Filter :
The gallbladder is a four-inch organ located in the upper-right area of the abdomen, under the liver. It helps produce, store, and transport bile, a yellowish-brown fluid produced by the liver.
This fluid is responsible for digesting and breaking down food with fats.
When problems arise, if first-line treatments do not work, and the issue is persistent, doctors may recommend removal to prevent further complications.
Though the gallbladder is a component of the biliary system, it is not considered to be an essential organ. Bile fluid can find it’s way directly to the small intestine through ducts in the liver.
Table of Contents
The procedure for removal of the gallbladder is called Cholecystectomy. Two types of procedures come under cholecystectomy:
This is the most common choice of surgery used to remove over 95% of gallbladders. This method is less invasive and entails 3 to 4 small incisions.
The procedure involves the use of a small tube through the incision. This tube holds a camera (called a laparoscope) along with surgical devices.
The surgeon extracts the gallbladder through one of the incisions.
A conventional method that involves making a single large incision at the site and extracting the gallbladder through it.
There could be many reasons to opt for gallbladder removal. There could be blockages due to bile being thick or even deposits of hard substances known as gallstones.
Mostly, these gallstones pass naturally. Your doctor may recommend surgery if there is notable pain or larger stones.
Other reasons for cholecystectomy could be:
Common factors that could increase the risk of gallbladder problems are:
Gallbladder removal is a low-risk and frequently performed surgery. While any form of surgery has threats, the risk of not having the procedure when recommended could be far worse.
Some of the possible gallbladder removal complications could be:
Above are general risks of a cholecystectomy procedure. However, each individual may face different risks depending on their history and body composition.
Disclose your complete history to your doctor and discuss any fears about complications that may arise.
If you smoke, let the surgical team know and plan on quitting before the surgery to decrease the risk of complications.
If you have a laparoscopic cholecystectomy, you would mostly be discharged the same day. An open cholecystectomy may need you to stay overnight for monitoring.
While your doctor will give you a comprehensive download, here are some things to keep in mind:
You would be placed under anaesthesia, the surgery would be conducted, and if needed, fluid might be drained.
The surgeon will make incisions after anaesthesia. Carbon dioxide will be used to inflate your abdomen for easy visibility of organs.
Once the procedure is complete, the gas is let out through the incisions.
The following are common symptoms to watch out for:
Depending on the reason for surgery, the benefits may vary, but the general advantages of gallbladder surgery range from the following:
If you experience any of the above symptoms.
It is important to follow the instructions given by your doctor. Make sure to wash your hands and sterilize whenever caring for the wound. Avoid wearing tight clothing that might restrict the healing of the wound.
Patients usually take up to 3 weeks to return to normal activity. So, slowly increase your activity level and avoid abrupt exercises.
Maintain the health of your biliary and digestive system by eating right and keeping fit. Ensure to add nutritious high-fibre food like fresh vegetables and whole grains.
Avoid eating high-fat meals and processed food to prevent overloading your system. Drink 8 to 10 glasses of water daily to stay hydrated.
While the prevention of diseases with a healthy lifestyle should be your first priority, the cure for them is also advancing rapidly. If you have experienced any of the symptoms stated for a prolonged period, or are continually facing gastrointestinal issues, make sure to visit a doctor promptly.
Folic acid plays a vital role in the growth and development of your baby, especially in the first trimester of pregnancy.
Hence, folic acid supplements are often prescribed during pregnancy. Let’s explore the importance of folic acid during pregnancy.
Table of Contents
Folic acid, also called pteroylmonoglutamic acid, is the synthetic form of Folate (Vitamin B9). While folate is typically found in leafy vegetables, folic acid is present in fortified food items or supplements.
