identifying the gestational age accurately is the task of fertility experts and gynaecologists. The team of experts at the CK Birla Hospital, Mother and Child Department will not only help you plan your pregnancy smoothly but will also regularly assess your and your baby’s health and development to promptly identify any complications that can be completely averted.
Miscarriage is most likely to occur during the first trimester of the pregnancy itself. The commonly noted gestational age is around 12 weeks. However, it must be noted that the first trimester is the time when most miscarriages take place without the person knowing they are pregnant. Due to a hostile environment in the womb, the fertilised egg does not develop and the body miscarries the pregnancy.
When a pregnancy terminates before 24 weeks, it is termed a miscarriage. Miscarriages are common in the first trimester due to developmental problems with the baby in the womb. It can happen early on in the pregnancy, even before 14 weeks.
A full-term pregnancy lasts for 9 months. To assess the bodily changes and foetal development, these nine months have been divided into 3 equal parts of three months each. This is why they are called trimesters. However gestational age is measured in weeks, so it is not the same as a trimester. But if the pregnancy has completed 13 weeks of gestation, it has completed a trimester. Trimesters apply to the pregnant mother, gestational age applies to the growing baby.
Gestational age is measured from the first day of your LMP or last menstrual period. Fetal age is calculated from the actual date of conception, that is when the woman is ovulating. This implies that the fetal age is approximately two weeks behind the gestational age, which is the actual age of the fetus.