Backaches - a condition that’s soaring among almost every age group, from youngsters to the elderly. Most people experience back pain at some point in their lives. According to - World Health Organization (WHO), back pain affected 619 million people globally and the numbers are expected to rise in the coming years. Various factors add up to this number, while some factors are congenital, others are due to spinal injury, and age-related wear & tear, and one of the key contributing factors is poor posture, especially among young people leading to alarming levels of back & neck pain numbers.
One such spinal disorder that usually occurs with natural wear & tear of the spinal disc is degenerative disc disease. The spine is the main support structure of the body and is made up of a series of 24 bones called vertebrae. These bones are stacked on top of each other and separated by discs that work as cushions between the bones. These discs facilitate bending movement and different motions. Degenerative disc disease is a condition in which these discs start to degenerate naturally as we age causing the bones to start rubbing against each other.
Degenerative disc disease is more common in the upper and lower spine, causing neck and back pain as the most evident symptom. Individuals facing this issue can experience numbness or tingling in the arms, legs, and buttocks.
Degenerative disc disease is common in adults over 40. As we age, repeated stress from activities such as walking, twisting, lifting, bending etc. causes microscopic tears in the outer disc layer increasing the likelihood of damage leading to disc degeneration. Additionally, as we age we tend to lose water content in the body, since the spinal discs are made of 80% water they can withstand shocks and maintain their flexibility. However, the disc's capacity to absorb shocks is diminished as the water content drops and they thin and shrink. Additional factors that contribute to the prevalence of degenerative disc disease in the elderly include decreased blood flow, accumulated micro-injuries, oxidative stress & inflammation, spinal alignment changes, and other conditions of a similar nature.
The term degenerative disc disease refers to the gradual deterioration of spinal discs which can result in several different spinal disorders. The types of degenerative disc diseases based on region include,
The spine is a vital component of the human body. The spine is the primary structural element of the body supporting the body and protecting the nervous system. Any spinal deformities can affect overall health, flexibility, and mobility. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for reducing the serious effects and improving the quality of life. Early action can help in many ways including,
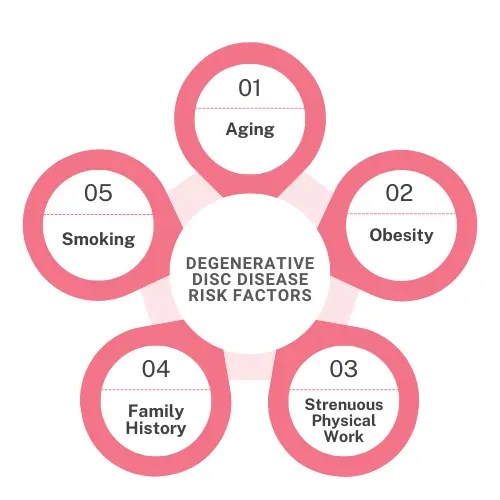
As we age our muscles tend to weaken, our skin gets thinner and drier, our heart rate decreases, and many other things change. Similarly, the health of our spines also deteriorates with age. As the discs between the spinal bones deteriorate a number of spinal disorders can result. Disc degeneration and related conditions can be brought on by aging but other factors like genetics injuries and lifestyle choices also play a role. The following are the primary causes of disc degeneration,
Disc degeneration usually occurs in elderly people. The symptoms may differ based on the location or the area of disc degeneration. Some of the common symptoms of disc degeneration based on location include,
Location-specific symptoms:
Cervical Spine (upper spine): Disc degeneration in the cervical spine may cause neck pain or stiffness, tingling, numbness, or weakness in shoulders, arms, and hands.
Thoracic Spine (Mid spine): Degeneration around the thoracic spine is not common, however, it can cause pain in the torso, abdomen, ribs, etc.
Lumbar Spine (lower spine): Disc degeneration in the lower spine is the most common. Individuals suffering from disc degeneration in the lower spine may experience lower back pain, sciatica, and leg weakness.
Common symptoms:
Chronic Pain: Persistent aching pain can be experienced in the neck or lower back. The pain can worsen with sitting, twisting, lifting, or while making any movements.
Numbness and Tingling: Numbness or loss of sensation and tingling can be experienced due to nerve compression.
Muscle Weakness: Weakness in the muscles can be experienced especially around the arms, hands, and legs.
A spine specialist can diagnose the degenerative disc disease by performing a physical examination. The specialist might inquire about numbness, pain locations and other symptoms. The specialist can further assess for:
Nerve Function: To evaluate nerve compression and monitor nerve response.
Muscle Strength: Recognise any weakening or contracting muscles.
Pain: Determine the degree of pain in the particular or impacted areas in response to touch.
Following a physical examination the Degenerative Disc doctor may recommend specific imaging tests to assess disc alignment and identify the precise location, type, and severity of the issue. Some of the frequently used imaging tests include,
CT Scan: Helps create 2D images of the spine & provides a detailed view.
Spine X-ray: Provides a basic view of the spine to help identify bone spurs, fractures, etc.
MRI: Gives a detailed image of the soft tissues, disc, ligaments, nerves, etc.
The severity of the condition and the underlying symptoms determine the treatment of degenerated discs. Stretching, low-impact exercise, hot and cold therapy, and adequate rest are all effective at-home treatments for mildly symptomatic degenerated discs. However non-invasive and invasive treatment methods are advised if the symptoms are severe and persist after treatment at home or if they are becoming worse.
Non-invasive Treatments:
Medications: Prescribed medicines and muscle relaxants can help reduce pain and discomfort.
Physical Therapy: This involves exercises, stretching, etc to help release strain on the muscles, and nerves, and help strengthen the surrounding muscles.
Alternative Therapy: Therapies like chiropractic, acupuncture, and massage, can be used to manage pain and release muscle tension around the nerve & surrounding muscles.
Invasive/Surgical Treatments:
Surgical treatments are recommended for individuals with more severe symptoms. Disc degeneration pain is typically treated and managed with non-invasive methods by specialists; however surgical procedures are the recommended course of action if non-surgical methods are insufficient to address problems and relieve pain. Among the surgical techniques used to manage disc degeneration are discectomy, foraminotomy, spinal fusion, laminectomy, etc.
To effectively manage degenerative disc disease a combined approach involving lifestyle adjustments, emotional support, and physical activity is recommended. Some of the coping strategies for degenerative disc disease include,
| Coping Strategy | Description |
| Lifestyle Modifications | Maintain proper posture, healthy weight |
| Physical Activity | Perform low-impact exercises, stretching |
| Pain Management | Use heat/cold therapy, prescribed medications |
| Alternative Therapies | Acupuncture, massage therapy, chiropractic care |
| Mind-Body Techniques | Meditation, deep breathing, yoga to reduce stress |
Degenerative disc is a condition that occurs due to natural wear & tear of the spinal disc as we age.
Degeneration of discs is the natural wearing off of the spinal discs as we age and thus can not be reversed, however, the symptoms can be managed and controlled from getting worse with various treatment options.
No, there is no cure for degenerative disc disease, though the symptoms can be managed and controlled from getting worse with various treatment options.
Degenerative disc disease occurs due to natural wear & tear of the spinal disc with age.
Yes, degenerative disc disease can have a hereditary component, though the primary causes are lifestyle and ageing factors.