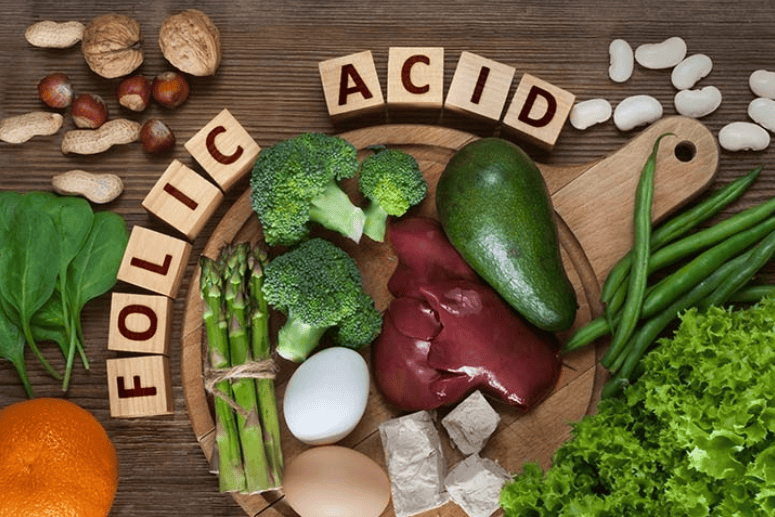
Doctors normally prescribe folic acid for pregnancy as it facilitates cell growth, production of red blood cells, and DNA formation. Thus, women who are pregnant or trying to get pregnant should start consuming folic acid daily before conception and must continue for at least three months after.
As stated earlier, folic acid aids the production of new cells. Naturally, when you are expecting, your body is dedicated to generating more cells for the baby’s development. Folic acid benefits the body as it helps in the creation of proteins, which form the building blocks of cells.
Here are the folic acid benefits for your baby’s developmental health:
Typically, the neural tubes develop into the spinal cord and brain by the 28th day since conception.
However, if the neural tubes fail to close properly, it results in a condition called neural tube defects (NTDs). The most prevalent forms of NTDs include:
Babies suffering from anencephaly may not survive, while those with spina bifida and encephalocele may struggle with a permanent disability.
Therefore, it comes as a relief that one of the greatest advantages of folic acid in pregnancy is that it prevents NTDs in babies.
In fact, it may cut down the risk of NTDs by an impressive 70%!
Congenital heart defects (CHDs) are abnormalities arising out of the underdevelopment of heart or nearby blood vessels before birth.
These developmental defects could adversely affect the heart, heart valves, arteries, and veins. Studies indicate that folic acid supplementation before pregnancy can reduce the risk of CHDs.
Folic acid can prevent structural anomalies and defects as it regulates homocysteine metabolism. As a result, it can prevent oral clefts in the lip or the palate.
Folic acid supplementation also inhibits uterine contractions, which could otherwise result in preterm birth (PTB) or miscarriage. PTB is a significant cause of neonatal mortality and morbidity.
Folic acid decreases the risk of developing anaemia during pregnancy, gestational diabetes, and other birth-related complications. Nearly 5% of women register a haemoglobin count that is less than 11.0g/dL, which is an indicator of anaemia.
The body requires folate, cobalamin (vitamin B12), and iron to produce more red blood cells. Hence, supplementing folic acid and vitamin B12 could bring down the chances of developing anaemia.
Similarly, folic acid supplementation can cut down the risk of developing gestational diabetes by 22% (for 400mcg supplements) and 30% (for 600mcg supplements).
Additional benefits of folic acid supplementation for pregnant women involve lower rates of placenta-related pregnancy complications.
This is because folic acid can regulate trophoblast invasion, which ensures regular implantation and placentation during gestation.

Ideally, the prescribed folic acid pregnancy dose is a minimum of 400 micrograms (mcg) per day.
However, a woman should typically consume about 600mcg of folic acid from all sources, including food and vitamin supplements.
Some women may be specifically advised to take folic acid supplements during pregnancy as their baby may be at higher risk of NTDs.
Mainly, this includes women who:
Folic acid admittedly has a few side effects. Certain individuals may find it hard to convert folic acid in the active 5-MTHF form.
As a result, their blood levels indicate a high concentration of unmetabolised folic acid. Chronically elevated levels of unmetabolized folic acid could increase cancer risk and vitamin B12 deficiency.
A study conducted in 2016 highlighted how women with high folate levels could birth a child with an autism spectrum disorder.
Adopting a healthy diet can supply naturally occurring folate to the body, alongside essential nutrients like calcium, fibre, and vitamins A and C.
Here are a few natural food sources of folic acid for intake during pregnancy:
Now that you understand the link between pregnancy and folic acid, you are in a better position to include it in your daily routine. It is an essential vitamin right from conception until you stop breastfeeding your child.
However, before you begin supplementation, it is wise to get your doctor’s opinion on the matter. To determine the correct folic acid dosage and any other pregnancy-related concerns, visit our specialists at CK Birla Hospital.
India is fighting an arduous battle to contain the spread of novel coronavirus disease. According to the latest stats released by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, as of 21 March 2020, a total of 298 COVID-19 cases have been reported in 22 states/union territories of India. Out of this, 23 patients have been cured, one has migrated, while four succumbed to the disease.
Table of Contents
Washing your hands regularly for a minimum of 20 seconds and avoiding contact with contaminated surfaces are the best methods to keep yourself from contracting the disease. Apart from these precautions, self-quarantine has also been recommended to all citizens of India.

India has been able to manage the outbreak until now with only a few reported cases. However, it is suspected that we are currently in the third stage of the pandemic, which means the number of infected people will multiply exponentially shortly unless we take proper precautions.
In light of this situation, the central and state governments have set up additional labs for free coronavirus testing. Moreover, for the good of the public, they have updated the protocols for screening for COVID-19.
Quarantines are generally used by governments to prevent the spread of contagious diseases. Quarantine is meant for people who do not have any symptoms of the disease but have been exposed to the sickness. This group of people includes relatives of patients, caregivers, friends, etc. Quarantine, however, must not be confused with isolation. Isolation is a precautionary measure for individuals who are already sick to keep them away from those who are healthy.
Amid the pandemic outbreak, the responsible citizens of the country need to make educated choices for their own health, as well as of others. To prevent the spread of coronavirus disease, the Ministry of Health and Welfare has advised a self-quarantine of 14-days for anyone who:
Presently, there’s no legal sanction behind this recommendation. However, it is an important step that will go a long way in helping India win this fight against COVID-19.
All quarantines are not the same. However, if you are home-quarantined for COVID-19, we have compiled a list of dos and don’ts to help you complete your quarantine successfully without adversely impacting your mental and physical health.
Stay at one place – This is the most crucial aspect of your quarantine. Limit yourself to one, well-ventilated room and avoid contact with others. You should strictly not entertain any visitors at this time. Instead, spend your time doing something you never had the time for – such as painting or writing or even catching up with friends over the phone.
Avoid mass gatherings – A person under quarantine must not attend any weddings, funerals or religious functions. They must also stay away from the elderly, small children, those with compromised immunity and pregnant women.
Maintain proper hygiene – Do not swap plates, share food, or use common cutlery. Instead, eat in your room and wash your utensils properly before replacing them in the common area. You should clean and keep your utensils and laundry separate during this period.
Your dog is safe – Dogs and cats cannot transmit coronavirus, and there’s no reason to abandon them. However, if you are under quarantine, avoid kissing, petting or hugging your pets for a few days.
Wash your hands often – At the cost of sounding repetitive, we would once again reiterate the importance of washing your hands with soap for at least 20 seconds after you touch any surface and before touching your face or having meals.
Wear and change masks regularly – Wear a mask at all times and change it after every 6 to 8 hours. Used masks should be first disinfected and then burnt, instead of being directly disposed of.

There is a lot of wisdom in this age-old saying that prevention is better than cure. That’s why we urge you to take proper precautions and play your part in helping India fight this global pandemic. Here are some tips to stay safe from COVID-19:
Table of Contents
CoV (Middle East Respiratory Syndrome), SARS-CoV (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome), and SARS-CoV-2 (Novel coronavirus) are the most severe. Of these, SARS-CoV-2 is responsible for the ongoing global pandemic. COVID-19 is the disease caused by the novel coronavirus (COronaVIrusDisease-19, as it was first detected in 2019)
SARS-CoV-2 more commonly known as the novel coronavirus was first detected in December 2019 in China. In March 2020, WHO declared the COVID-19 outbreak (the disease caused by novel coronavirus) to be a pandemic. Countries around the globe are struggling to bring the situation in control, organizations like WHO, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare-India, CDC are posting live updates on their websites to make it easier to track the progress of this pandemic.
Since SARS-CoV-2 is novel in nature, studies are still being done to understand the virus, how contagious it is, its mortality rate and the disease (COVID-19) it causes. At present, there exist no specific vaccines or treatments for this disease and the most effective way to control the spread of this disease is social distancing and maintaining good sanitization practices.
Mild to severe symptoms might manifest 2 to 14 days after exposure. The most common symptoms are:
In some cases, the affected individual may also exhibit the following symptoms
For more serious cases symptoms also include
In most cases the symptoms are mild or moderate, symptomatic treatment and self-isolation are prescribed. Severe symptoms are usually seen in individuals with preexisting conditions such as old age, diabetes, cardiac ailments, or any condition that has compromised their immune system.
Novel Coronavirus was first detected in December 2019 and has managed to impact the whole world in a span of a few months. Highly contagious in nature, this virus propagates mainly through droplets from the nose or mouth which are spread through forceful exhalation of a person with COVID-19. The virus can stay viable outside the host for several days depending on the surface it is on which makes it even more troubling.
As there are no cures or vaccines at present to tackle the novel coronavirus, the best practice would be to protect oneself from exposure to this virus. WHO has released certain safety procedures and guidelines which can minimize the risk of contracting COVID-19.
Please be aware that extra care has to be taken if you are at a higher risk from COVID-19, in such cases reach out to your doctor for any additional precautions that you could take.
Aarogya Setu is a mobile application developed by the ministry of electronics. It has been designed to enable individuals to carry out a self-assessment test while also tracking the presence of COVID-19 cases in the vicinity.
The users are asked a number of questions including exposure to any suspected coronavirus case or presence of symptoms and based on the answers as well as the density of COVID positive patients in the area, the app reflects whether the user is safe or high risk.
This app is especially useful to decide if it is time to self-isolate while giving government authorities the necessary information to track and monitor the rise of cases in the surrounding area.
At CK Birla Hospital, your health and safety are paramount to us. We are constantly monitoring and taking steps to minimize the risk of COVID-19 to ensure that our facility is your safe space.
In order to ensure that our patients, employees, and visitors are protected from this pandemic, we have taken several measures. Some of these are:
Anyone entering the facility is screened thoroughly as per government guidelines, hospital policy, and under the advice of the internal medicine specialist.
As a part of our current safety procedures, visiting hours have been suspended until further notice. One attendant can accompany a patient. At present only attendants, patients, and hospital staff are allowed inside the hospital premises.
Stringent hand washing and sanitization protocols are being followed throughout the hospital including an hourly signal reminding everyone to sanitize their hands. Cleaning rates of all high touch surfaces within the hospital surfaces such as doorknobs, reception desk areas etc. have been increased. Personal protection equipment such as masks and glasses have been provided to all our clinical and patient-facing teams and are mandatory while on hospital premises.
To clear any confusion and to ensure that everyone stays up to date with the best practices regarding the prevention of COVID-19, we follow the Government of India and WHO guidelines to conduct extensive training for our staff. We emphasize following the right and latest protocols as laid out by the authorities.

While our OPD department is fully functioning and completely safe for you to visit, if you feel that you would rather consult your doctor over a video call, we now offer this service as well.
Please call us on +91 124 4882200 and our hospital representatives will guide you on the process and help you book an appointment.
Ageing has various effects on the body. One of the most important areas that the ageing process affects, is bone strength. With advancing age bone strength tends to decrease and joints lose their mobility.
Knee joints are one of the most affected joints of the body which affects almost every ageing person. Knee pain due to osteoarthritis is an extremely disturbing condition that people go through. It affects the daily lives of the affected individuals significantly.
When all medical remedies have stopped bringing you relief, knee pain can be so pronounced that you might be unable to manage daily activities, and there could be swelling and even bowing of the knee.
In such a case, it is recommended to see a doctor who may advise knee replacement surgery as the best solution to improve your quality of life.
Your orthopaedic surgeon will make you go through diagnostic scans to ascertain if your knee joint is deformed or damaged in addition to a physical exam before deciding on knee replacement surgery.
Table of Contents
Surgery is not the only solution to treat knee pain. Only about 20% of patients need knee replacement surgery, whereas 80% of patients don’t.
Increasing the amount of calcium, vitamin D and other essential nutrients in your diet also helps in maintaining bone health.
Surgery may be required only in case of chronic conditions such as constant problems in walking, unbearable pain, having to take pain relief medicines daily and difficulty in doing day-to-day activities.
In a knee replacement surgery, the damaged cartilage and the bony tissues are removed from the knee cap and replaced with high-grade plastic or metal alloys that act as the joint.
The procedure is intended to relieve pain and restore the normal functioning of the joint. The replaced knee performs almost as good as the previous normal ones, but the patient might take some time to adjust to the new knee.
A proper rehabilitation process is important so that you adjust to the knee joint and return to an active life. It not only helps in the long term but also helps you recover from the surgery quickly and properly.
With advancements in medical technology, within a day of your surgery, your orthopaedic specialist will make you stand, walk with assisted equipment like crutches, canes or walkers.
Your physiotherapist plays a very key role in the recovery and rehabilitation process. The endeavour is to use the new joint as much as possible and so will build out an exercise regime for you to strengthen your muscles.
Within 2-3 days of the surgery, your orthopaedic and physiotherapist will make you walk short distances, climb 2-3 steps, bend the knee to a certain angle and undertake daily activities like taking bath and using the toilet with minimal assistance.
In most cases, patients may take up to 6-8 weeks to perform most of the activities as normally as they used to with a normal knee joint.
Complete recovery and regaining of full strength might take from six months to a year. 90% of people who undergo a total knee replacement report to have a better quality of life.
Usually, if everything goes well, a patient is expected to stay in the hospital for 2 to 3 days following a total knee replacement surgery.
The doctor encourages movement from the next postoperative day itself with the help of some support. The patient should be able to walk without any support within two to three weeks of the surgery.
The patients will be able to perform activities which they were not able to do earlier, within a year’s time.
Adhering to an active lifestyle and exercising regularly will be helpful in regaining the strength of the joint quickly.
Though very close to the normal knee, the artificial knee does have certain limitations. It would not bend as much as the normal knee.
Also, one might find it difficult to perform activities like kneeling, jumping, running and heavy laborious work. Getting involved in contact sports might not be advisable.
It is important to talk to the orthopaedic surgeon before going for it.
There are risks of the artificial joint being broken and damaging surrounding tissues to a great extent! Feeling some sort of achiness or pain is common when initiating activities.
Some patients complain of cramps and stiffness after prolonged walking or bicycle riding. Few patients even experience a feeling of heat around the knees, they can apply an ice pack or take simple over-the-counter pain medications for relief.
It is extremely important to maintain a healthy weight. An increase in weight can cause sooner wear and tear of the joint, it may even cause the artificial joint to break under undue pressure.
As the knees bear the complete weight of the body, it is important to maintain a healthy weight so that the knees are subjected to lesser stress.
Patients who undergo a knee replacement are at a higher than normal risk of infection as with any other surgery. A surgical procedure carries the risk of infection along with it.
The patient might be advised to take antibiotics before any invasive or even a dental procedure. Microbes gaining access to body fluids can flourish more easily and can cause infections.
It is thus recommended to take antibiotics before undergoing any procedure which has chances of exposure to microbes.
The success rate is usually very high. There are 90-95% chances of a replaced knee joint to last for about 10 years. And as high as 80-85% chances of the joint to last for 20 years.
With betterment in technology and advancements in surgical techniques, the likelihood of this time span to increase is high.
A patient who is beyond the age of 60 years at the time of surgery and takes proper care of the replaced knee is most likely to live the rest of living comfortably with an artificial knee.
Monitoring of the overall health and condition of the replaced knee is important to ensure the proper functioning of the joint.
Total knee replacement surgeries are usually very successful among people over the age of 60 years. People are very likely to return to their almost normal functioning joint following a replacement within a year.
They can perform most of the activities that they used to with a relatively high level of ease and comfort.
Proper exercising, staying active, managing a healthy weight and regular health checks are however extremely important.
The chances of damage are inevitable if not taken care of properly. Patients might require pain medications on and off and might need to take antibiotics when undergoing any invasive procedure.
However, the benefits and the quality of life that a patient gets after a knee replacement are worth these minor adjustments and cautiousness.
If continuous pain has pushed your daily walking to a back seat, it is time for you to visit an expert. Book an appointment today with Dr Debashish Chanda, an expert orthopaedic doctor in Gurgaon.
Table of Contents
Gestational diabetes is a condition where a pregnant female has a high level of blood sugar. It is important that the female had normal blood sugar levels prior to pregnancy to be called gestational diabetes. This condition usually resolves as the baby is born. There are very high chances of a female who has had gestational diabetes to develop type 2 diabetes eventually later on in her life.
Most of the women with gestational diabetes usually do not present with any symptoms. The condition is diagnosed while conducting routine tests. If the blood sugar levels are raised beyond a certain level, a female may experience:
The main cause of gestational diabetes is the changes in the hormonal level that leads to increased blood sugar during pregnancy. Our body makes enough insulin to cater to that increase in blood glucose levels during pregnancy. However, in certain cases the blood sugar may continue to remain high and hence be diagnosed as gestational diabetes.
A woman is prone to gestational diabetes if she:
The condition usually surfaces in the second half of the pregnancy between 24 to 28 weeks, however, some females who are at risk of gestational diabetes may be tested sooner. The doctor may advise undergoing a Glucose Challenge Test/ Glucose Screening Test or a Glucose Tolerance Test or both.
The pregnant female will be required to follow a diet consisting of food low in glycemic index. Keeping blood sugar levels under check is extremely important.
Women who have been diagnosed with gestational diabetes must get screened for diabetes 12 weeks after birth and keep undergoing screening tests every one or two years.
Some important steps to control gestational diabetes are having a diet that is low in refined or processed sugar. Managing weight is important as obese women are more likely to develop gestational diabetes.
Light exercises during pregnancy is recommended to keep blood sugar level under check. Proper antenatal care is important for the proper development and overall growth of the baby.
Consult Dr. Astha Dayal, an expert obstetrician-gynecologist at the CK Birla Hospital in Gurgaon to learn more about this condition and possible treatment. For an appointment click here!
The hand and the wrist bones are flexible which offer the body with support and elasticity to move objects in many ways according to their wishes. The ulna and radius of the forearm, support many of the hand’s muscles. There are 27 bones in the hand and all of them have an incredibly precise range of flexibility.
The carpal tunnel is a narrow, tunnel-like structure in the wrist, with the carpal (wrist) bones forming the bottom and sides and the transverse carpal ligament, a strong band of connective tissue, forming the top of the tunnel.
The median nerve, which controls sensation in the palm side of the thumb, index finger, and long fingers as well as the muscles around the base of the thumb, extends from the forearm to the hand via the carpal tunnel.
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a hand and arm condition that occurs when synovium (tissues) surrounding the flexor tendons in the wrist is inflamed and as a result, puts pressure on the median nerve.
The swelling of the synovium narrows the already-limited space within the carpal tunnel and crowds the median nerve.
Women are more liked to develop carpal tunnel syndrome than men and there are several different ailments and conditions contribute to the development of the condition, including heredity, age, medical conditions such as diabetes or thyroid gland imbalance, as well as hormonal changes caused by pregnancy.
Individuals who have developed carpal tunnel syndrome commonly have the following symptoms:
Shrugging of the hand offers relaxation or relief from pain – this is often a typical explanation by the patient when they explain the pain to the Doctor.
Early diagnosis and treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome can greatly help in reducing symptoms and avoiding more permanent damage to the nerves and muscles.
Therefore, it is strongly advised to visit a physician if and individual experiences any of the symptoms or suspect carpal tunnel syndrome.
The diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome is generally made upon a physical examination only. Sometimes imaging and nerve conduction studies are also needed in severe condition to quantify the problem.
After taking a full history of the symptoms and any prior injuries, the physician will examine the hand for feeling in the fingers and the strength of the muscles in the hand.
The physician might put pressure on the median nerve by bending the wrist or simply pressing or tapping on the nerve to see if symptoms worsen. If the individual has limited motion in the wrist, the physician may order x-rays to rule out other conditions.
To confirm the diagnosis and identify the best treatment option, the physician may also conduct electrical testing of the median nerve.
Early diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome will typically respond quite well to non-operative treatment, and for most people, the condition will only worsen if left untreated.
The main objective of treatment is controlling inflammation and reducing symptoms. Operative treatment is typically a last resort after non-operative approaches have been exhausted.
Recovery after surgery depends on the initial symptoms of the patient and delay in undertaking the procedure. Surgery done properly and in time results in 100% recovery within a week.
The signs and symptoms start disappearing just after the surgery. Each patient is unique, and their recovery will depend on the treatment method prescribed by the physician.
Sometimes recovery after surgery may be delayed if the treatment is delayed till severe injury to nerve has already happened.
Hence, it is recommended that the patient should consult the physician/orthopedic specialist soon after experiencing the symptoms initially.
The prostate is a gland in the body that produces the fluid which carries sperm during ejaculation. It surrounds the urethra and bladder.
An enlarged prostate represents a prostate gland that has grown bigger than its normal size which is about 18-22 grams.
It is a very common condition and almost every male undergoes through a prostate enlargement as they age. The condition is also called as benign prostatic hyperplasia.
This is not a cancerous condition and does not increase the risk of developing a prostate cancer.
The actual cause of a prostatic enlargement remains unknown. Age is considered to be a risk factor leading to the prostatic enlargement. The process of aging leads to changes in the cellular structure of testicles (which has a role in growth of the prostate gland) and in the levels of testosterone in the body.
Males who have undergone testicle removal at a very young age due to some condition like a testicular cancer do not develop benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Similarly, when testicles are removed following development of a benign prostate enlargement, (doctor for enlarged prostate) the prostate shrinks in size.
Diagnosis may be done with a rectal examination to feel the prostate gland.
The treatment modality is usually based on the intensity and severity of the symptoms and their effects on the daily life of the patient.
In some cases, watchful waiting is suggested and patient is advised not undergo any treatments if the symptoms are not too bothersome. In certain cases, self-care, medicines or surgery may be required.
Prostate surgery may be recommended for people who have incontinence, blood in urine, retention of urine, recurrent infections, kidney damage or other bothersome conditions not responding to medicines.
Depending on the severity of the symptoms and the size and shape of prostate gland different procedures can be recommended. Transurethral resection of prostate or TURP is the most commonly performed procedure for a benign prostatic hyperplasia.
In this procedure, a scope is inserted through the penis and the prostate gland is removed.
Men who are diagnosed with prostatic hyperplasia since a long time and the symptoms are worsening over time, are at the risk of developing urinary tract infections, severe damage to Kidneys and presence of blood in urine.
A benign prostatic hyperplasia may recur even after undergoing a surgical procedure. One must contact the doctor in case of less urine output than normal, fever or chills, pain in the back or sides of abdomen or presence of blood in urine. In modern day, medical treatment can help reverse prostate enlargement when started at the right time.
If you have any urinary symptoms like increase in frequency, sudden compelling urge to pass urine, getting up more than once to visit the washroom, poor stream, straining to pass urine, or feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder then you should visit a urologist near you and get a uroflowmetry test and ultrasound to treat this common problem in time.
Varicocele is a common cause of pain in the scrotum in men and often a cause of infertility or the inability to bear children in men. It is with these complaints the patient comes to a urologist.
But many times, the varicocele problem is detected incidentally through an ultrasound. Hence, a small percentage of cases who come to the Urologist show no symptoms.
Varicocele means that the veins which are taking blood from the testes to the heart get abnormally dilated because they have some valves which get damaged.
Due to this, the blood starts to collect in these veins. When the blood starts to collect in these veins, these veins become dilated and the blood flow back from the testes to the heart is impaired.
Since the blood persists in these veins, the temperature of the testes increases. The testes have been placed outside the body so that their temperature can remain about two to four degrees lower than the core temperature of the body as this is the temperature that is required for the optimal production of the sperms.
Most commonly what is found in these patients is that in the sperm parameters on semen analysis such as the motility of the sperms is impaired, which means that even though the sperms may be good in number, they are not able to move to the extent that they should be able to move to be able to fertilize the egg.
The most common symptom usually would be an impaired semen parameter which means that there will be some problem in the motility or the number or the shape of the sperms.
Also, there could be a pain in the scrotum which is usually a constant dragging pain. This pain increases or aggravates on standing for prolonged periods of time.
Usually when the patient gets up in the morning, there is no pain. Only when he is standing for prolonged periods, he would experience a discomfort or pain in the scrotum.
The third common symptom that the patient often notices is a swelling in the scrotum. He will find a wormy sort of a swelling, which means that he will feel that veins or the vascular structures around the testes appears to be dilated and enlarged.
The diagnosis is usually done through a clinical examination. When the patient comes to the Varicocele Enlargement doctor who checks the scrotum, he will find that there are dilated veins felt on examination of the scrotum.
This in medical science is called the ‘bag of worms’ feeling as if there are worms in a bag and you are kind of trying to feel them. To confirm the diagnosis a scrotal ultrasound is used. This is not a normal ultrasound, but a Doppler powered ultrasound.
Through a Doppler Ultrasound, the radiologist will be able to see the veins as engorged and there would be reversal of the flow of blood in these veins, which means that some blood will be going back from these veins into the testis.
So, based on the diameter of these veins, the radiologist will give a grade to the Varicocele which will also help the clinician to understand how severe the Varicocele is and how it should be best managed.
With regards to the clinical staging of the Varicocele, there are three grades of Varicocele.
So, these are the three grades of Varicocele on clinical examination and there are four grades of Varicocele on ultrasound, which are based on the diameter of these veins.
Usually grade one and two Varicocele can be managed or controlled with medicines. The medicines in the form of tablets can increase the strength of the veins by depositing calcium in the wall of the veins.
Hence, they stop the further deterioration or damage to the veins and try and control the situation.
However, if it is the grade three, Varicocele, where a surgery is required wherein the veins must be ligated so that the blood does not flow in them any further.
It is also important to understand that many times if there is pain or discomfort in the testis despite the grade not being very high and all other causes have been ruled out, urologist consider surgical treatment for these patients as well because surgical treatment is more effective in pain management.
Surgery is also indicated when the size of the testicle is shrinking.
Till few years back, a laparoscopic surgery was done and the root of the veins, from where the veins arise was ligated or tied which helped cure Varicocele.
But this laparoscopic surgery required the administration of general anaesthesia and was also an expensive surgery. Also, because of the other complications associated with this type of surgery such as hydrocele, recurrence and damage to the testis, the laparoscopic surgery became less in vogue.
The other treatment options used to be an inguinal approach to tying the veins in which a large cut was made just like for a hernia operation and the veins were exposed and individually tied.
And since this required a large scar of about three to four inches and because several complications were associated with this process, it became less common.
The recovery period after any sort of procedure is about a week because there may be some swelling around the area and the tied veins still have accumulated clotted blood in them.
The veins slowly shrink in size and the swelling recedes and disappears completely in about 4-6 weeks. However, the patient can resume his normal work in a couple of days after the procedure.
Hence, Varicocele management is simple in today’s time. If it’s a high-grade Varicocele, the suggested treatment is a sub-inguinal microscopic surgical repair. And if it is a low-grade Varicocele, the patient can be treated through medication.
For more details on Varicocele surgery and management, you can contact our experts from the Urology center at the CK Birla Hospital. Book an appointment on +91 124 4882200 to evaluate and provide customized treatment options based on your condition.